Abstract
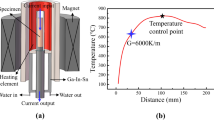
The effects of withdrawal rate and temperature gradient on the microstructure and growth interface morphology in directionally solidified Ni-29Al-36Cr-6Mo(at.%) hypereutectic alloy were investigated. Under the temperature gradient of 250 K/cm, well-aligned eutectic microstructure with lamellar morphology was obtained at the withdrawal rate of 6 μm/s. When the withdrawal rate was 10 μm/s, the microstructure changed to Cr(Mo) dendrites + eutectic lamellae. With the increasing withdrawal rate, the interdendritic eutectic growth interface changed from planar to cellular, the number of primary Cr(Mo) dendrites became greater, and the microstructure was refined. When the temperature gradient increased to 600 K/cm, the coupled eutectic growth zone of NiAl-Cr(Mo) alloy was expanded; a well-aligned eutectic microstructure could be obtained at higher rate of 10 μm/s. Furthermore, the planar/cellular transition rate of the interdendritic eutectic growth interface increased. Even at the same withdrawal rate, the number of primary Cr(Mo) dendrites was less and the microstructure was finer under the temperature gradient of 600 K/cm.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.D. Noebe, R.R. Bowman, and M.V. Nathal, Inter. Mater. Rev. 38, 193 (1993).
D.B. Miracle, Acta Metall. Mater. 41, 649 (1993).
K.O. Yu, J.A. Oti, and W.S. Walston, JOM 45, 49 (1993).
R. Darolia, JOM 43, 44 (1991).
Y. Chen and H.M. Wang, J. Alloy Compd. 391, 49 (2005).
R. Darolia, W.S. Walston, R. Noebe, A. Garg, and B.F. Oliver, Intermetallics 7, 1195 (1999).
H.E. Cline and J.L. Walter, Metall. Trans. 1, 2907 (1970).
X.F. Chen, D.R. Johnson, and B.F. Oliver, Scr. Metall. Mater. 30, 975 (1994).
H. Bei and E.P. George, Acta Mater. 53, 69 (2005).
S.M. Joslin, X.F. Chen, B.F. Oliver, and R.D. Noebe, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 196, 9 (1995).
J.M. Yang, JOM 49, 40 (1997).
J.M. Yang, S.M. Jeng, K. Bain, and R.A. Amato, Acta Mater. 45, 295 (1997).
X.F. Chen, D.R. Johnson, R.D. Noebe, and B.F. Oliver, J. Mater. Res. 10, 1159 (1995).
J.D. Whittenberger, S.V. Raj, I.E. Locci, and J.A. Salem, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 33, 1385 (2002).
S.V. Raj and I.E. Locci, Intermetallics 9, 217 (2001).
W. Kurz and D.J. Fisher, Fundamentals of Solidification, 4th ed. (Switzerland: Trans Tech Publications Ltd., 1998).
R.S. Barclay, H.W. Kerr, and P. Niessen, J. Mater. Sci. 6, 1168 (1971).
S. Milenkovic, A. Schneider, and G. Frommeyer, Intermetallics 19, 342 (2011).
Z. Shang, J. Shen, J.F. Zhang, L. Wang, and H.Z. Fu, Intermetallics 22, 99 (2012).
F. Mollard and M.C. Flemings, Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 239, 1534 (1967).
P. Villars, A. Prince, and H. Okamoto, Handbook of Ternary Alloy Phase Diagrams (Materials Park, OH: ASM International, 1995).
D.M. Stefanescu, Science and Engineering of Casting Solidification, 2nd ed. (New York: Springer, 2009).
M.H. Burden and J.D. Hunt, J. Cryst. Growth 22, 328 (1974).
J.D. Hunt and K.A. Jackson, Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 239, 864 (1967).
D.G. Mccartney, J.D. Hunt, and R.M. Jordan, Metall. Trans. A 11A, 1243 (1980).
M. Plapp and A. Karma, Phys. Rev. E 60, 6865 (1999).
H.E. Cline, Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 242, 1613 (1968).
P.R. Sahm and H.R. Killias, J. Mater. Sci. 12, 1027 (1970).
J.T. Guo, C.Y. Cui, Y.X. Chen, D.X. Li, and H.Q. Ye, Intermetallics 9, 287 (2001).
J.F. Zhang, J. Shen, Z. Shang, Z.R. Feng, L.S. Wang, and H.Z. Fu, Intermetallics 21, 18 (2012).
J.D. Hunt and S.Z. Lu, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 27, 611 (1996).
D. Bouchard and J.S. Kirkaldy, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 28, 651 (1997).
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Natural Science Foundation of Shannxi Province for their financial supports under contract No. 51074128 and No. 2010JM6002. This work is also supported by the Doctorate Foundation of Northwestern Polytechnical University under contract No. CX201009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, Z., Shen, J., Zhang, JF. et al. Effects of Withdrawal Rate and Temperature Gradient on the Microstructure Evolution in Directionally Solidified NiAl-36Cr-6Mo Hypereutectic Alloy. JOM 66, 1877–1885 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1008-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1008-x