Abstract
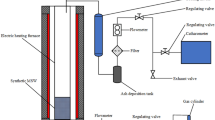
Korean anthracite is too high in ash contents and low in calorific value to be used as an industrial energy source, the demand for anthracite has rapidly decreased and its competitiveness weakened. To overcome the problem, a mixture of Korean anthracite and plastic wastes low in ash and high in calorific value was manufactured. A 1.0T/D fixed bed gasification process was developed to understand the gasification characteristics of the mixtures and secure operation technology using Korean and Chinese anthracite. For the Korean anthracite, the syngas composition and heating value are varied from 10 to 20% and from 300 to 800 kcal/Nm3 as a function of steam/air/fuel ratio. Therefore, it is concluded that Korean anthracite is hard to gasify because of low reactivity. For the Chinese anthracite low ash content and higher heating value than domestic anthracite, the syngas composition was maintained at about 20–40% and the calorific value was 800–1,300 kcal/Nm3. A reformer using high-temperature air/steam was installed just after the gasifier to combust and convert tar and soot into syngas. We confirmed that the amount of generated tar and soot showed a salient difference after running the reformer. In the future, gasification experiments of manufactured mixtures of anthracite and plastic waste using 1.0T/D fixed bed gasifier will be performed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Young and C. C. P. Pian, Energy, 28, 655 (2003).
K. Yoshikawa, Proc. of 2000 Int. Joint Power Generation Conference, 2000-15076 (2000).
C. C. P. Pian and K. Yoshikawa, Bioresource Technology, 79, 231 (2001).
Y. C. Choi, J. G. Lee, J. H. Kim, J. C. Hong, Y. G. Kim, S. J. Yoon, S. H. Lee and M. H. Park, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 23, 380 (2006).
Y. C. Choi, X. Y. Li, T. J. Park, J. H. Kim and J. G. Lee, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 18, 376 (2001).
Y. C. Choi, X. Y. Li, T. J. Park, J. H. Kim and J. G. Lee, Fuel, 80, 2193 (2001).
Y. C. Choi, T. J. Park, J. H. Kim, J. G. Lee, J. C. Hong and Y. G. Kim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 18, 493 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was presented at the 6th Korea-China Workshop on Clean Energy Technology held at Busan, Korea, July 4–7, 2006.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, YC., Lee, JG., Kim, JH. et al. High temperature air-blown gasification of Korean anthracite and plastic waste mixture. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 24, 706–710 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-007-0030-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-007-0030-x