Abstract
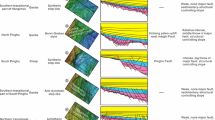
Located at the intersection between a NW-trending slip system and NE-trending rift system in the northern South China Sea, the Qiongdongnan Basin provides key clues for us to understand the proposed extrusion of the Indochina Block along with Red River Fault Zone and extensional margins. In this paper we for the first time systematically reveal the striking structural differences between the western and eastern sector of the Qiongdongnan Basin. Influenced by the NW-trending slip faults, the western Qiongdongnan Basin developed E–W-trending faults, and was subsequently inverted at 30–21 Ma. The eastern sector was dominated by faults with NE orientation before 30 Ma, and thereafter with various orientations from NE, to EW and NW during the period 30–21 Ma; rifting display composite symmetric graben instead of the composite half graben or asymmetric graben in the west. The deep and thermal structures in turn are invoked to account for such deformation differences. The lithosphere of the eastern Qiongdongnan Basin is very hot and thinned because of mantle upwelling and heating, composite symmetric grabens formed and the faults varied with the basal plate boundary. However, the Southern and Northern Uplift area and middle of the central depression is located on normal lithosphere and formed half grabens or simple grabens. The lithosphere in the western sector is transitional from very hot to normal. Eventually, the Paleogene tectonic development of the Qiongdongnan Basin may be summarized into three stages with dominating influences, the retreat of the West Pacific subduction zone (44–36 Ma), slow Indochina block extrusion together with slab-pull of the Proto-South China Sea (36–30 Ma), rapid Indochina block extrusion together with the South China Sea seafloor spreading (30–21 Ma).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen CR, Gillespie AR, Han Y, Sieh KE, Zhang LB, Zhu C (1984) Red River and associated faults, Yunnan Province, China: quaternary geology, slip rates, and seismic hazard. Geol Soc Am Bull 95:686–700
Barckhausen U, Roeser HA (2004) Seafloor spreading anomalies in South China Sea revisited. In: Clift P, Wang P, Kuhnt W, Hayes D (eds) Continent-ocean interactions within east Asian marginal seas. Geophysical monograph 149. AGU, Washington, DC, pp 121–125
Briais A, Patriat P, Tapponnier P (1993) Updated interpretation of magnetic anomalies and seafloor spreading in the South China Sea: implications for the Tertiary tectonics of Southeast Asia. J Geophys Res 98(B4):6299–6328
Callot JP, Grigné C, Geoffroy L, Brun JP (2001) Development of volcanic passive margins: two-dimensional laboratory models. Tectonics 20(1):148–159
Callot JP, Geoffroy L, Brun JP (2002) Development of volcanic passive margins: three-dimensional laboratory model. Tectonics 21(6):1052
Chung SL, Lee TY, Lo CH, Wang PL, Chen CY, Yem NT, Hoa TT, Wu G (1997) Intraplate extension prior to continental extrusion along the Ailao Shan–Red River shear zone. Geology 25:311–314
Clift PD, Sun Z (2006) The sedimentary and tectonic evolution of the Yinggehai–Song Hong Basin and the southern Hainan margin, South China Sea: implications for Tibetan uplift and monsoon intensification. J Geophys Res 111:B06405
Clift P, Lee GH, Nguyen AD, Barckhausen U, Hoang VL, Sun Z (2008) Seismic reflection evidence for a dangerous grounds mini-plate: no extrusion origin for the South China Sea. Tectonics 27(3):TC3008. doi:19.1029/2007TC002216
Fyhn MBW, Boldreel LO, Nielsen LH (2009) Geological development of the Central and South Vietnamese margin: implications for the establishment of the South China Sea, Indochinese escape tectonics and Cenozoic volcanism. Tectonophysics 478(3–4):184–214
Gilley LD, Harrison TM, Leloup PH, Ryerson FJ, Lovera OM, Wang JH (2003) Direct dating of left-lateral deformation along the Red River shear zone, China and Vietnam. J Geophy Res 108:2127
Gong ZS, Li ST (1997) Continental margin basin analysis and hydrocarbon accumulation of the northern South China Sea (in Chinese). Science Press, Beijing
Gradstein FM, Ogg JG, Smith AG (2004) A geologic time scale 2004. Columbia University Press, New York
Guo L, Zhong Z, Wang L, Shi Y, Li H, Liu S (2001) Regional tectonic evolution around Yinggehai Basin of South China Sea (in Chinese with English abstract). Geol J China Univ 7(1):1–12
Hall R (2002) Cenozoic geological and plate tectonic evolution of SE Asia and the SW Pacific: computer-based reconstructions, model and animations. J Asian Earth Sci 20(4):353–431
Harrison TM, Chen W, Leloup PH, Ryerson FJ, Tapponnier P (1992) An early Miocene transition in deformation regime within the Red River Fault Zone, Yunnan, and its significance for Indo-Asian tectonics. J Geophy Res 97:7159–7182
Hoang LV, Clift PD, Schwab AM, Huuse M, Nguyen DA, Zhen S (2010) Large-scale erosional response of SE Asia to monsoon evolution reconstructed from sedimentary records of the Song Hong-Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan Basins, South China Sea. In: Clift PD, Tada R, Zheng H (eds) Monsoon evolution and tectonic-climate linkage in Asia. Geological Society Special Publications 342, London, pp 219–244
Lei C, Ren J, Pei J, Lin H, Yin X, Tong D (2011) Tectonic framework and multiple episode tectonic evolution in deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin, northern continental margin of South China Sea (in Chinese with English abstract). Earth Sci J China Univ Geosci 36(1):151–163
Leloup PH, Kienast JR (1993) High-temperature metamorphism in a major strike-slip shear zone: the Ailao Shan–Red River, People’s Republic of China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 118:213–234
Leloup PH, Lacassin R, Tapponnier P, Schärer U, Zhong D, Liu X, Zhang L, Ji S, Trinh PT (1995) The Ailao Shan–Red River shear zone (Yunnan, China), tertiary transform boundary of Indochina. Tectonophysics 251:3–84
Leloup PH, Arnaud N, Lacassin R, Kienast JR, Harrison TM, Trinh P, Replumaz A, Tapponnier P (2001) New constraints on the structure, thermochronology, and timing of the Ailao Shan–Red River shear zone, SE Asia. J Geophys Res 106:6683–6732
Li PL (1994) Structural features and oil-and-gas accumulation in Peal River Mouth Basin (in Chinese with English abstract). Guangdong Geol 9(4):21–28
Li S, Lin C, Zhang Q, Yang S, Wu P (1998) Dynamic process of the periodic rifting and tectonic events since 10 Ma in the marginal basins north of the South China Sea (in Chinese with English abstract). Chin Sci Bull 43:797–810
Li Y, Shi X, Xu H, Liu B (2011) Analysis on the characteristics of Paleogene basement faults’ activity in Qiongdongnan Basin (in Chinese with English abstract). J Trop Oceanogr 30(6):74–83
Liao J, Wang H, Xiao J, Li J, Yan D, Li G, Xia C, Li Y, Ren G (2012) Episodic rifting and integrated response process of tectonic, sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary filling in Paleogene of Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea (in Chinese with English abstract). J Jilin Univ Earth Sci Ed 42(4):970–983
Li X, Zhu G (2005) The faults system and its hydrocarbon carrier significance in Qiongdongnan Basin ( in Chinese with English abstract). China Offshore Oil Gas 17(1):1–7
Morley CK (1994) Interaction of deep and shallow processes in the evolution of the Kenya rift. Tectonophysics 236(1–4):81–91
Morley CK (1999) Marked along-strike variation in dip of normal faults-the Lokichar Fault, N. Kenya rift: a possible cause for metamorphic core complexes. J Struct Geol 21(5):479–492
Morley CK (2001) Combined escape tectonics and subduction rollback-back arc extension: a model for the evolution of tertiary rift basins in Thailand, Malaysia and Laos. J Geol Soc Lond 158:461–474
Morley CK (2002) A tectonic model for the tertiary evolution of strikeslip faults and rift basins in SE Asia. Tectonophysics 347:189–215
Qiu X, Ye S, Wu S, Shi X, Zhou D, Xia K, Flueh ER (2001) Crustal structure across the Xisha trough, northwestern South China Sea. Tectonophysics 341:179–193
Rangin C, Huchon P, Le Pichon X, Bellon H, Lepvrier C, Roques D, Hoe ND, van Quynh P (1995) Cenozoic deformation of central and south Vietnam. Tectonophysics 251:179–196
Ren JY, Lei C (2011) Tectonic stratigraphic framework of Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan Basin and its implication for tectonic province division in South China Sea (in Chinese with English abstract). Chin J Geophys 54:3303–3314
Replumaz A, Lacassin R, Tapponnier P, Leloup PH (2001) Large river offsets and Plio-Quaternary dextral slip rate on the Red River fault (Yunnan, China). J Geophys Res Solid Earth 106(B1):819–836
Ru K (1988) The development of the superimposed basin on the northern margin of the South China Sea and its tectonic significance (in Chinese with English abstract). Oil Gas Geol 9(1):22–31
Schlüter HU, Hinz K, Block M (1996) Tectono-stratigraphic terranes and detachment faulting of the South China Sea and Sulu Sea. Mar Geol 130:39–78
Searle MP (2006) Role of the Red River shear zone, Yunnan and Vietnam, in the continental extrusion of SE Asia. J Geol Soc Lond 163:1025–1036
Shi X, Zhou D, Qiu X, Zhang Y (2002) Thermal and rheological structures of the Xisha trough, South China Sea. Tectonophysics 351:285–300
Shi X, Qiu X, Xia K, Zhou D (2003) Characteristics of surface heat flow in the South China Sea. J Asian Earth Sci 22:265–277
Su DQ, Liu YQ, Chen X, Chen YB, Li TG, Zeng WJ, Lin CS (2004) Moho depth in South China Sea. In: Zhang ZJ, Gao R, Lv QT, Liu ZK (eds) Deep structure and dynamics in the continent of China. Science Press, Beijing, pp 357–365
Sun Z, Zhou D, Zhong Z, Zeng Z, Wu S (2003) Experimental evidence for the dynamics of the formation of the Yinggehai Basin, NW South China Sea. Tectonophysics 372:41–58
Sun Z, Zhou D, Zhong Z, Qiu X, Zeng Z (2005) A study of basal controlling fault pattern of Ying-Qiong Basin through analogue modeling (in Chinese with English abstract). J Trop Oceanogr 24:70–78
Sun Z, Zhou D, Wu S, Zhong Z, Keep M, Jiang J, Fan H (2009) Patterns and dynamics of rifting on passive continental margin from shelf to slope of the northern South China Sea: evidence from 3D analogue modeling. J Earth Sci 20(1):136–146
Tapponnier P, Peltzer G, Armijo R (1986) On the mechanism of the collision between India and Asia. In: Coward MP, Ries AC (eds) Collision tectonics. Geological Society Special Publications 19, London, pp 155–157
Tapponnier P, Lacassin R, Leloup PH, Schärer U, Dalai Z, Haiwei W, Xiaohan L, Shaocheng J, Liansheng Z, Jiayou Z (1990) The Ailao Shan/Red River metamorphic belt: tertiary left-lateral shear between Indochina and South China. Nature 343(6257):431–437
Taylor B, Hayes DE (1980) The tectonic evolution of the South China Sea Basin. In: Hayes DE (ed) The tectonic and geologic evolution of southeast Asian seas and islands. Geophysical monograph series 23. AGU, Washingtong, DC, pp 89–104
Taylor B, Hayes DE (1983) Origin and history of the South China Sea Basin. In: Hayes DE (ed) The tectonic and geologic evolution of southeast Asian seas and islands. Part 2, geophysical monograph 27. AGU, Washingtong, DC, pp 23–56
Tong D, Ren J, Lei C, Yang H, Yin X (2009) Lithosphere stretching model of deep water in Qiongdongnan Basin, northern continental margin of South China Sea, and controlling of the post-Rift subsidence (in Chinese with English abstract). Earth Sci J China Univ Geosci 34(6):963–974
Wang PL, Lo CH, Lee TY, Chung SL, Lan CY, Yem NT (1998) Thermochronological evidence for the movement of the Ailao Shan–Red River shear zone: a perspective from Vietnam. Geology 26:887–890
Wang PL, Lo CH, Chung SL, Lee TY, Lan CY, Yem NT (2000) Onset timing of left-lateral movement along the Ailao Shan–Red River shear zone: 40Ar/39Ar dating constraint from the Nam Dinh Area, northeastern Vietnam. J Asian Earth Sci 18:281–292
Wang J, Yin A, Harrison TM, Grove M, Zhang Y, Xie G (2001) A tectonic model for Cenozoic igneous activities in the eastern Indo-Asian zone. Earth Planet Sci Lett 188:123–133
Wang Z, Sun Z, Qiu N, Liu J, Wang Z, Sun Z (2013) The crustal structure of Chang-chang Sag, deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin. Mar Geol Lett 29(6):8–16
Xie W, Sun Z, Zhang Y, Jiang J (2007a) The dynamic and hydrocarbon accumulation analysis of the inversion structures on the northern marginal basins of the South China Sea (in Chinese with English abstact). Earth Sci J China Univ Geosci 32:32–40
Xie W, Zhang Y, Sun Z, Jiang J (2007b) Characteristics and formation mechanism of faults in Qiongdongnan Basin (in Chinese with English abstract). Mar Geol Quat Geol 27(1):71–78
Xie X, Müller RD, Ren J, Jiang T, Zhang C (2008) Stratigraphic architecture and evolution of the continental slope system in offshore Hainan, northern South China Sea. Mar Geol 247:129–144
Xu Z, Sun Z, Zhou D, Zhang Y, Sun L, Zhao Z (2012) Discussion on the influence of weakness body on inversion structure deformation through analogue modeling and its application. J Trop Oceanogr 31(3):144–154
Zhang Q, Hao F (1997) Evolution and hydrocarbon system in Ying-Qiong basin (in Chinese with English abstract). Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci 27(2):149–154
Zhong ZH (2000) The dynamics and hydrocarbon accumulation of Ying-Qiong basin, west of South China Sea (in Chinese with English abstract). Doctoral degree dissertation, Nanjing University
Zhou D, Ru K, Chen HZ (1995) Kinematics of Cenozoic extension on the South China Sea continental margin and its implications for the tectonic evolution of the region. Tectonophysics 251(1–4):161–177
Zhu W, Jiang W (1998) Relations between fractures and hydrocarbon reservoirs in Weixinan sag. Acta Pet Sinica 19(3):6–11
Zhu M, Graham S, McHargue T (2009) The Red River Fault Zone in the Yinggehai Basin, South China Sea. Tectonophysics 476:397–417
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development, Nanhai West Oil Corporation of China National Offshore Oil Company for providing the geological data. Dr. Ming Su provided many constructive suggestions in his review of the paper, which were much appreciated. We are grateful to two anonymous reviewers for their thorough comments on the manuscript. This study was jointly supported financially by the National Science and Technology Major Project (2011ZX05025-002-01), Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41106055), Young Talents Frontier Program of South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. SQ201010), and the open Foundation of Key laboratory of Submarine Geosciences, State Oceanic Administration (KLSG1101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Wang, Z., Sun, Z. et al. Structural differences between the western and eastern Qiongdongnan Basin: evidence of Indochina block extrusion and South China Sea seafloor spreading. Mar Geophys Res 34, 309–323 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-013-9187-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-013-9187-3