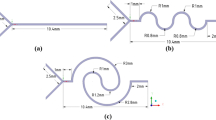
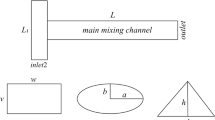
Abstract
In this paper, we evaluate the influence of various micromixer designs on the mixing efficiency of passive micromixers. We analyze the designs of various passive micromixers to identify the most efficient micromixer. Among them, the toroidal micromixer and 3D zig-zag micromixer demonstrated the highest mixing efficiency. We investigated the key factors influencing mixing in the toroidal and 3D zig-zag micromixer, identifying and confirming optimal designs. Ultimately, when comparing the mixing efficiency of the two micromixers, the 3D zig-zag micromixer achieved full mixing in a very short time of 0.8 ms. Through this research, it is anticipated that a benchmark will be provided for micromixer design in microfluidic devices when manufacturing micromixers of various forms.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.-C. Leong, C.-H. Tsai, C.-L. Chang, C.-F. Lin, L.-M. Fu, Rapid microfluidic mixers utilizing dispersion effect and interactively time-pulsed injection. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 5345 (2007)
T.H. Schulte, R.L. Bardell, B.H. Weigl, Microfluidic technologies in clinical diagnostics. Clin. Chim. Acta 321, 1–10 (2002)
S.Z. Razzacki, P.K. Thwar, M. Yang, V.M. Ugaz, M.A. Burns, Integrated microsystems for controlled drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 56, 185–198 (2004)
Y. He et al., Numerical investigation of the mixing process in a Twin Cam Mixer: influence of triangular cam height-base ratio and eccentricity. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 38, 552–564 (2021)
A.G. Niculescu, C. Chircov, A.C. Birca, A.M. Grumezescu, Fabrication and applications of microfluidic devices: a review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22(4), 2011 (2021).
I. Ji, J.W. Kang, T. Kim, M.S. Kang, S.B. Kwon, J. Hong, 3D printing-based ultrafast mixing and injecting systems for time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography. Korean Chem. Eng. Res. 60(2), 300–307 (2022)
S.-H. Jang, I.-J. Kang, Drug delivery study on chitosan nanoparticles using iron oxide (II, III) and valine. Korean Chem. Eng. Res. 59, 514–520 (2021)
W.-H. Choi, B. Kim, Fabrication and characterization of dissolving microneedles containing lecithin for transdermal drug delivery. Korean Chem. Eng. Res. 59, 429–434 (2021)
M. Maeki, S. Uno, A. Niwa, Y. Okada, M. Tokeshi, Microfluidic technologies and devices for lipid nanoparticle-based RNA delivery. J. Control. Release 344, 80–96 (2022)
K.K.V. Canlas et al., Trends in nano-platforms for the treatment of viral infectious diseases. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 40, 706–713 (2023)
E. Hong, J. Jeon, H.U. Kim, Recent development of machine learning models for the prediction of drug-drug interactions. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 40, 276–285 (2023)
G. Zhang, J. Sun, Lipid in chips: a brief review of liposomes formation by microfluidics. Int. J. Nanomed. 16, 7391–7416 (2021).
M. Maeki, N. Kimura, Y. Sato, H. Harashima, M. Tokeshi, Advances in microfluidics for lipid nanoparticles and extracellular vesicles and applications in drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 128, 84–100 (2018)
M.S. Ali, N. Hooshmand, M. El-Sayed, H.I. Labouta, Microfluidics for development of lipid nanoparticles: paving the way for nucleic acids to the clinic. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 6, 3566–3576 (2021)
M. Faryadi, M. Rahimi, S. Safari, N. Moradi, Effect of high frequency ultrasound on micromixing efficiency in microchannels. Chem. Eng. Process. 77, 13–21 (2014)
K.-I. Min, Fabrication of 3D multilayered microfluidic channel using fluorinated ethylene propylene nanoparticle dispersion. Korean Chem. Eng. Res. 59, 639–643 (2021)
B. Zhou et al., Design and fabrication of magnetically functionalized flexible micropillar arrays for rapid and controllable microfluidic mixing. Lab Chip 15, 2125–2132 (2015)
D. Ahmed, X. Mao, J. Shi, B.K. Juluri, T.J. Huang, A millisecond micromixer via single-bubble-based acoustic streaming. Lab Chip 9, 2738–2741 (2009)
K. Karthikeyan, L. Sujatha, Study of permissible flow rate and mixing efficiency of the micromixer devices. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 17, 20180047 (2018)
A. Cosentino et al., An efficient planar accordion-shaped micromixer: from biochemical mixing to biological application. Sci. Rep. 5, 17876 (2015)
A. Agarwal, A. Salahuddin, H. Wang, M.J. Ahamed, Design and development of an efficient fluid mixing for 3D printed lab-on-a-chip. Microsyst. Technol. 26, 2465–2477 (2020)
H. Lv, X. Chen, Novel study on the mixing mechanism of active micromixers based on surface acoustic waves. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 61, 10264–10274 (2022)
M. Bayareh, M.N. Ashani, A. Usefian, Active and passive micromixers: a comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intens. 147, 107771 (2020)
J. Sun et al., Numerical and experimental investigation of a magnetic micromixer under microwires and uniform magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 551, 169141 (2022)
D. Bahrami, A.A. Nadooshan, M. Bayareh, Effect of non-uniform magnetic field on mixing index of a sinusoidal micromixer. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 39, 316–327 (2022)
S.-G. Jeong et al., Nanoliter scale microloop reactor with rapid mixing ability for biochemical reaction. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 35, 2036–2042 (2018)
B. Yin et al., Micromixer with fine-tuned mathematical spiral structures. ACS Omega 6, 30779–30789 (2021)
E. Nady, G. Nagy, R. Huszánk, Improvement in mixing efficiency of microfluidic passive mixers functionalized by microstructures created with proton beam lithography. Chem. Eng. Sci. 247, 117006 (2022)
S. Hossain, M. Ansari, K.-Y. Kim, Evaluation of the mixing performance of three passive micromixers. Chem. Eng. J. 150, 492–501 (2009)
J. Choe, Y. Kwon, Y. Kim, H.-S. Song, K.H. Song, Micromixer as a continuous flow reactor for the synthesis of a pharmaceutical intermediate. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 20, 268–272 (2003)
M. Nimafar, V. Viktorov, M. Martinelli, Experimental comparative mixing performance of passive micromixers with H-shaped sub-channels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 76, 37–44 (2012)
V. Viktorov, M.R. Mahmud, C. Visconte, Comparative analysis of passive micromixers at a wide range of Reynolds numbers. Micromachines 6, 1166–1179 (2015)
P. Li, J. Cogswell, M. Faghri, Design and test of a passive planar labyrinth micromixer for rapid fluid mixing. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 174, 126–132 (2012)
T. Tofteberg, M. Skolimowski, E. Andreassen, O. Geschke, A novel passive micromixer: lamination in a planar channel system. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 8, 209–215 (2010)
J.J. Chen, Y.S. Shie, Interfacial configurations and mixing performances of fluids in staggered curved-channel micromixers. Microsyst. Technol. 18, 1823–1833 (2012)
M.K. Parsa, F. Hormozi, D. Jafari, Mixing enhancement in a passive micromixer with convergent–divergent sinusoidal microchannels and different ratio of amplitude to wave length. Comput. Fluids 105, 82–90 (2014)
X. Chen, Z. Zhao, Numerical investigation on layout optimization of obstacles in a three-dimensional passive micromixer. Anal. Chim. Acta 964, 142–149 (2017)
S.O. Hong et al., Gear-shaped micromixer for synthesis of silica particles utilizing inertio-elastic flow instability. Lab Chip 21, 513–520 (2021)
S. Kim et al., Monolithic 3D micromixer with an impeller for glass microfluidic systems. Lab Chip 20, 4474–4485 (2020)
A.D. Stroock et al., Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science 295, 647–651 (2002)
Wild, Andre, Timothy Leaver, and Robert James Taylor. "Bifurcating mixers and methods of their use and manufacture." U.S. Patent No. 10,076,730. (2018)
H. Kim et al., Submillisecond organic synthesis: Outpacing Fries rearrangement through microfluidic rapid mixing. Science 352, 691–694 (2016)
B. Lee et al., Characterization of passive microfluidic mixer with a three-dimensional zig-zag channel for cryo-EM sampling. Chem. Eng. Sci. 281, 119161 (2023)
C. Wang, Y. Hu, Mixing of liquids using obstacles in y-type microchannels. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 13, 385–394 (2010)
M.A. Ansari, K.-Y. Kim, Shape optimization of a micromixer with staggered herringbone groove. Chem. Eng. Sci. 62, 6687–6695 (2007)
T.J. Kwak et al., Convex grooves in staggered herringbone mixer improve mixing efficiency of laminar flow in microchannel. PLoS ONE 11, e0166068 (2016)
P.B. Howell Jr., D.R. Mott, J.P. Golden, F.S. Ligler, Design and evaluation of a Dean vortex-based micromixer. Lab Chip 4, 663–669 (2004)
C. Webb et al., Using microfluidics for scalable manufacturing of nanomedicines from bench to GMP: a case study using protein-loaded liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 582, 119266 (2020)
J. Li, G. Xia, Y. Li, Numerical and experimental analyses of planar asymmetric split-and-recombine micromixer with dislocation sub-channels. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 88, 1757–1765 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2021R1A2C3004936 and 2021R1A5A8032895). ※ MSIT: Ministry of Science and ICT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, S.y., Lee, CS. Comparison and Analysis of Mixing Efficiency in Various Micromixer Designs. Korean J. Chem. Eng. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-024-00161-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-024-00161-x