Abstract
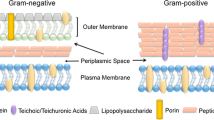
Staphylococcus aureus is a common marine foodborne pathogen. In this study, antibiotics ciprofloxacin and enrofloxacin were used to induce drug-resistance in S. aureus. The differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) were analyzed and compared with those in the bacteria cultured without antibiotics. The primary proteomic alterations were in the levels of cell membrane components and proteins related to lysine and folic acid biosynthesis, which were all significantly up-regulated. The minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) for both test drugs were elevated to 10 µg mL−1 following serial passaging. These results indicated that, for both ciprofloxacin and enrofloxacin, drug-resistance were developed even in the subinhibitory levels and the primary response was a major alteration in the cell membrane proteome. These changes were similar to those observed in S. aureus cultured with super-MIC levels of these antibiotics. The current study provides a theoretical basis for in-depth study of the related changes of marine foodborne pathogens in subinhibitory concentrations that are commonly found in situ.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldred, K. J., Kerns, R. J., and Osheroff, N., 2014. Mechanism of quinolone action and resistance. Biochemistry, 53(10): 1565–1574, https://doi.org/10.1021/bi5000564.
Costa, S. S., Sobkowiak, B., Parreira, R., Edgeworth, J. D., Viveiros, M., Clark, T. G., et al., 2019. Genetic diversity of norA, coding for a main efflux pump of Staphylococcus aureus. Frontiers in Genetics, 9: 710, https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00710.
Cox, J., Hein, M. Y., Luber, C. A., Paron, I., Nagaraj, N., and Mann, M., 2014. Accurate proteome-wide label-free quantification by delayed normalization and maximal peptide ratio extraction, termed MaxLFQ. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics: MCP, 13(9): 2513–2526, https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M113.031591.
Craft, K. M., Nguyen, J. M., Berg, L. J., and Townsend, S. D., 2019. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): Antibiotic-resistance and the biofilm phenotype. MedChemComm, 10(8): 1231–1241, https://doi.org/10.1039/c9md00044e.
Czeczot, H., 2008. Kwas foliowy w fizjologii i patologii (Folic acid in physiology and pathology). Postepy Higieny i Medycyny Doswiadczalnej (online), 62: 405–419.
Dashtbani-Roozbehani, A., and Brown, M. H., 2021. Efflux pump mediated antimicrobial resistance by Staphylococci in health-related environments: Challenges and the quest for inhibition. Antibiotics, 10(12): 1502, https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10121502.
Dawan, J., and Ahn, J., 2020. Assessment of cross-resistance potential to serial antibiotic treatments in antibiotic-resistant Salmonella typhimurium. Microbial Pathogenesis, 148: 104478, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104478.
Foster, T. J., 2017. Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Current status and future prospects. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 41(3): 430–449, https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fux007.
Guo, Y., Song, G., Sun, M., Wang, J., and Wang, Y., 2020. Prevalence and therapies of antibiotic-resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 10: 107, https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2020.00107.
Hashizume, H., Takahashi, Y., Masuda, T., Ohba, S. I., Ohishi, T., Kawada, M., et al., 2017. In vivo efficacy of β-lactam/tripropeptin C in a mouse septicemia model and the mechanism of reverse β-lactam resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus mediated by tripropeptin C. The Journal of Antibiotics, 71: 79–85, https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2017.88.
Hooper, D. C., and Jacoby, G. A., 2015. Mechanisms of drug resistance: Quinolone resistance. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1354(1): 12–31, https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12830.
Lee, Y. D., and Park, J. H., 2016. Phage conversion for β-lactam antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus from foods. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 26(2): 263–269, https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1508.08042.
Lekshmi, M., Ammini, P., Adjei, J., Sanford, L. M., Shrestha, U., Kumar, S., et al., 2018. Modulation of antimicrobial efflux pumps of the major facilitator superfamily in Staphylococcus aureus. AIMS Microbiology, 4(1): 1–18, https://doi.org/10.3934/microbiol.2018.1.1.
Liu, C., Shen, Y., Yang, M., Chi, K., and Guo, N., 2022. Hazard of staphylococcal enterotoxins in food and promising strategies for natural products against virulence. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 70(8): 2450–2465, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c06773.
Mlynarczyk-Bonikowska, B., Kowalewski, C., Krolak-Ulinska, A., and Marusza, W., 2022. Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15): 8088, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158088.
Phillips-Jones, M. K., and Harding, S. E., 2018. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) nanomachines-mechanisms for fluoroquinolone and glycopeptide recognition, efflux and/or deactivation. Biophysical Reviews, 10(2): 347–362, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-018-0404-9.
Qiao, Z., 2021. Epidemiological study of intestinal S. aureus from different sources. Master thesis. Yangzhou University (in Chinese).
Shen, Y. B., Shi, X. M., Shen, J. Z., Wang, Y., and Wang, S. L., 2019. Application of whole genome sequencing and bioinformatics analysis in the study of bacterial drug resistance. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 35(4): 541–557 (in Chinese with English absract).
Thai, V. C., Lim, T. K., Le, K., Lin, Q., and Nguyen, T., 2017. iTRAQ-based proteome analysis of fluoroquinolone-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance, 8: 82–89, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2016.11.003.
Tretter, E. M., and Berger, J. M., 2012. Mechanisms for defining supercoiling set point of DNA gyrase orthologs: II. The shape of the GyrA subunit C-terminal domain (CTD) is not a sole determinant for controlling supercoiling efficiency. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287(22): 18645–18654, https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.345736.
Wang, G., Song, G., and Xu, Y., 2021. A rapid antimicrobial susceptibility test for Klebsiella pneumoniae using a broth microdilution combined with MALDI TOF MS. Infection and Drug Resistance, 14: 1823–1831, https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S305280.
Xie, Y. Z., Mi, K., Li, J., Chen, Z. X., Peng, H., Ma, C. X., et al., 2012. Establishment of two-dimensional electrophoresis assay for proteome analysis of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 48(10): 31–33 (in Chinese with English absract).
Yang, J. J., Cheng, A., Tai, H. M., Chang, L. W., Hsu, M. C., and Sheng, W. H., 2020. Selected mutations by nemonoxacin and fluoroquinolone exposure among relevant gram-positive bacterial strains in Taiwan. Microbial Drug Resistance, 26(2): 110–117, https://doi.org/10.1089/mdr.2019.0048.
Zárate, S. G., Morales, P., Świderek, K., Bolanos-Garcia, V. M., and Bastida, A., 2019. A molecular modeling approach to identify novel inhibitors of the major facilitator superfamily of efflux pump transporters. Antibiotics, 8(1): 25, https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8010025.
Zhao, S., Xu, W., Jiang, W., Yu, W., Lin, Y., Zhang, T., et al., 2010. Regulation of cellular metabolism by protein lysine acetylation. Science, 327(5968): 1000–1004, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1179689.
Acknowledgement
This research was funded by the Professional Innovation and Integration Project of Qingdao University (2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Lin, H., Guo, J. et al. Subinhibitory Levels of Fluoroquinolones Result in Enrichment of the Membrane Proteome of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Ocean Univ. China 22, 1439–1445 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-023-5489-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-023-5489-5