Abstract
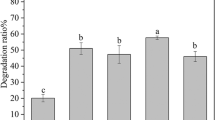
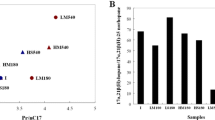
High salt and low temperature are the bottlenecks for the remove of oil contaminants by enriched crude-oil degrading microbiota in Liaohe Estuarine Wetland (LEW), China. To improve the performance of crude-oil removal, microbiota was further immobilized by two methods, i.e., sodium alginate (SA), and polyvinyl alcohol and sodium alginate (PVA+SA). Results showed that the crude oil was effectively removed by the enrichment with an average degrading ratio of 19.42–31.45 mg(L d)−1. The optimal inoculum size for the n-alkanes removal was 10% and 99.89%. Some members of genera Acinetobacter, Actinophytocola, Aquabacterium, Dysgonomonas, Frigidibacter, Sphingobium, Serpens, and Pseudomonas dominated in crude-oil degrading microflora. Though the removal efficiency was lower than free bacteria when the temperature was 15 °C, SA and PVA+SA immobilization improved the resistance to salinity. The composite crude-oil degrading microbiota in this study demonstrated a perspective potential for crude oil removal from surface water under high salinity and low temperature conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alysson, L., Angelim, S., Bárbara, C., Lyanderson, F., amd Vânia, M., 2013. An innovative bioremediation strategy using a bacterial consortium entrapped in chitosan beads. Journal of Environmental Management, 127: 10–17.
Bayat, Z., Mehdi, H., and Majid, A., 2015. Enrichment and isolation of crude oil degrading bacteria from some mussels collected from the Persian Gulf. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 101: 85–91.
Beddow, J., Björn, C., Lead, J., Sapp, M., Lyons, B., McKew, B., et al., 2014. Estuarine sediment hydrocarbon-degrading microbial communities demonstrate resilience to nanosilver. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 96: 206–215.
Cueva, S. C., César, H. R., Nicolás, O. S. J., Antonio, R. C., and Javier, L. M., 2016. Changes in bacterial populations during bioremediation of soil contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 227: 1–12.
Curtis, D., Elango, V., Collins, A. W., Rodrigue, M., and Pardue, J., H., 2018. Transport of crude oil and associated microbial populations by washover events on coastal headland beaches. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 130: 229–239.
Duan, M., Li, C., Wang, X., Fang, S., Xiong, Y., and Shi, P., 2019. Solid separation from the heavy oil sludge produced from Liaohe Oilfield. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 172: 1112–1119.
Gao, Y. S., Wang, X. P., Li, J. L., Lee, C. T., Ong, P. Y., Zhang, Z. J., et al., 2019. Effect of aquaculture salinity on nitrification and microbial community in moving bed bioreactors with immobilized microbial granules. Bioresource Technology, 297: 122427.
Gentili, A. R., María, A. C., Marcela, F., and María, S. R., 2006. Bioremediation of crude oil polluted seawater by a hydrocarbon-degrading bacterial strain immobilized on chitin and chitosan flakes. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 57: 222–228.
González, N., Simarro, R., Molina, M. C., Bautista, L. F., Delgado, L., and Villa, J. A., 2011. Effect of surfactants on PAH biodegradation by a bacterial consortium and on the dynamics of the bacterial community during the process. Bioresource Technology, 102: 9438–9446.
Gray, N. D., Sherry, A., Grant, R. J., Rowan, A. K., Hubert, C. R. J., Callbeck, C. M., et al., 2011. The quantitative significance of syntrophaceae and syntrophic partnerships in methanogenic degradation of crude oil alkanes. Environmental Microbiology, 13: 2957–2975.
Hassanshahian, M., Emtiazi, G., and Cappello, S., 2012. Isolation and characterization of crude-oil-degrading bacteria from the Persian Gulf and the Caspian Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64: 7–12.
Hassanshahian, M., Zeynalipour, M. S., and Musa, F. H., 2014. Isolation and characterization of crude oil degrading bacteria from the Persian Gulf (Khorramshahr provenance). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 82: 39–44.
He, H., Chen, Y., Li, X., Cheng, Y., Yang, C., and Zeng, G., 2017. Influence of salinity on microorganisms in activated sludge processes: A review. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 119: 520–527.
Huang, X., Bai, J., Li, K., Zhao, Y., Tian, W., and Dang, J., 2017a. Characteristics of two novel cold-and salt-tolerant ammonia-oxidizing bacteria from Liaohe Estuarine Wetland. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 114: 192–200.
Huang, X., Dong, W., Wang, H., and Jiang, S., 2017b. Biological nutrient removal and molecular biological characteristics in an anaerobic-multistage anaerobic/oxic (A-MAO) process to treat municipal wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 241: 969–978.
Hou, D., Shen, X., Luo, Q., He, Y., Wang, Q., and Liu, Q., 2013. Enhancement of the diesel oil degradation ability of a marine bacterial strain by immobilization on a novel compound carrier material. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 67: 146–151.
Jeong, S. W., and Kim, J., 2015. Oil-degrading strain Aquabacterium olei sp. nov., isolated from oil-contaminated soil in a US army base in South Korea. I. J. S., International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 65: 3597–3602.
Koma, D., Hasumi, F., Yamamoto, E., Ohta, T., and Yong, S., 2001. Biodegradation of long-chain n-paraffins from waste oil of car engine by Acinetobacter sp. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 91: 94–96.
Kostka, J. E., Prakash, O., Overholt, W. A., Green, S. J., Freyer, G., Canion, A., et al., 2011. Hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria and the bacterial community response in Gulf of Mexico beach sands impacted by the deepwater horizon oil spill. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77: 7962–7974.
Kujawinski, E. B., Kido, S. M. C., Valentine, D. L., Boysen, A. K., Longnecker, K., and Redmond, M. C., 2011. Fate of dispersants associated with the deepwater horizon oil spill. Environmental Science & Technology, 45: 1298–1306.
Lal, B., and Khanna, S., 1996. Degradation of crude oil by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and Alcaligenes odorans. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 81: 355–362.
Lau, K. L., Tsang, Y. Y., and Chiu, S. W., 2003. Use of spent mushroom compost to bioremediate PAH-contaminated samples. Chemosphere, 52: 1539–1546.
Lauber, C. L., Strickland, M. S., Bradford, M. A., and Fierer, N., 2008. The influence of soil properties on the structure of bacterial and fungal communities across land-use types. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40: 2407–2415.
Liao, J., Wang, J., and Huang, Y., 2015. Bacterial community features are shaped by geographic location, physicochemical properties, and oil contamination of soil in main oil fields of China. Microbial Ecology, 70: 380–389.
Lin, T., Ye, S., Ma, C., Ding, X., Brix, H., Yuan, H., et al., 2013. Sources and preservation of organic matter in soils of the wetlands in the Liaohe (Liao River) Delta, North China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 71: 276–285.
Liu, B., Ju, M., Liu, J., Wu, W., and Li, X., 2016. Isolation, identification, and crude oil degradation characteristics of a high-temperature, hydrocarbon-degrading strain. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 106(1): 301–307.
Liu, C., Yu, D., Wang, Y., Chen, G., Tang, P., and Huang, S., 2020. A novel control strategy for the partial nitrification and anammox process (PN/A) of immobilized particles: Using salinity as a factor. Bioresource Technology, 302: 122864.
Liu, Y., Hu, X., and Liu, H., 2016. Industrial-scale culturing of the crude oil-degrading marine Acinetobacter sp. strain HC8-3S. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 107: 56–61.
Luo, X. X., and Xing, Z. Q., 2010. Comparative study on characteristics and influencing factors of soil respiration of reed wetlands in yellow river estuary and Liaohe river estuary. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2: 888–895.
Magoč, T. J., and Steven L. S., 2011. FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics, 27: 2957–2963.
Mahmoudi, N., Porter, T. M., Zimmerman, A. R., Fulthorpe, R. R., Kasozi, G. N., Silliman, B. R., et al., 2013. Rapid degradation of deepwater horizon spilled oil by indigenous microbial communities in Louisiana saltmarsh sediments. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(23): 13303–13312.
Neethu, C. S., Purvaja, S. R., and Ramesh, R. R., 2019. Oil-spill triggered shift in indigenous microbial structure and functional dynamics in different marine environmental matrices. Scientific Reports, 9: 1–13.
Nie, H. Y., Nie, M. Q., Diwu, Z. J., Wang, L., Yan, H., Lin, Y. Y., et al., 2019. Biological treatment of high salinity and low pH produced water in oilfield with immobilized cells of P. aeruginosa NY3 in a pilot-scale. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 381: 121232.
Pourmand, S., Abdouss, M., and Rashidi, A., 2015. Fabrication of nanoporous graphene by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and its application in oil spill removal as a recyclable nanosorbent. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 22: 8–18.
Prince, R. C., McFarlin, K. M., Butler, J. D., Febbo, E. J., Wang, F. C. Y., and Nedwed, T. J., 2013. The primary biodegradation of dispersed crude oil in the sea. Chemosphere, 90: 521–526.
Qin, T., Shen, B., Zhou, Q., and Liu, J., 2014. Biodegradation performance of an inner-loop three-phase fluidized-bed bio-reactor to treat petrochemical wastewater. Petroleum Science and Technology, 32: 848–855.
Rahman, K. S. M., Rahman, J. T., Lakshmanaperumalsamy, P., and Banat, M., 2002. Towards efficient crude oil degradation by a mixed bacterial consortium. Bioresource Technology, 85: 257–261.
Rowland, H. A. L., Boothman, C., Pancost, R., Gault, A. G., Polya, D. A., and Lloyd, J. R., 2009. The role of indigenous microorganisms in the biodegradation of naturally occurring petroleum, the reduction of iron, and the mobilization of arsenite from West Bengal aquifer sediments. Journal of Environmental Quality, 38: 1598–1607.
Saha, T. K., and Pal, S., 2019. Exploring physical wetland vulnerability of Atreyee river basin in India and Bangladesh using logistic regression and fuzzy logic approaches. Ecological Indicators, 98: 251–265.
Santisi, S., Gentile, G., Volta, A., Bonsignore, M., Mancini, G., Quatrini, P., et al., 2015. Isolation and characterization of oil-degrading bacteria from Bilge water. International Journal of Microbiology and Application, 17: 18.
SEPAC, 2002. Analytical and Monitoring Methods of Water and Wastewater. 4th edition, China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, 41–46.
Shahi, A., Aydin, S., and Ince, B., 2016. Evaluation of microbial population and functional genes during the bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil as an effective monitoring approach. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 125: 153–160.
Sekaran, G., Karthikeyan, S., Gupta, V. K., Boopathy, R., and Maharaja, P., 2013. Immobilization of Bacillus sp. in mesoporous activated carbon for degradation of sulphonated phenolic compound in wastewater. Materials Science & Engineering C, 33: 735–745.
Shetaia, Y. M. H., Khalik, W. A. A., Mohamed, T. M., Farahat, L. A., and ElMekawy, A., 2016. Potential biodegradation of crude petroleum oil by newly isolated halotolerant microbial strains from polluted Red Sea area. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 111: 435–442.
Simister, R. L., Antzis E. W., and White, H. K., 2015. Examining the diversity of microbes in a deep-sea coral community impacted by the deepwater horizon oil spill. Deep-Sea Research Part II, 96: 21a.
Suja, F., Rahim, F., Taha, M. R., Hambali, N., Razali, M. R., Khalid, A., et al., 2014. Effects of local microbial bioaugmentation and biostimulation on the bioremediation of total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) in crude oil contaminated soil based on laboratory and field observations. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 90: 115–122.
Tao, X., Lu, G., Liu, J., Li, T., and Yang, L., 2009. Rapid degradation of phenanthrene by using Sphingomonas sp. GY2B immobilized in calcium alginate gel beads. IJERPH, 6: 2470–2480.
Varjani, S. J., and Upasani, V. N., 2016. Biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons by oleophilic strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa NCIM 5514. Bioresource Technology, 222: 195–201.
Vyrides, L., and Stuckey, D. C., 2017. Compatible solute addition to biological systems treating waste/wastewater to counteract osmotic and other environmental stresses: A review. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 37: 865–879.
Wang, P., Li, Z., Bai, J., Lang, Y., and Hu, H., 2016. Optimization of microalgal bead preparation with Scenedesmus obliquus for both nutrient removal and lipid production. Ecological Engineering, 92: 236–242.
Wang, Q., Garrity, G. M., Tiedje, J. M., and Cole, J. R., 2007. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73: 5261–5267.
Woodward, R. T., and Wui, Y. S., 2011. The economic value of wetland services: A meta-analysis. Ecological Economics, 37: 257–270.
Xue, J., Yu, Y., Bai, Y., Wang, L., and Wu, Y., 2015. Marine oil-degrading microorganisms and biodegradation process of petroleum hydrocarbon in marine environments: A review. Current Microbiology, 71: 220–228.
Yuste, L., Corbella, M. E., Turiégano, M. J., Karlson, U., Puyet, A., and Rojo, F., 2000. Characterization of bacterial strains able to grow on high molecular mass residues from crude oil processing. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 32: 69–75.
Zhang, D., Zhang, Y., Shen, F., Wang, J., Li, W., Li, E., et al., 2014. Removal of cadmium and lead from heavy metals loaded PVA—SA immobilized Lentinus edodes. Desalination and Water Treatment, 52: 4792–4801.
Zhao, Y., Zheng, Y., Tian, W., Bai, J., Feng, G., Guo, L., et al., 2016. Enrichment and immobilization of sulfide removal microbiota applied for environmental biological remediation of aquaculture area. Environmental Pollution, 214: 307–313.
Wang, Z., Xu, Y., Wang, H., Zhao, J., Gao, D., Li, F., et al., 2012. Biodegradation of crude oil in contaminated soils by free and immobilized microorganisms. Pedosphere, 22: 717–725.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFD0900805) and the Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Zhou, T., Chen, X. et al. Enhanced Biodegradation of High-Salinity and Low-Temperature Crude-Oil Wastewater by Immobilized Crude-Oil Biodegrading Microbiota. J. Ocean Univ. China 21, 141–151 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-022-4907-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-022-4907-4