Abstract
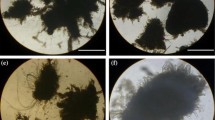
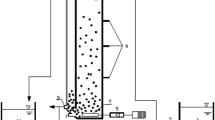
We constructed a bench-scale up-flow anaerobic sludge reactor to systematically investigate the physicochemical characteristics of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) anaerobic granular sludge and evaluate the granular size by a grey relational analysis. Results indicated that the granulation proportion was improved from 17.9% to 68.7% with the sulfate reduction efficiency larger than 90% under gradually shortened hydraulic retention time (HRT) and increased organic loading. Larger SRB granule sludge showed a higher specific gravity and settling velocity. The seed sludge was negatively charged, and the surface charge decreased with the incremental granular diameter. The maximal hydrophobicity and granulation proportion were 69.9% and 42.4%, respectively, for the granular diameter ranging from 1.5 to 2.5 mm. Extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) of the sludge exhibited the highest ratio of protein to polysaccharide (PN/PS) for the granular diameter in the range of 0.5 to 1.5mm. Based on the grey relational analysis of the SRB anaerobic sludge granulation, the correlation degree of the inherent influencing factors was PN/PS>surface charge> hydrophobicity. The theoretical evaluation would be conducive to granulation control during the potential application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.X. Zhang, Y. B. Zhang, X. Quan, Y.W. Liu, X. L. An, S. Chen and H. M. Zhao, Chem. Eng. J., 174, 159 (2011).
T. W. Hao, J. H. Luo, W. Li, H. R. Mackey, R. L. Liu, G. R. Morito and G. H. Chen, Water Res., 71, 74 (2015).
P. N. L. Lens, A. Visser, A. J. H. Janssen, L. W. Hulshoff and G. Lettinga, Sci. Technol., 28, 41 (1998).
E. Blázquez, D. Gabriel, J. A. Baeza and A. Guisasola, Water Res., 105, 395 (2016).
Y. W. Liu, Y. B. Zhang and B. J. Ni, Water Res., 75, 292 (2015).
L. Zhu, J. H. Zhou, M. l. Lv, H.T. Yu, H. Zhao and X.Y. Xu, Chemosphere, 121, 26 (2015).
Y. Liu and J. H. Tay, Biotechnol. Adv., 22, 533 (2004).
Z. Q. Jing, Y. Hu, Q. G. Niu, Y. Y. Liu, Y.-Y. Li and X.-c.C. Wang, Bioresour. Technol., 137, 349 (2013).
H. T. Q. Kieu, E. Müller and H. Horn, Water Res., 45, 3863 (2011).
J. Li, L. Yu, D. S. Yu, D. Wang, P.Y. Zhang and Z. G. Ji, Biodegradation, 25, 127 (2014).
M. K. Tiwari, S. Guha, C. S. Harendranath and S. Tripathi, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 71, 145 (2006).
T. Abbasi and S. A. Abbasi, Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 16, 1696 (2012).
L. Appels, J. Baeyens, J. Degrève and R. Dewil, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci., 34, 755 (2008).
N. Mirzoyan and A. Gross, Water Res., 47, 2843 (2013).
K. S. Singh and T. Viraraghavan, Water Sci. Technol., 48, 211 (2003).
M. Isik and D. T. Sponza, Bioresour. Technol., 96, 633 (2005).
T. H. Erguder, E. Guven and G. N. Demirer, Chemosphere, 50, 165 (2003).
X. S. Jia, H. H. Fang and H. Furumai, Water Sci. Technol., 34, 309 (1996).
X.Y. Li and S. F. Yang, Water Res., 41, 1022 (2007).
G. P. Sheng, H.Q. Yu and X.Y. Li, Biotechnol. Adv., 28, 882 (2010).
J. Quarmby and C. F. Forster, Water Res., 29, 2449 (1995).
T. Seviour, Z. Yuan and V. M. C. M. Loosdrecht, Water Res., 46, 4803 (2012).
J.M. Morgan, C.F. Forster and L. Evison, Water Res., 24, 743 (1990).
J. L. Deng, J. Grey. Syst., 1, 1 (1989).
C. Zhang and H. Zhang, J. Environ. Sci., 25, 710 (2013).
G.M. Zeng, R. Jiang, G. H. Huang, M. Xu and J.B. Li, J. Environ. Manage., 82, 250 (2007).
A. Kadier, P. Abdeshahian, Y. Simayi, M. Ismail, A. A. Hamid and M. S. Kalil, Energy, 90, 1556 (2015).
J. Xu, G. P. Sheng, H.W. Luo, F. Fang, W.W. Li, R. J. Zeng, Z.H. Tong and H.Q. Yu, Water Res., 45, 674 (2011).
J. E. Schmidt and B.K. Ahring, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 49, 229 (1996).
J. Guo, Y. Kang and Y. Feng, J. Environ. Manage., 203, 278 (2017).
APHA, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, twenty-first ed. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC (2005).
H. Bai, Y. Kang, H.-e. Quan, Y. Han, J. Sun and Y. Feng, Bioresour. Technol., 128, 818 (2013).
O. H. Lowry, N. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Farr and R. J. Randall, J. Biol. Chem., 193, 265 (1951).
I. Chang and C. Lee, Desalination, 120, 221 (1998).
M. Sun, W.W. Li, H.Q. Yu, and H. Harada, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 96, 1577 (2012).
H. Bai, Y. Kang, H.-e. Quan, Y. Han, J. Sun and Y. Feng, J. Environ. Manage., 129, 350 (2013).
T. Hao, H. Lu, H. K. Chui, V. M.C. M. Loosdrecht and G.H. Chen, Water Sci. Technol., 68, 560 (2013).
J.X. Ye, Y. J. Mu, X. Cheng and D. Z. Sun, Bioresour. Technol., 102, 5498 (2011).
M.A. Willow and R.R.H. Cohen, J. Environ. Qual., 32, 1212 (2003).
H. H. Beeftink and J.V.D. Heuvel, Physical properties of bacterial aggregates in a continuous-flow reactor with biomass retention, G. Letting, A. J. B. Zehnder, J.T.C. Grotenhuis and L.W. Hulshoff-Pol Eds., The Netherlands (1988).
Z. P. Wang, L. L. Liu, J. Yao and W. M. Cai, Chemosphere, 63, 1728 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Kang, Y. Characterization of sulfate-reducing bacteria anaerobic granular sludge and granulometric analysis with grey relation. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 35, 1829–1835 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-018-0092-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-018-0092-y