Abstract
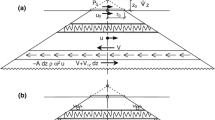
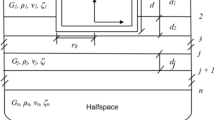
In this paper, the cone model is applied to the vibration analysis of two foundations on a layered soil half space. In the analysis, the total stress field in the subsoil is divided into the free-field and the scattering field. Seed’s simplified method is adopted for the free-field analysis, while the cone model is proposed for analyzing the dynamic scattering stress wave field. The shear stress field and the compressive stress field in the layered stratum with two scattering sources are calculated by shear cone and compressive cone, respectively. Furthermore, the stress fields in the subsoil with two foundations are divided into six zones, and the P wave and S wave are analyzed in each zone. Numerical results are provided to illustrate features of the added stress field for two surface foundations under vertical and horizontal sinusoidal force excitation. The proposed cone model may be useful in handling some of the complex problems associated with multi-scattering sources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Men Fulu (1982), “On Wave Propagation in Fluidsaturated, Porous Media,” Proc. Int. Conf. Soil Dyn. earthq. Eng., 1: 225–238.
Men Fulu and Cui Jie (1997), “Influence of Building Existence on Seismic Liquefaction of Subsoils,” Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 26: 691–699.
Men Fulu (1990), “Effect of Deep-deposited Groundwater Layer on Propagation of Earthquake Waves,” Acta Geophysica Sinica, 38: 678–688.
Meek JW and Wolf JP (1992), “Cone Models for Homogeneous Soil,” J. Geot. Eng., ASCE, 118: 667–685.
Meek JW and Wolf JP (1993), “Why Cone Models Can Represent the Elastic Half-space,” Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 22:759–771.
Seed HB (1971), “Simplified Procedure for Evaluation of Soil Liquefaction Potential,” Soil Mechanics and Foundations, ASCE, 97:75–81.
Chen Wenhua (2000), “Seismic Liquefaction of Inhomogeneous Subsoil with Buildings,” Hydraudic Engineering, 10: 54–59. (in Chinese)
Chen Wenhua (2003), “Cone Model and Dynamical Nonlinear Seismic Liquefaction of Subsoil,” Mechanics of Rock and Soil, 24: 41–45. (in Chinese)
Chen Wenhua (2003), “Evaluation of Dynamical Settlement of Unfree-field,” Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 23: 456–460. (in Chinese)
Wolf John P (1994), Foundation Vibration Analysis Using Simple physical Models, PTR Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by: National Natural Science Foundation of China Under Grant No.50678021
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W. Cone model for two surface foundations on layered soil. Earthq. Engin. Engin. Vib. 5, 183–187 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11803-006-0580-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11803-006-0580-7