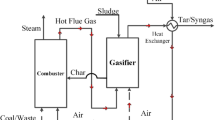
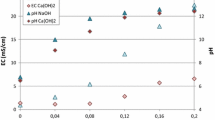
Abstract
We evaluated the effects of Na, K, Ca, and the steam-to-biomass (S/B) ratio on gasification efficiency during syngas production. The results show that H2 production was positively correlated with the S/B ratio. However, increases in the S/B ratio were limited because excessive steam decreased the reactor temperature and hampered the gasification process. Regarding the effects of alkali metals on syngas composition, we found that the addition of either Na or K increased the molar percentages of H2 and CO, but decreased CH4 and CO2. The results also clearly show that the addition of Na or K improved the yield of syngas, the carbon conversion efficiency, and the cold gas efficiency. Improvements were especially pronounced with K. Furthermore, Ca had different interactions with Na and K during gasification. When Na and Ca existed simultaneously, H2 production was enhanced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.H. Lee, G.T. Kim and J.G. Choi, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 28, 1468 (2011).
H. Namkung, T. J. Kang, L.H. Xu, Y. S. Jeon and H.T. Kim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 29, 464 (2012).
J.M. Lee, D.W. Kim and J. S. Kim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 29, 452 (2012).
P. Basu, Combustion and gasification in fluidized beds, CRC Press in Taylor & Francis Group, Florida, USA (2006).
M. Ni, D.Y. C. Leung, M. K.H. Leung and K. Sumathy, Fuel Proc. Technol., 87, 461 (2006).
L. Devi, K. J. Ptasinski and F. J. J.G. Janssen, Biomass Bioenergy, 24, 125 (2003).
D. Ross, R. Noda, M. Horio, A. Kosminski, P. Ashman and P. Mullinger, Fuel, 86, 1417 (2007).
U. Arena, L. Zaccariello and M. L. Mastellone, Waste Manage., 29, 783 (2009).
P. Weerachanchai, M. Horio and C. Tangsathitkulchai, Bioresour. Technol., 100, 1419 (2009).
L. García, M. L. Salvador, J. Arauzo and R. Bilbao, Fuel Proc. Technol., 69, 157 (2001).
S. Hurley, H. Li and C. Xu, Bioresour. Technol., 101, 9301 (2010).
J. Wang, M. Jiang, Y. Yao and J. Zhang, Fuel, 88, 1572 (2009).
C. L. Lin, M. Y. Wey and S. D. You, Powder Technol., 126, 297 (2002).
S. Luo, B. Xiao, Z. Hu, S. Liu, X. Guo and M. He, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 34, 2191 (2009).
L. Shen, Y. Gao and J. Xiao, Biomass Bioenergy, 32, 120 (2008).
J. T. Sears, H. S. Muralidhara and C.Y. Wen, Ind. Eng. Chem. Proc. Des. Dev., 19, 58 (1980).
J. A. Mouijin, M. B. Cenfontain and F. Kapteijn, Fuel, 63, 1043 (1984).
J.M. Saber, J. L. Falconer and L. F. Brown, Fuel, 65, 1356 (1986).
D.W. Mckee, Fuel, 62, 170 (1983).
N. H. Florin and A. T. Harris, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 31, 945 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, TH., Lin, CL. & Chen, H. Effects of alkali- and alkaline-earth-metals on hydrogen generation during fluidized bed gasification of artificial waste. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 31, 248–252 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0216-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0216-3