Abstract
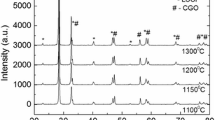
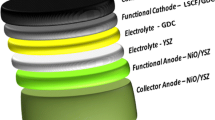
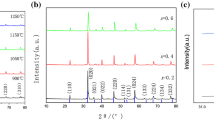
Composite cathodes with La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ (LSCF) and Ce0.9Gd0.1O1.95 (GDC) are investigated to assess for solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) applications at relatively low operating temperatures (650–800 °C). LSCF with a high surface area of 55 m2g−1 is synthesized via a complex method involving inorganic nano-dispersants. The fuel cell performances of anode-supported SOFCs are characterized as a function of compositions of GDC with a surface area of 5 m2g−1. The SOFCs consist of the following: LSCF-GDC composites as a cathode, GDC as an interlayer, yttrium stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an electrolyte, Ni-YSZ (50: 50 wt%) as an anode functional layer, and Ni-YSZ (50: 50 wt%) for support. The cathodes are prepared for 6LSCF-4GDC (60: 40 wt%), 5LSCF-5GDC (50: 50 wt%), and 4LSCF-6GDC (40: 60 wt%). The 5LSCF-5GDC cathode shows 1.29 Wcm−2, 0.97 Wcm−2, and 0.47 Wcm−2 at 780 °C, 730 °C, and 680 °C, respectively. The 6LSCF-4GDC shows 0.92 Wcm−2, 0.71 Wcm−2, and 0.54 Wcm−2 at 780 °C, 730 °C, and 680 °C, respectively. At 780 °C, the highest fuel cell performance is achieved by the 5LSCF-5GDC, while at 680 °C the 6LSCF-4GDC shows the highest performance. The best composition of the porous composite cathodes with LSCF (55 m2g−1) and GDC (5 m2g−1) needs to be considered with a function of temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Dusastre and J. A. Kilner, Solid State Ionics, 126, 163 (1999).
D. Kus¡s¡cer, J. Holc, S. Hrovat and D. Kolar, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 21, 1817 (2001).
A. Mai, V. A. C. Haanappel, S. Uhlenbruck, F. Tietz and D. Stöver, Solid State Ionics, 176, 1341 (2005).
A. Mai, V. A. C. Haanappel, S. Uhlenbruck, F. Tietz and D. Stöver, Solid State Ionics, 177, 2103 (2006).
Y. Teraoka, H.M. Zhang, K. Okamoto and N. Yamazoe, Mater. Res. Bull., 23, 51 (1988).
J. Fleig, J. Power Sources, 105, 228 (2002).
J.W. Hwang, J.Y. Lee, D. H. Jo, H.W. Jung and S. H. Kim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 28, 143 (2011).
V. A. C. Haanappel, J. Mertens, D. Rutenbeck, C. Tropartz, W. Herzhof, D. Sebold and F. Tietz, J. Power Sources, 141, 216 (2005).
S. B. Adler, J.A. Lane and B. C. H. Steele, J. Electrochem. Soc., 143, 3554 (1996).
J. A. Kilner, R. A. De Souza and I.C. Fullarton, Solid State Ionics, 86–88, 703 (1996).
J. Fleig, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 33, 361 (2003).
V.V. Srdic, R. P. Omorjan and J. Seidel, Mater. Sci. Eng. B., 116, 119 (2005).
E. P. Murray, M. J. Sever and S. A. Barnett, Solid State Ionics, 148, 27 (2002).
N. Gunasekaran, S. Saddawi and J. J. Carberry, J. Catal., 159, 107 (1996).
Y. Liu, H. Zheng, J. R. Liu and T. Zhang, Chem. Eng. J., 89, 213 (2002).
A. Dutta, J. Mukhopadhyay and R.N. Basu, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 29, 2003 (2009).
S. Shukla, S. Seal, R. Vij and S. Bandyopadhyay, Nano Lett., 3, 397 (2003).
J. H. Kim, Y. M. Park and H. Kim, J. Power Sources, 196, 3544 (2011).
Y. Leng, S. Chan and Q. Liu, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 33, 3808 (2008).
J.W. Kim, A.V. Virkar, K. Z. Fung, K. Mehta and S. C. Singhal, J. Electrochem. Soc., 146(1), 69 (1999).
H. Schichlein, A. C. Muller, M. Voigts, A. Krugel and E. Ivers-tiffee, J. Appl. Electrochem., 32, 875 (2002).
A. Leonide, V. Sonn, A. Weber and E Ivers-Tiffée, J. Electrochem. Soc., 155, B36 (2008).
Y. M. Park, J.H. Kim and H. Kim, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 36, 5617 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.H., Park, Y.M., Kim, T. et al. Characterizations of composite cathodes with La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ and Ce0.9Gd0.1O1.95 for solid oxide fuel cells. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 29, 349–355 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-011-0131-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-011-0131-4