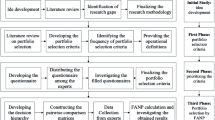
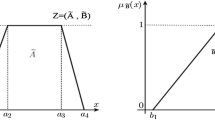
Abstract
This systematic review aims to evaluate the efficacy of fuzzy multi-objective optimization techniques in supporting decision-making in financial portfolio management under conditions of uncertainty. The review will critically appraise and compare different approaches to identify the most suitable technique for addressing the challenges posed by uncertain environments. Specifically, the review will investigate the use of mathematical models to find the optimal balance between competing objectives, such as maximizing return while minimizing risk, and provide a range of possible solutions based on different levels of uncertainty. Real-life decision-making scenarios involving the selection of investment options, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or real estate, in the face of economic instability, political unrest, or natural disasters will be examined to provide practical insights. Through this review, we aim to contribute to the body of knowledge regarding effective strategies for financial portfolio management under conditions of uncertainty.



































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuschel N, Rackwitz R (1997) Two basic problems in reliability-based structural optimization. Math Methods Oper Res 46:309-333
Gupta N et al (2022) Enhanced virtualization-based dynamic bin-packing optimized energy management solution for heterogeneous clouds. Math probl Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8734198
Alferaidi A, Yadav K, Alharbi Y, Viriyasitavat W, Kautish S, Dhiman G (2022) Federated learning algorithms to optimize the client and cost selections. Math probl Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8514562
Ammar EE (2005) On computational solution of vector maximum problem. Appl Math Comput 167(1):167-178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2004.06.098
Minami M (1983) Weak Pareto-optima necessary conditions in a nondifferentiable multiobjective program on a Banach space. J Optim Theory Appl 41(3):451-461. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00935364
Jiménez M, Bilbao A (2009) Pareto-optima solutions in fuzzy multi-objective linear programming. Fuzzy Sets Syst 160(18):2714-2721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2008.12.005
Yazdani M, Zarate p, KazimierasZavadskas E, Turskis Z (2019) A combined compromise solution (CoCoSo) method for multi-criteria decision-making problems. Manag Decis 57(9):2501-2519. https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-05-2017-0458
Bhati D, Singh p (2017) Branch and bound computational method for multi-objective linear fractional optimization problem. Neural Comput Appl 28(11):3341-3351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2243-6
RajabalipourCheshmehgaz H, Desa MI, Wibowo A (2013) A flexible three-level logistic network design considering cost and time criteria with a multi-objective evolutionary algorithm. J Intell Manuf 24(2):277-293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-011-0584-7
da Silva AF, Marins FAS (2014) A Fuzzy Goal programming model for solving aggregate production-planning problems under uncertainty: a case study in a Brazilian sugar mill. Energy Econ 45:196-204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2014.07.005
Wu Y et al (2020) Urban traffic signal control based on multiobjective joint optimization. Sci program. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8839720
Huang Z, Fang B, Deng J (2020) Multi-objective optimization strategy for distribution network considering V2G-enabled electric vehicles in building integrated energy system. prot Control Mod power Syst. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41601-020-0154-0
Cui Y, Geng Z, Zhu Q, Han Y (2017) Review: multi-objective optimization methods and application in energy saving. Energy 125:681-704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.02.174
Wang H, Olhofer M, Jin Y (2017) A mini-review on preference modeling and articulation in multi-objective optimization: current status and challenges. Complex Intell Syst 3(4):233-245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-017-0053-9
Soltanifar M (2021) An investigation of the most common multi-objective optimization methods with propositions for improvement. Decis Anal J 1:100005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dajour.2021.100005
de Carvalho VR, Özcan E, Sichman JS (2021) Comparative analysis of selection hyper-heuristics for real-world multi-objective optimization problems. Appl Sci 11(19):9153. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199153
Khodadadi N, Abualigah L, Al-Tashi Q, Mirjalili S (2023) Multi-objective chaos game optimization. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-08432-0
Ding Z, Chen Z, Liu J, Evrendilek F, He Y, Xie W (2022) Co-combustion, life-cycle circularity, and artificial intelligence-based multi-objective optimization of two plastics and textile dyeing sludge. J Hazard Mater 426:128069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.128069
Alkurd R, Abualhaol IY, Yanikomeroglu H (2020) personalized resource allocation in wireless networks: an AI-enabled and big data-driven multi-objective optimization. IEEE Access 8:144592-144609. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3014301
Gupta SK, pandey K, Kumar R (2018) Artificial intelligence-based modelling and multi-objective optimization of friction stir welding of dissimilar AA5083-O and AA6063-T6 aluminium alloys. proc Inst Mech Eng L 232(4):333-342. https://doi.org/10.1177/1464420715627293
Reynoso-Meza G, Blasco X, Sanchis J, Martínez M (2014) Controller tuning using evolutionary multi-objective optimisation: current trends and applications. Control Eng pract 28:58-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conengprac.2014.03.003
Tzeng Y, Chen F (2007) Multi-objective optimisation of high-speed electrical discharge machining process using a Taguchi fuzzy-based approach. Mater Des 28(4):1159-1168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2006.01.028
Sinuany-Stern Z (2023) Foundations of operations research: from linear programming to data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 306(3):1069-1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2022.10.046
Dantzig GB (1983) Reminiscences about the origins of linear programming. In: Mathematical programming the state of the art. Springer, Berlin, pp 78-86. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-68874-4_4
Lemke CE (1954) The dual method of solving the linear programming problem. Nav Res Logist Q 1(1):36-47. https://doi.org/10.1002/nav.3800010107
Russell B (1923) Vagueness. Australas J psychol philos 1(2):84-92. https://doi.org/10.1080/00048402308540623
Lodwick WA, Jamison KD (2008) Interval-valued probability in the analysis of problems containing a mixture of possibilistic, probabilistic, and interval uncertainty. Fuzzy Sets Syst 159(21):2845-2858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2008.03.013
Zadeh LA (2005) From imprecise to granular probabilities. Fuzzy Sets Syst 154(3):370-374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2005.02.007
Zimmermann H-J (n.d.) An application-oriented view of modeling uncertainty. www.elsevier.com/locate/orms
Wong BK, Lai VS (2011) A survey of the application of fuzzy set theory in production and operations management: 1998-2009. Int J prod Econ 129(1):157-168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2010.09.013
Dubois D, prade H (2003) Fuzzy set and possibility theory-based methods in artificial intelligence. Artif Intell 148(1-2):1-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0004-3702(03)00118-8
Steimann F (2001) On the use and usefulness of fuzzy sets in medical AI. Artif Intell Med 21(1-3):131-137. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0933-3657(00)00077-4
Deschrijver G, Kerre EE (2003) On the relationship between some extensions of fuzzy set theory. Fuzzy Sets Syst 133(2):227-235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(02)00127-6
Heilpern S (1992) The expected value of a fuzzy number. Fuzzy Sets Syst 47(1):81-86. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0114(92)90062-9
Dubois D, prade H (1993) Fuzzy numbers: an overview. In: Readings in fuzzy sets for intelligent systems. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 112-148. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4832-1450-4.50015-8
Bellman RE, Zadeh LA (1970) Decision-making in a fuzzy environment. Manag Sci 17(4):B-141-B−164. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.17.4.b141
Tanaka H, Asai K (1984) Fuzzy linear programming problems with fuzzy numbers. Fuzzy Sets Syst 13(1):1-10
Ghanbari R, Ghorbani-Moghadam K, Mahdavi-Amiri N, de Baets B (2020) Fuzzy linear programming problems: models and solutions. Soft Comput 24(13):10043-10073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04519-w
Sharma S et al (2022) Deep learning model for the automatic classification of white blood cells. Comput Intell Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7384131
Dinesh Kumar R, Golden Julie E, Harold Robinson Y, Vimal S, Dhiman G, Veerasamy M (2022) Deep convolutional nets learning classification for artistic style transfer. Sci program. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2038740
Sharma S et al (2022) Recognition of Gurmukhi handwritten city names using deep learning and cloud computing. Sci program. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5945117
Ma W, Wan L, Yu C, Zou L, Zheng J (2020) Multi-objective optimization of traffic signals based on vehicle trajectory data at isolated intersections. Transp Res C. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2020.102821
Shih L-H (1999) Cement transportation planning via fuzzy linear programming. Int J prod Econ 58(3):277-287. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5273(98)00206-0
Chanas S, Delgado M, Verdegay JL, Vila MA (1993) Interval and fuzzy extensions of classical transportation problems. Transp plan Technol 17(2):203-218. https://doi.org/10.1080/03081069308717511
Yang C, Wang Z, Oh SK, pedrycz W, Yang B (2022) Ensemble fuzzy radial basis function neural networks architecture driven with the aid of multi-optimization through clustering techniques and polynomial-based learning. Fuzzy Sets Syst 438:62-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2021.06.014
Yue Q, Zhang F, Wang Y, Zhang X, Guo p (2021) Fuzzy multi-objective modelling for managing water-food-energy-climate change-land nexus towards sustainability. J Hydrol (Amst). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125704
Jafarian-Moghaddam AR (2021) Economical speed for optimizing the travel time and energy consumption in train scheduling using a fuzzy multi-objective model. Urban Rail Transit 7(3):191-208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40864-021-00151-w
Ozdemir R et al (2021) Fuzzy multi-objective model for assembly line balancing with ergonomic risks consideration. Int J prod Econ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2021.108188
Ahmed JS, Mohammed HJ, Chaloob IZ (2021) Application of a fuzzy multi-objective defuzzification method to solve a transportation problem. Mater Today proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.1062
Zimmermann H-J (1978) Fuzzy programming and linear programming with several objective functions. Fuzzy Sets Syst 1(1):45-55
Singh SK, Yadav Sp (2018) Intuitionistic fuzzy multi-objective linear programming problem with various membership functions. Ann Oper Res 269(1-2):693-707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-017-2551-y
Karimi N, Feylizadeh MR, Govindan K, Bagherpour M (2022) Fuzzy multi-objective programming: a systematic literature review. Expert Syst Appl. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.116663
Vasant pM (2005) Solving fuzzy linear programming problems with modified S-curve membership function. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 13(01):97-109. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218488505003321
Vasant pM, Nagarajan R, Yaacob S (2002) Decision making using modified S-curve membership function in fuzzy linear programming problem. J Inf Commun Technol 2(2):1-16
Sakawa M (1983) Interactive computer programs for fuzzy linear programming with multiple objectives. Int J Man-Mach Stud 18(5):489-503
peidro D, Vasant p (2009) Fuzzy multi-objective transportation planning with modified S-curve membership function. AIp Conf proc. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3223935
Oliinyk V, Kozmenko O (2019) optimization of investment portfolio management. Serb J Manag 14(2):373-387. https://doi.org/10.5937/sjm14-16806
Wu Q, Liu X, Qin J, Zhou L, Mardani A, Deveci M (2022) An integrated multi-criteria decision-making and multi-objective optimization model for socially responsible portfolio selection. Technol Forecast Soc Change 184:121977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121977
Saborido R, Ruiz AB, Bermúdez JD, Vercher E, Luque M (2016) Evolutionary multi-objective optimization algorithms for fuzzy portfolio selection. Appl Soft Comput 39:48-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.11.005
Ruiz AB, Saborido R, Bermúdez JD, Luque M, Vercher E (2020) preference-based evolutionary multi-objective optimization for portfolio selection: a new credibilistic model under investor preferences. J Glob Optim 76(2):295-315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-019-00782-1
Bermúdez JD, Segura JV, Vercher E (2012) A multi-objective genetic algorithm for cardinality constrained fuzzy portfolio selection. Fuzzy Sets Syst 188(1):16-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2011.05.013
Zarjou M, Khalilzadeh M (2022) optima project portfolio selection with reinvestment strategy considering sustainability in an uncertain environment: a multi-objective optimization approach. Kybernetes 51(8):2437-2460. https://doi.org/10.1108/K-11-2020-0737
Shaw AK, Roy TK (2012) Some arithmetic operations on Triangular Intuitionistic Fuzzy Number and its application on reliability evaluation. http://www.ripublication.com
Sudha T, Jayalalitha G (2020) Fuzzy triangular numbers in-Sierpinski triangle and right angle triangle. J phys Conf Ser. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1597/1/012022
Ramik J, Imanek J (1985) Inequality relation between fuzzy numbers and its use in fuzzy optimization
Lai Y-J, Hwang C-L (1992) A new approach to some possibilistic linear programming problems. Fuzzy Sets Syst 49(2):121-133
Yang Xp, Cao BY, Lin HT (2014) Multi-objective fully fuzzy linear programming problems with triangular fuzzy numbers. In: 2014 11th International conference on fuzzy systems and knowledge discovery, FSKD 2014, December 2014. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc., pp 171-177. https://doi.org/10.1109/FSKD.2014.6980827
Ezzati R, Khorram E, Enayati R (2015) A new algorithm to solve fully fuzzy linear programming problems using the MOLP problem. Appl Math Model 39(12):3183-3193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2013.03.014
Kumar A, Kaur J, Singh p (2011) A new method for solving fully fuzzy linear programming problems. Appl Math Model 35(2):817-823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2010.07.037
Khemiri R, Naija M, Exposito E (2022) Dispatching and rebalancing for ride-sharing autonomous mobility-on-demand systems based on a fuzzy multi-criteria approach. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07377-1
Gulia p, Kumar R, Kaur A, Dhiman G (2022) A comparative study of fuzzy linear and multi-objective optimization. In: AI-enabled multiple-criteria decision-making approaches for healthcare management. IGI Global, pp 117-136
Jana B, Roy TK (2005) Multi-objective fuzzy linear programming and its application in transportation model. Tamsui Oxf J Math Sci 21(2):243-269
Gupta p, Mehlawat MK (2009) Bector-Chandra type duality in fuzzy linear programming with exponential membership functions. Fuzzy Sets Syst 160(22):3290-3308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2009.04.012
Jana B, Kumar Roy T (nd) Multi-objective intuitionistic fuzzy linear programming and its application in transportation model
Zangiabadi M, Maleki HR (2013) Fuzzy goal programming technique to solve multiobjective transportation problems with some non-linear membership functions. www.SID.ir
Shen D, Saab SS (2021) Noisy output based direct learning tracking control with Markov nonuniform trial lengths using adaptive gains. IEEE Trans Autom Control 67(8):4123-4130
Sayour MH, Kozhaya SE, Saab SS (2022) Autonomous robotic manipulation: real-time, deep-learning approach for grasping of unknown objects. J Robot 2022:2585656
Shen D, Huo N, Saab SS (2021) A probabilistically quantized learning control framework for networked linear systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 33(12):7559-7573
Saab SS, Jaafar RH (2021) A proportional-derivative-double derivative controller for robot manipulators. Int J Control 94(5):1273-1285
Saab SS, Shen D, Orabi M, Kors D, Jaafar RH (2021) Iterative learning control: practical implementation and automation. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 69(2):1858-1866
Dayan F, Rafiq M, Ahmed N, Baleanu D, Raza A, Ahmad MO, Iqbal M (2022) Design and numerical analysis of fuzzy nonstandard computational methods for the solution of rumor based fuzzy epidemic model. physica A 600:127542
Kouatli I (2020) The use of fuzzy logic as augmentation to quantitative analysis to unleash knowledge of participants’ uncertainty when filling a survey: case of cloud computing. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 34(3):1489-1500
Ben Abdallah S, Kouatli I (2020) Fuzzy volatility of project option value based on trapezoidal membership functions. In: Intelligent and fuzzy techniques in big data analytics and decision making: proceedings of the INFUS 2019 conference, Istanbul, Turkey, 23-25 July 2019. Springer, pp 1307-1314
Abdallah SB, Kouatli I (2018) Fuzzy volatility effect on major projects timing. In: 2018 IEEE international conference on fuzzy systems (FUZZ-IEEE), 2018. IEEE, pp 1-6
Azadeh A, Kalantari M, Ahmadi G, Eslami H (2019) A flexible genetic algorithm-fuzzy regression approach for forecasting: the case of bitumen consumption. Constr Innov 19(1):71-88
Taheri R, Kabuli M, Vryzas Z (2020) Fracturing and permeability enhancement with laser technology employing fuzzy logic. J pet Sci Eng 188:106830
Kouatli I (2018) Fuzzimetric employee evaluations system (FEES): a multivariable-modular approach. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 35(4):4717-4729
Salloum G, Tekli J (2021) Automated and personalized nutrition health assessment, recommendation, and progress evaluation using fuzzy reasoning. Int J Hum-Comput Stud 151:102610
Abboud R, Tekli J (2020) Integration of nonparametric fuzzy classification with an evolutionary-developmental framework to perform music sentiment-based analysis and composition. Soft Comput 24(13):9875-9925
Ghanem CR, Gereige EN, Bou Nader WS, Mansour CJ (2022) Stirling system optimization for series hybrid electric vehicles. proc Inst Mech Eng D 236(2-3):407-423
Abbas N, Fawaz W, Sharafeddine S, Mourad A, Abou-Rjeily C (2022) SVM-based task admission control and computation offloading using Lyapunov optimization in heterogeneous MEC network. IEEE Trans Netw Serv Manag 19(3):3121-3135
Marrouche W, Farah R, Harmanani HM (2018) A multiobjective optimization method for the SOC test time, TAM, and power optimization using a strength Pareto evolutionary algorithm. In: Information technology-new generations: 14th international conference on information technology, 2018. Springer, pp 685-695
Yusuf A, Sulaiman TA, Alshomrani AS, Baleanu D (2022) Optical solitons with nonlinear dispersion in parabolic law medium and three-component coupled nonlinear Schrödinger equation. Opt Quantum Electron 54(6):390
Issa JS (2022) A nonlinear absorber for the reflection of travelling waves in bars. Nonlinear Dyn 108(4):3279-3295
Tiwari AK, Bathia D, Bouri E, Gupta R (2021) Investor sentiment connectedness: evidence from linear and nonlinear causality approaches. Ann Financ Econ 16(04):2150016
Tekli J, Tekli G, Chbeir R (2021) Almost linear semantic XML keyword search. In: proceedings of the 13th international conference on management of digital ecosystems, 2021, pp 129-138
Chamoun S, Nour C (2021) A nonlinear ϕ0-convexity result for the bilateral minimal time function
Kassis MT, Tannir D, Toukhtarian R, Khazaka R (2019) Moments-based sensitivity analysis of X-parameters with respect to linear and nonlinear circuit components. In: 2019 IEEE 28th conference on electrical performance of electronic packaging and systems (EpEpS), 2019. IEEE, pp 1-3
Saab SS, Saab KK (2019) Shuffled linear regression with erroneous observations. In: 2019 53rd annual conference on information sciences and systems (CISS), 2019. IEEE, pp 1-6
Bouri E, Gupta R, Wang S (2022) Nonlinear contagion between stock and real estate markets: international evidence from a local Gaussian correlation approach. Int J Finance Econ 27(2):2089-2109
Hussain M, Kaassamani S, Auguste T, Boutu W, Gauthier D, Kholodtsova M, Gomes J-T et al (2021) Spectral control of high order harmonics through non-linear propagation effects. Appl phys Lett 119(7):071101
Haraty RA, Mansour N, Zeitunlian H (2018) Metaheuristic algorithm for state-based software testing. Appl Artif Intell 32(2):197-213
Tarhini A, Harfouche A, De Marco M (2022) Artificial intelligence-based digital transformation for sustainable societies: the prevailing effect of COVID-19 crises. pac Asia J Assoc Inf Syst 14(2):1
Nour C, Takche J (2020) A general result about inner regularization of sets. J Convex Anal 27(3):943-958
Chicha E, Al Bouna B, Nassar M, Chbeir R, Haraty RA, Oussalah M, Benslimane D, NaserAlraja M (2021) A user-centric mechanism for sequentially releasing graph datasets under blowfish privacy. ACM Trans Internet Technol 21(1):1-25
Mourad A, Tout H, Wahab OA, Otrok H, Dbouk T (2020) Ad hoc vehicular fog enabling cooperative low-latency intrusion detection. IEEE Internet Things J 8(2):829-843
AbdulRahman S, Tout H, Mourad A, Talhi C (2020) FedMCCS: multicriteria client selection model for optima IoT federated learning. IEEE Internet of Things J 8(6):4723-4735
Rahman SA, Tout H, Talhi C, Mourad A (2020) Internet of Things intrusion detection: centralized, on-device, or federated learning? IEEE Netw 34(6):310-317
Khabbaz M, Assi C, Sharafeddine S (2021) Multihop V2U path availability analysis in UAV-assisted vehicular networks. IEEE Internet Things J 8(13):10745-10754
Sorkhoh I, Ebrahimi D, Assi C, Sharafeddine S, Khabbaz M (2020) An infrastructure-assisted workload scheduling for computational resources exploitation in the fog-enabled vehicular network. IEEE Internet Things J 7(6):5021-5032
Arafeh M, El Barachi M, Mourad A, Belqasmi F (2019) A blockchain based architecture for the detection of fake sensing in mobile crowdsensing. In: 2019 4th International conference on smart and sustainable technologies (SpliTech), 2019. IEEE, pp 1-6
Haraty RA, Boukhari B, Kaddoura S (2021) An effective hash-based assessment and recovery algorithm for healthcare systems. Arab J Sci Eng 47:1-14
Yunis M, Markarian C, El-Kassar AN (2020) A conceptual model for sustainable adoption of eHealth: role of digital transformation culture and healthcare provider’s readiness. In: proceedings of the IMCIC, 2020
Helwan A, Ma’aitah MKS, Uzelaltinbulat S, Altobel MZ, Darwish M (2021) Gaze prediction based on convolutional neural network. In: International conference on emerging technologies and intelligent systems, 2021. Springer, Cham, pp 215-224
Gerges F, Shih F, Azar D (2021) Automated diagnosis of Acne and Rosacea using convolution neural networks. In: 2021 4th International conference on artificial intelligence and pattern recognition, 2021, pp 607-613
Abbas N, Nasser Y, Shehab M, Sharafeddine S (2021) Attack-specific feature selection for anomaly detection in software-defined networks. In: 2021 3rd IEEE Middle East and North Africa COMMunications conference (MENACOMM), 2021. IEEE, pp 142-146
Tarhini A, Danach K, Harfouche A (2020) Swarm intelligence-based hyper-heuristic for the vehicle routing problem with prioritized customers. Ann Oper Res 308:1-22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gulia, P., Kumar, R., Viriyasitavat, W. et al. A Systematic Review on Fuzzy-Based Multi-objective Linear programming Methodologies: Concepts, Challenges and Applications. Arch Computat Methods Eng 30, 4983–5022 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-023-09966-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-023-09966-1