Abstract
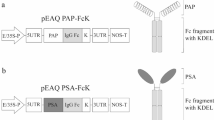
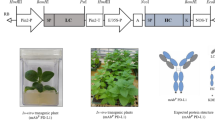
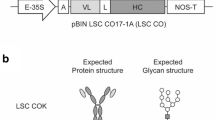
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is a protein highly expressed in cancer cells of the prostate gland. In this study, the PSA recombinant protein was fused to the human immunoglobulin G crystallizable fragment (Fc) with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu (KDEL) retention signal tag for the plant expression system. Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation was applied to generate transgenic tobacco plants expressing PSA tagged to KDEL (PSAK), PSA-Fc, and PSA-Fc fused to KDEL (PSA-FcK). Western blot analysis showed that the PSA-FcK protein was the most highly expressed among the three different proteins in the transgenic plant leaf. The PSAK, PSA-Fc, and PSA- FcK proteins were successfully purified from plant leaves. Reduced and non-reduced sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis revealed that the PSA proteins fused to Fc and FcK were dimerized, whereas the PSA itself was not dimerized. N-glycan analysis demonstrated that the N-glycan profile of the PSA-Fc was mainly the structure with α(1,3)-fucose (Fuc) or β(1,2)-xylose (Xyl) glycan residues, whereas the PSA-Fc tagged with the KDEL ER retention signal had mainly an oligomannose-type structure. ELISA and SPR showed that PSA-FcK had a higher binding activity to Fc gamma receptor I than PSA-Fc and human Fc. In addition, PSA-FcK induced anti-PSA, and thus has the potential to be utilized as a prostate cancer vaccine.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adhyam M, Gupta AK (2012) A review on the clinical utility of PSA in cancer prostate. Indian J Surg Oncol 3:120–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-012-0142-6
Arcalis E, Stadlmann J, Rademacher T et al (2013) Plant species and organ influence the structure and subcellular localization of recombinant glycoproteins. Plant Mol Biol 83:105–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-013-0049-9
Beck A, Reichert JM (2011) Therapeutic Fc-fusion proteins and peptides as successful alternatives to antibodies. Proceedings of the MAbs 3:415–416. https://doi.org/10.4161/mabs.3.5.17334
Burnett MJ, Burnett AC (2020) Therapeutic recombinant protein production in plants: Challenges and opportunities. Plants People Plant 2:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppp3.10073
Cabanes-Macheteau M, Fitchette-Lainé A-C, Loutelier-Bourhis C et al (1999) N-glycosylation of a mouse IgG expressed in transgenic tobacco plants. Glycobiology 9:365–372. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/9.4.365
Chakraborty NG, Stevens RL, Mehrotra S et al (2003) Recognition of PSA-derived peptide antigens by T cells from prostate cancer patients without any prior stimulation. Cancer Immunol Immunother 52:497–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-003-0377-8
Donini M, Marusic C (2019) Current state-of-the-art in plant-based antibody production systems. Biotechnol Lett 41:335–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02651-z
Doran PM (2006) Foreign protein degradation and instability in plants and plant tissue cultures. Trends Biotechnol 24:426–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2006.06.012
Dungan KM, Povedano ST, Forst T et al (2014) Once-weekly dulaglutide versus once-daily liraglutide in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes (AWARD-6): a randomised, open-label, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 384:1349–1357. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60976-4
Fay EK, Graff JN (2020) Immunotherapy in Prostate. Cancer Cancers 12(7):1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071752
Gavin A, Hulett M, Hogarth P (1998) Molecular basis for the interaction of Fc receptors with immunoglobulins. Immunoglobulin Receptors Their Physio Pathological Roles Immunity 26:11–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-5018-7_2
Ghose S, Hubbard B, Cramer SM (2007) Binding capacity differences for antibodies and Fc-fusion proteins on protein a chromatographic materials. Biotechnol Bioeng 96:768–779. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.21044
Ghosh A, Heston WDW (2004) Tumor target prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) and its regulation in prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem 91:528–539. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.10661
Heier JS, Brown DM, Chong V et al (2012) Intravitreal aflibercept (VEGF trap-eye) in wet age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 119:2537–2548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.09.006
Junker F, Gordon J, Qureshi O (2020) Fc gamma receptors and their role in antigen uptake, presentation, and T cell activation. Front Immunol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01393
Kang YJ, Kim D-S, Myung S-C, Ko K (2017) Expression of a human prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP)-IgM Fc fusion protein in plants using in vitro tissue subculture. Front Plant Sci 8:274
Kantoff PW, Schuetz TJ, Blumenstein BA et al (2010) Overall survival analysis of a phase ii randomized controlled trial of a Poxviral-Based PSA-targeted immunotherapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clinical Oncology 28:1099
Karan D, Holzbeierlein JM, Van Veldhuizen P, Thrasher JB (2012) Cancer immunotherapy: a paradigm shift for prostate cancer treatment. Nat Rev Urol 9:376–385
Kim H-S, Jeon J-H, Lee KJ, Ko K (2014) N-glycosylation modification of plant-derived virus-like particles: an application in vaccines. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/249519
Kim K, Kang YJ, Park SR et al (2021) Effect of leaf position and days post-infiltration on transient expression of colorectal cancer vaccine candidate proteins GA733-Fc and GA733-FcK in Nicotiana benthamiana plant. PeerJ 9:e10851. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.10851
Kim Y-K, So Y-K, Park D-Y et al (2010) Plant-based production of therapeutic antibodies. J Plant Biot. https://doi.org/10.5010/JPB.2010.37.3.262
Lim C-Y, Kim D-S, Kang Y, Lee Y-R, Kim K, Kim M-S, Ko (2022) Immune responses to plant-derived recombinant colorectal cancer glycoprotein EpCAM-FcK fusion protein in mice. Biomolecules Therapeutics 30:546–552. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2022.103
Madan RA, Arlen PM, Mohebtash M, Hodge JW, Gulley JL (2009) Prostvac-VF: a vector-based vaccine targeting PSA in prostate cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther 18:1001–1011. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543780902997928
Manabe Y, Marchetti R, Takakura Y et al (2019) The Core Fucose on an IgG antibody is an endogenous ligand of dectin-1. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 131:18870–18875. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201911875
Moradi A, Srinvasan S, Clements J et al (2019) Beyond the biomarker role: prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in the prostate cancer microenvironment. Cancer Metastasis Rev 38(3):333–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-019-09815-3
Napier RM, Fowke LC, Hawes C, Lewis M, Pelham HR (1992) Immunological evidence that plants use both HDEL and KDEL for targeting proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci 102:261–271. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.102.2.261
Oesterling JE (1991) Prostate specific antigen: a critical assessment of the most useful tumor marker for adenocarcinoma of the prostate. J Urol 145:907–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)38491-4
Park SR, Lee J-H, Kim K et al (2020) Expression and in vitro function of anti-breast cancer llama-based single domain antibody VHH expressed in tobacco plants. Int J Mol Sci 21:1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041354
Pincetic A, Bournazos S, Dilillo DJ et al (2014) Type I and type II Fc receptors regulate innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Immunol 15:707–716. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2939
Pricop L, Redecha P, Teillaud J-L et al (2001) Differential modulation of stimulatory and inhibitory Fcγ receptors on human monocytes by Th1 and Th2 cytokines. J Immunol 166:531–537. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.166.1.531
Quayle JA, Watson F, Bucknall R, Edwards SJI (1997) Neutrophils from the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis express the high affinity immunoglobulin G receptor, FcγRI (CD64): role of immune complexes and cytokines in induction of receptor expression. Immunology 91:266–273. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2567.1997.00249.x
Reiter RE, Gu Z, Watabe T et al (1998) Prostate stem cell antigen: a cell surface marker overexpressed in prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1735–1740. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.4.1735
Roopenian DC, Akilesh S (2007) FcRn: the neonatal Fc receptor comes of age. Nat Rev Immunol 7:715–725. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2155
Saif JM, Vadakekolathu J, Rane SS et al (2014) Novel prostate acid phosphatase-based peptide vaccination strategy induces antigen-specific T-cell responses and limits tumour growth in mice. Eur J Immunol 44:994–1004. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201343863
Seidah NG, Chrétien M (1997) Eukaryotic protein processing: endoproteolysis of precursor proteins. Curr Opin Biotechnol 8:602–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0958-1669(97)80036-5
Shin C, Kang Y, Kim H-S, Shin YK, Ko K (2019) Immune response of heterologous recombinant antigenic protein of viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) in mice. Anim Cells Syst (seoul) 23:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1080/19768354.2019.1575904
Siegel, R.L., Miller, K.D., Goding Sauer A, et al., (2020). Colorectal cancer statistics. 70, 145–64. doi: https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21601
Silva-Alvim FA, An J, Alvim JC et al (2018) Predominant Golgi residency of the plant K/HDEL receptor is essential for its function in mediating ER retention. Plant Cell 30:2174–2196. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00426
Song I, Kang Y, Lee YK, Myung S-C, Ko K (2018) Endoplasmic reticulum retention motif fused to recombinant anti-cancer monoclonal antibody (mAb) CO17-1A affects mAb expression and plant stress response. PLoS ONE 13:e0198978. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198978
Song I, Kang YJ, Choi S-L et al (2019) Purification of plant-derived anti-virus mAb through optimized pH conditions for coupling between protein a and epoxy-activated beads. PeerJ 7:e6828. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6828
Song I, Kang YJ, Kim DH, Kim MK, Ko K (2020) Expression and in vitro function of anti-cancer mAbs in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. BMB Rep 53:229. https://doi.org/10.5483/BMBRep.2020.53.4.106
Song I, Lee YK, Kim JW et al (2021) Effect of an Endoplasmic Reticulum Retention Signal Tagged to Human Anti-Rabies mAb SO57 on Its Expression in Arabidopsis and Plant Growth. Mol Cells 44:770. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2021.2002
Swanson JA, Hoppe AD (2004) The coordination of signaling during Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis. J Leukoc Biol 76:1093–1103. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0804439
Yousef GM, Diamandis EP (2001) The new human tissue kallikrein gene family: structure, function, and association to disease. Endocr Rev 22:184–204. https://doi.org/10.1210/edrv.22.2.0424
Funding
This work was carried out with the support of “Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project No. PJ0162662022)” Korean Rural Development Administration, and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) [2021R1F1A1063869].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, CHS, and KK; methodology, KBK, SRP, YJK, DS., and YJS; validation, CHS, KKB, SRP, YKS, and YJK; formal analysis, KBK.; investigation, CHS., YKS and DSK.; resources, KBK, YKL, KMK, and KK.; data curation, KBK, and YJK; writing—original draft preparation, CHS; writing—review and editing, KSK.; visualization, KBK., and KMK; supervision, KSK; project administration, KBK., and YJK.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, C., Kim, K., Kang, Y.J. et al. Effect of IgG Fc-fusion and KDEL-ER retention signal on prostate-specific antigen expression in plant and its immune in mice. Plant Biotechnol Rep 16, 729–740 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-022-00810-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-022-00810-9