Abstract
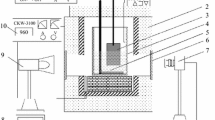
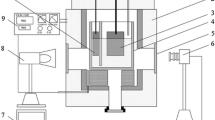
The bubble behavior is one of the key factors for the design and the process of aluminum reduction cell using inert anode. A see-through cell is constructed to investigate the bubble flow behavior and the electrolyte flow pattern induced by bubbles. The test results show that the electrolyte is driven by the bubble to move around the cathode, and also some vortices occur in local areas. The bubble generated at the anode bottom undergoes the processes of formation, growth, sliding, detachment and coalescence. However, the bubble generated at the middle of anode detaches rapidly from the anode surface and moves upward and collides with other bubbles, which results in coalescence or break-up. Most bubbles are released into the atmosphere at the liquid surface, while some other bubbles taken by the electrolyte flush to the height higher than the mean horizontal level of the liquid and then drop down and move horizontally and they are released finally. Some bubbles are kept unbroken and are sliding on the electrolyte surface. The diameter of bubble generated at inert anode is smaller than that of bubble generated at graphite anode. Moreover, the bubbles on inert anode are spherical, which was different from those in tubular or disk form on graphite anode.
摘要
气泡的行为是惰性阳极铝电解槽设计和工艺控制必须考虑的重要因素。为了研究气泡的行为和 电解质的流动形态,构建了透明铝电解槽以进行观察。试验结果表明:受阳极气体的驱动,槽内电解 质围绕阴极作循环运动,并在局部区域形成旋涡。气体产生于阳极底掌和垂直工作面。在阳极底掌, 能够观察到气泡的形成、长大、滑移和脱离等现象。然而,阳极垂直工作面产生的气体则迅速脱离, 然后向上运动,途中与别的气泡碰撞,导致气泡的并聚或破碎。大部分气泡达到液面时立即逸出至空 气中,少部分气泡被冲出水平液面的电解质携带着继续向上运动,形成一个波峰,然后作水平运动并 最终逸出。在电解质表面,部分气泡能保持不破裂,并在电解质上滑动。通过对比分析,惰性阳极上 产生的气泡比石墨阳极上产生气泡的直径小。另外,石墨阳极上的气泡不呈球形,而呈圆盘状或扁平 状,惰性阳极上的气泡则近似呈球状。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Xing-hua, Dimilia R A, Dynys J M, Martello J S. Systems and methods of protecting electrolysis cells: USA, US9340887[P]. 2016–05–17.
Dimilia R A, Liu Xing-hua, Weirauch J D. Stable anodes including iron oxide and use of such anodes in metal production cells: USA, US7507322[P]. 2009–03–15.
Christian B, Sylvie B, Armand G, Veronique L, Ariane M. Electrode material and use thereof for the manufacture of an inert anode: France, WO2015198128[P]. 2015–06–23.
Olegovich G A, Viktorovich A E, Vladimirovich I V, Vasilevich B V. Electric contact unit of inert anode for obtaining aluminium fused salt and method for its erection: Russia, RU20090119067[P]. 2009–05–21.
Wang Biao, Liang Feng, Wang Yu-dong, Peng Kun. Pilot test of aluminum electrolysis by the NiFe2O4-M inert anode [C]// WILLIAMS E. Light Metals 2016. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2016: 429–431.
Lai Yan-qing, Huang Li-feng, Tian Zhong-liang, Wang Jia-wei, Zhang Gang, Zhang Yong. Effect of CaO doping on corrosion resistance of Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO) cermet inert anode for aluminum electrolysis[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2008, 15(6): 743–747.
Shi Kai-hua, Zhou Ke-chao, Zhang Lei, Li Zhi-you. Microstructure characterization of NiFe2O4-NiO solid-solid diffusion couple [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2012,19(9): 2411–2415.
Tian Zhong-liang, Lai Yan-qing, Li Jie, Liu Ye-xiang. Electrical conductivity of Cu(/10NiO-NiFe2O4) cermet inert anode for aluminum electrolysis [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 14(5): 643–646.
Li Jie, Wang Zhi-gang, Lai Yan-qing, Liu Wei, Ye Shao-long. Effect of working condition on thermal stress of NiFe2O4-based cermet inert anode in aluminum electrolysis [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 14(4): 478–484.
Zhan Shui-qing, Li Mao, Zhou Jie-min, Yang Jian-hong, Zhou Yi-wen. CFD simulation of effect of anode configuration on gas–liquid flow and alumina transport process in an aluminum reduction cell [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(7): 2482–2492.
Xu Jun-li, Shi Zhong-ning, Gao Bing-liang, Qiu Zhu-xian. Bubble behavior on metal anode of aluminum electrolysis [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(2): 298–301. (in Chinese)
Eigeldinger J, Vogt H. The bubble coverage of gas-evolving electrodes in a flowing electrolyte [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2000, 45(27): 4449–4456.
Vogt H. On the gas-evolution efficiency of electrodes I–eheoretical [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56: 1409–1416.
Vogt H. On the gas-evolution efficiency of electrodes II–numerical analysis [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56: 2404–2410.
Hyde T M, Welch B J. The gas under anodes in aluminium smelting cells part I: Measuring and modelling bubble resistance under horizontally oriented electrodes [C]// HUGLEN R. Light Metals 1997. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 1997: 333–340.
Wang Y, Zhang L, Zuo X. Fluid flow and bubble behaviour in the aluminium electrolysis cell [C]// GEOFF B. Light Metals 2009. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2009: 581–586.
Xue Yu-qing, Zhou Nai-jun, Bao Sheng-zhong. Normal temperature analogue experiment of anode bubble's behavior in aluminum electrolysis cells [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(10): 1823–1828. (in Chinese)
Morshed A, Morsi Y, Yang W. Investigation of electrolytic bubble behavior in aluminium smelting cell [C]// SADLER B A. Light Metals 2013. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2013: 591–596.
Qian K, Chen J J J, Matheou N. Visual observation of bubbles at horizontal electrodes and resistance measurements on vertical electrodes [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1997, 27(4): 434–440.
Qian K, Chen Z D, Chen J J J. Bubble coverage and bubble resistance using cells with horizontal electrode [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1998, 28(10): 1141–1145.
Zhang Gang. Densification and strengthening of Fe2O4-10NiO based cermet inert anode for aluminum electrolysis [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2007, 48–57. (in Chinese)
Yang J H, Hryn J N, Krumdic G K. Aluminum electrolysis tests with inert anodes in KF-AlF3-based electrolytes [C]// GALLOWAY T J. Light Metals 2006. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2006: 421–424.
Fortin S, Gerhardt M, Gesing A J, Physical modelling of bubble behaviour and gas release from aluminum reduction cell anodes [C]// MCGEER J P. Light Metals 1984. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 1984: 721–741.
Zoric J, Solheim A. On gas bubbles in industrial aluminium cells with prebaked anodes and their influence on the current distribution [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2000, 30(7): 787–794.
Cassayre L, Utigard T, Bouvet S. Visualizing gas evolution on graphite and oxygen-evolving anodes [J]. Journal of Metals, 2002, 54(5): 41–45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(51304216, 51371161) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Yw., Zhou, Jm., Chen, Sh. et al. Bubble behavior in aluminum reduction cell with inert anode. J. Cent. South Univ. 25, 482–489 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3752-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3752-5