Abstract
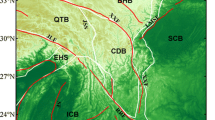
The Ying-Qiong Basin is located on the northwestern margin of the South China Sea and at the junction of the South China Block and the Indochina Block. It is characterized by complex geological structures. The existing seismic data in the study area is sparse due to the lack of earthquake activities. Because of the limited source energy and poor coverage of seismic data, the knowledge of deep structures in the area, including the spatial distribution of deep faults, is incomplete. Contrarily, satellite gravity data cover the entire study area and can reveal the spatial distribution of faults. Based on the wavelet multi-scale decomposition method, the Bouguer gravity field in the Ying-Qiong Basin was decomposed and reconstructed to obtain the detailed images of the first- to sixth-order gravitational fields. By incorporating the known geological features, the gravitational field responses of the main faults in the Ying-Qiong Basin were identified in the detailed fields, and the power spectrum analysis yielded the depths of 1.4, 8, 15, 26.5, and 39 km for the average burial depths of the bottom surfaces from the first- to fifth-order detailed fields, respectively. The four main faults in the Yinggehai Basin all have a large active depth range: fault A (No.1) is between 5 and 39 km, fault B is between 26.5 and 39 km, and faults C and D are between 15 and 39 km. However, the depth of active faults in the Qiongdongnan Basin is relatively shallow, mainly between 8 and 26.5 km.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bansal, A. R., and Dimri, V. P., 2001. Depth estimation from the scaling power spectral density of nonstationary gravity profile. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 158(4): 799–812.
Bhattacharyya, B. K., 1966. Continuous spectrum of the total magnetic field anomaly due to a rectangular prismatic body. Geophysics, 31(1): 97–121.
Bo, H., Wang, L. S., Yan, W. B., Liu, S. W., Cai, D. S., Zhang, G. C., et al., 2013. The tectonic evolution of the Qiongdongnan Basin in the northern margin of the South China Sea. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 77: 163–182.
Bonvalot, S., 2012. The international gravimetric Bureau. Journal of Geodesy, 86(10): 946–949.
Chen, Z., and Feng, T. J., 1999. Research developments and prospects of wavelet neural networks. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 29(4): 663–668 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Cianciara, B., and Marcak, H., 1976. Interpretation of gravity anomalies by means of local spectra. Geophysical Prospecting, 24(2): 273–286, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2478.1976.tb00925.x.
Clift, P. D., and Sun, Z., 2006. The sedimentary and tectonic evolution of the Yinggehai-Song Hong Basin and the southern Hainan margin, South China Sea: Implications for Tibetan uplift and monsoon intensification. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 111(B6): B06405, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JB004048.
Cui, T., Xie, X. N., Ren, J. Y., and Zhang, C., 2008. Dynamic mechanism of anomalous post-rift subsidence in the Yinggehai Basin. Earth Science, 33(3): 349–356 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Feng, L. D., Sun, X. G., and Xu, K. H., 2002. Edge detection of coastline based on wavelet transform method. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 32(5): 777–781 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Gao, J. Y., and Liu, B. H., 2014. China Offshore Ocean: Marine Geophysics. China Ocean Press, Beijing, 100pp (in Chinese).
Grossmann, A., and Morlet, J., 1984. Decomposition of Hardy functions into square integrable wavelets of constant shape. SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, 15(4): 723–736.
Han, J. H., Leng, J. G., and Wang, Y. M., 2016. Characteristics and genesis of the polygonal fault system in southern slope of the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 70: 163–174, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.11.022.
Hannan, E. J., 1966. Spectral analysis for geophysical data. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 11(1): 225–236, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.1966.tb03502.x.
He, C., Wu, S. M., and Long, G. Y., 2017. Lithospheric stretching modeling of Qiongdongnan Basin: Based on line 1. Marine Geology Frontiers, 33(8): 24–31 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hou, C. C., and Li, B. G., 1988. Estimating depths and thickness of rock stratum by using the power spectra of potential fields and their derivatives of different order. Chinese Journal of Geophysics-Chinese Edition, 31(1): 92–100 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lei, C., Ren, J. Y., Clift, P. D., Wang, Z. F., Li, X. S., and Tong, C. X., 2011. The structure and formation of diapirs in the Yinggehai-Song Hong Basin, South China Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 28(5): 980–991, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.01.001.
Lei, C., Ren, J. Y., Sternai, P., Matthew, F., Willett, S., Xie, X. N., et al., 2015. Structure and sediment budget of Yinggehai-Song Hong-Basin, South China Sea: Implications for Cenozoic tectonics and river basin reorganization in Southeast Asia. Tectonophysics, 655: 177–190, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2015.05.024.
Li, C. L., Xie, C. L., and Lu, Q. T., 1998. Calculating top and bottom depth effect of geological body by applying potential field power spectrum. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 17(5): 45–48 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, X. X., Zhong, Z. H., Dong, W. L., Sun, Z., Xia, B., and Zhang, M. Q., 2006. Paleogene rift structure and its dynamics of Qiongdongnan Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 33(6): 70–78 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, Y. M., Shi, X. B., Xu, H. L., and Liu, B., 2011. Analysis on the characteristics of Paleogene basement fault’s activity in Qiongdongnan Basin. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 30(6): 74–83 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liao, J. H., Wang, H., Xiao, J., Li, J. L., Yan, D., Li, G. L., et al., 2012. Episodic rifting and integrated response process of tectonic, sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary filling in Paleogene of Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 42(4): 970–983 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, F., Zhu, Y. Q., and Chen, S., 2013. Multi-scale decomposition of wavelet of the temporal gravity variation in North China. Earthquake Research in China, 29(1): 124–131 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, J. B., Sun, Z., Wang, Z. F., Sun, Z. P., Zhao, Z. X., Wang, Z. W., et al., 2015. Tectonic differences between eastern and western sub-basins of the Qiongdongnan Basin and their dynamics. Marine Geophysical Research, 36(1): 61–79, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-014-9247-3.
Liu, S. J., Zeng, G. P., Qiu, X. L., Fu, G., Wu, S. M., Ye, S. Y., et al., 2011. The crustal profile and onshore-offshore seismic exploration in the marine area southwest to Hainan Island. Progress in Geophysics, 26(3): 922–933 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lu, B. L., Wang, W. Y., Zhang, G. C., and Wang, P. J., 2015. Geophysical evidence of the Red River Fault extending position in the South China Sea and the relationship with seafloor spreading. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 34(5): 64–74 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Luo, D., Cai, F., Yan, G. J., Wang, L. L., and Tong, C. X., 2014. Tectonic characteristics and deep crustal structure of Yinggehai-Song Hong Basin. Progress in Geophysics, 29(6): 2917–2926 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Mallat, S. G., 1989. A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: The wavelet representation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 11(7): 647–693, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/34.192463.
Mazur, S., Green, C., Stewart, M. G., Whittaker, J. M., Williams, S., and Bouatmani, R., 2012. Displacement along the Red River Fault constrained by extension estimates and plate reconstructions. Tectonics, 31(5): TC5008, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2012TC003174.
Mi, L. J., Yuan, Y. S., Zhang, G. C., Hu, S. B., He, L. J., and Yang, S. C., 2009. Characteristics and genesis of geothermal field in deep-water area of the northern South China Sea. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 30(1): 27–32 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Pal, P. C., Khurana, K. K., and Unnikrishnan, P., 1978. Two examples of spectral approach to source depth estimation in gravity and magnetics. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 117(4): 772–783, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00879978.
Qiu, N., Wang, Z. F., Xie, H., Sun, Z. P., Wang, Z. W., Sun, Z., et al., 2013. Geophysical investigations of crust-scale structural model of the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Marine Geophysical Research, 34: 259–279, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-013-9182-8.
Qiu, N., Wang, Z. W., Wang, Z. F., Sun, Z. P., Sun, Z., and Zhou, D., 2014. Tectonostratigraphic structure and crustal extension of the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Chinese Journal of Geophysics-Chinese Edition, 57(10): 3189–3207 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Shan, J. N., Zhang, G. C., Tang, X. Y., Wu, J. F., Zhao, C. Y., Song, Y., et al., 2011. Thermal structure and Moho temperature of Qiongdongnan Basin, northern margin of the South China Sea. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(4): 516–525.
Shi, X. B., Burov, E., Leroy, S., Qiu, X. L., and Xia, B., 2005. Intrusion and its implication for subsidence: A case from the Baiyun Sag, on the northern margin of the South China Sea. Tectonophysics, 407(1–2): 117–134, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2005.07.004.
Shi, X. B., Jiang, H. Y., Yang, J., Yang, X. Q., and Xu, H. H., 2017. Models of the rapidpost-rift subsidence in the eastern Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea: Implications for the development of the deep thermal anomaly. Basin Research, 29(3): 340–362, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/bre.12179.
Song, H. B., Hao, T. Y., Jiang, W. W., Qiu, X. L., Xu, Y., and Liu, J. H., 2002. Researches on geophysical field characteristics and basement fault system of South China Sea. Progress in Geophysics, 17(1): 24–33 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Song, W. Y., 2012. Characteristics and dynamic evolution of inverted structure in Yinggehai Basin. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 32(2): 77–83 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun, Z., Wang, Z. F., Sun, Z. P., Wang, Z. W., Zhang, W., and He, L. J., 2015. Structure and kinematic analysis of the deep waterarea of the Qiongdongnan Basin through a seismic interpretation and analogue modeling experiments. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 34: 32–40, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-015-0585-z.
Sun, Z., Zhou, D., Zhong, Z. H., Qiu, X. L., and Zeng, Z. X., 2005. A study on basal controlling fault pattern of YingQiong Basin through analogue modeling. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 24(2): 73–81 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun, Z., Zhou, D., Zhong, Z. H., Zeng, Z. X., and Wu, S. M., 2003. Experimental evidence for the dynamics of the formation of the Yinggehai Basin, NW South China Sea. Tectonophysics, 372(1): 41–58, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-1951(03)00230-0.
Tanaka, A., Okubo, Y., and Matsubayashi, O., 1999. Curie point depth based on spectrum analysis of the magnetic anomaly data in East and Southeast Asia. Tectonophysics, 306(3–4): 461–470, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-1951(99)00072-4.
Tian, T., Zhang, J. F., Jiang, W. L., and Tian, Y. F., 2020. Quantitative study of crustal structure spatial variation based on gravity anomalies in the eastern Tibetan Plateau: Implication for earthquake susceptibility assessment. Earth and Space Science, 7(3): e2019EA000943, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2019EA000943.
Tian, T., Zhang, J. F., Liu, T. Y., Jiang, W. L., and Zhao, Y. B., 2017. Morphology, tectonic significance, and relationship to the Wenchuan earthquake of the Xiaoyudong fault in western China based on gravity and magnetic data. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 138: 672–684, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.10.008.
Tselentis, G., Drakopoulos, J., and Dimitriadis, K., 1988. A spectral approach to Moho depths estimation from gravity measurements in Epirus (NW Greece). Journal of Physics of the Earth, 36(6): 255–266, DOI: https://doi.org/10.4294/jpe1952.36.255.
Wu, S. M., Qiu, X. L., Zhou, D., Zeng, G. P., Xia, K. Y., and Ye, S. Y., 2009. Crustal structure beneath Yinggehai Basin and adjacent Hainan Island, and its tectonic implications. Journal of Earth Science, 20: 13–26, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-009-0002-7.
Xia, K. Y., Zhou, D., Su, D. Q., Flueh, E., Ye, S. Y., He, H. Y., et al., 1998. The velocity structure of the Yinggehai Basin and its hydrocarbon implication. Chinese Science Bulletin, 43: 2047–2054, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183503.
Xie, W. Y., Zhang, Y. W., Sun, Z., and Jiang, J. Q., 2007. Characteristics and formation mechanism of faults in Qiongdongnan Basin. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 27(1): 71–78 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xie, Y. H., Tong, C. X., Fan, C. W., Song, P., Zhang, H., and Tong, H. M., 2015. Characteristics and evolution of fault system in Qiongdongnan Basin. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 39(5): 795–807, DOI: https://doi.org/10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2015.05.004 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang, F. L., Zhou, Z. Y., Zhang, N., Liu, N., and Ni, B., 2013. Stress field modeling of northwestern South China Sea since 5.3 Ma and its tectonic significance. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 32(12): 31–39, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-013-0385-2.
Yin, X. Y., Ren, J. Y., Pei, J. X., and Lei, C., 2010. Quantitative calculation on fault activity and fault propagation mechanism in Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Geological Journal of China Universities, 16(3): 388–396 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, C. M., Wang, Z. F., Sun, Z. P., and Sun, Z., 2013. Structural differences between the western and eastern Qiongdongnan Basin: Evidence of Indochina block extrusion and South China Sea seafloor spreading. Marine Geophysical Research, 34(3–4): 309–323, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-013-9187-3.
Zhang, J. A., 2013. Research on the tectonic boundary of Ying-Qiong Basin and adjacent faults’ features based on gravity and magnetic data. Master thesis. Chang’an University.
Zhang, Y. F., Sun, Z., Zhou, D., Guo, X. W., Shi, X. B., Wu, X. J., et al., 2008. Stretching characteristics and its dynamics significance of the northern continental margin of South China Sea. Science in China, 51(3): 422–430, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-008-0019-2.
Zhang, Z. J., Liu, Y. F., Zhang, S. F., Zhang, G. C., and Fan, W. M., 2009. Crustal P-wave velocity structure and layering beneath Zhujiangkou-Qiongdongnan Basin, the northern continental margin of South China Sea. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(10): 2461–2471 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao, B., Zhang, S. F., and Li, S. L., 2011. Crustal density and composition models beneath Qiongdongnan Basin. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(1): 98–107 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao, J. Z., Li, Z. W., Lin, J. M., Hao, T. Y., Bao, F., Xie, J., et al., 2019. Ambient noise tomography and deep structure in the crust and mantle of the South China Sea. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 62(6): 2070–2087 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao, Z. X., Sun, Z., Sun, L. T., Wang, Z. F., and Sun, Z. P., 2016. Cenozoic tectonic subsidence in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Basin Research, 30(S1): 269–288.
Zhao, Z. X., Sun, Z., Wang, Z. F., and Sun, Z. P., 2015a. The mechanics of continental extension in Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Marine Geophysical Research, 36(2–3): 197–210, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-014-9238-4.
Zhao, Z. X., Sun, Z., Wang, Z. F., Sun, Z. P., and Zhang, C. M., 2015b. The high resolution sedimentary filling in Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Marine Geology, 361: 11–24, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2015.01.002.
Zhao, Z., Sun, Z., Sun, L., Wang, Z., and Sun, Z., 2018. Cenozoic tectonic subsidence in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Basin Research, 30: 269–288, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/bre.12220.
Zhu, M., Graham, S., and Mchargue, T., 2009. The Red River Fault zone in the Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea. Tectonophysics, 476(3–4): 397–417.
Acknowledgements
We thank Wessel & Smith (u]https://www.soest.hawaii.edu/gmt) for the free use of GMT software, by which most figures in this paper were produced. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41530963, 91858215 and 41906048), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 201964015) and the Laboratory for Marine Mineral Resources, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (No. MMRZZ201801).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, L., Yu, C., Gong, W. et al. Active Depths of Main Faults in the Ying-Qiong Basin Investigated by Multi-Scale Wavelet Decomposition of Bouguer Gravity Anomalies and Power Spectral Methods. J. Ocean Univ. China 21, 1174–1188 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-022-4879-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-022-4879-4