Abstract
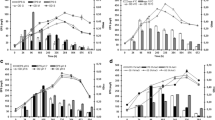
A bioflocculant producing potential bacteria was isolated from the circulating seawater of bio-filter using streak plate methods. The bacteria was identified through biochemical characteristics, partial 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acids (rRNA), nucleotide sequencing, and BLAST analysis of the gene sequence that showed the bacteria have 99% similarity to Pseudoalteromonas sp. and deposited in GenBank as Pseudoalteromonas sp. NUM8 with accession number JX435820. Influences of time course assay, carbon sources, nitrogen sources, inoculum size, as well as initial pH on the bacteria producing extracellular bioflocculant activity were investigated. The results showed that the strain optimal production period of microbial bioflocculant was at 72 h (flocculating activity of 94.5%), then dropped slowly. The bacteria optimally produced the bioflocculant when 1.0% sucrose and 0.5% sodium nitrate were used as sole sources of carbon and nitrogen with flocculating activities of 92.8% and 93.8% respectively. Also, the bacteria produced the bioflocculant optimally when initial pH of the medium was 5.0 (flocculating activity 93.2%), and when Ca2+ was used as cation (flocculating activity 93.4%). The culture condition of inoculum size of 3% (v/v) was optimal flocculant production (flocculating activity 94.4%). Composition analyses indicated the bioflocculant to be principally a glycoprotein made up of about 34.3% protein and 63.4% total carbohydrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks, W. A., Niehoff, M. L., Drago, D., and Zatta, P., 2006. Aluminum complexing enhances amyloid protein penetration of blood-brain barrier. Brain Research, 1116(1): 215–221.
Bouchotroch, S., Quesada, E., Del Moral, A., Llamas, I., and Béjar, V., 2001. Halomonasmaura sp. nov., a novel moderately halophilic, exopolysaccharide-producing bacterium. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 51(5): 1625–1632.
Chen, T., Gao, B., and Yue, Q., 2010. Effect of dosing method and pH on color removal performance and floc aggregation of polyferric chloride-polyamine dual coagulant in synthetic dyeing wastewater treatment. Colloids and Surfaces A, 355(1): 121–129.
Cosa, S., Mabinya, L. V., Olaniran, A. O., Okoh, O. O., and Bernard, K., 2011. Bioflocculant production by Virgibacillus sp. Rob isolated from the bottom sediment of Algoa Bay in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. Molecules, 16(3): 2431–2442.
Elkady, M. F., Soha, F., Sahar, Z., Gadallah, A., and Desouky, A., 2011. Bacillus mojavensis strain 32A, a bioflocculantproduing bacteria isolated from an Egyptian salt production pond. Bioresource Technology, 102(17): 8143–8151.
Essandoha, M., Garcia, R. A., Nieman, C. M., and Strahanb, G. D., 2020. Influence of methylation on the effectiveness of meat and bone meal protein as a bioflocculant. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 122: 55–61.
Gao, J., Bao, H. Y., Xin, M. X., Liu, Y. X., Li, Q., and Zhang, Y. F., 2006. Characterization of a bioflocculant from a newly isolated Vagococcus sp. W31. Journal of Zhejiang University Science, 7(3): 186–192.
Giri, S. S., Harshiny, M., Sen, S. S., Sukumaran, V., and Park, S. C., 2015. Production and characterization of a thermostable bio-flocculant from Bacillus subtilis F9, isolated from waste-water sludge. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 121: 45–50.
Gong, W. X., Wang, S. G., Sun, X. F., Liu, X. W., Yue, Q. Y., and Gao, B. Y., 2008. Bioflocculant production by culture of Serratia ficaria and its application in wastewater treatment. Bioresource Technology, 99(11): 4668–4674.
He, J., Zhen, Q., Qiu, N., Liu, Z., Wang, B., Shao, Z., and Yu, Z., 2009. Medium optimization for the production of a novel bioflocculant from Halomonas sp. V3a′ using response surface methodology. Bioresource Technology, 100: 5922–5927.
He, J., Zou, J., Shao, Z., Zhang, J., Liu, Z., and Yu, Z., 2010. Characteristics and flocculating mechanism of a novel bioflocculant HBF-3 produced by deep-sea bacterium mutant Halomonas sp. V3a′. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 26(6): 1135–1141.
He, N., Li, Y., and Chen, J., 2004. Production of a polygalacturonic acid bioflocculant REA-11 by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Bioresource Technology, 94(1): 99–105.
Jiang, J. P., Liu, L. H., Nie, W., Chen, Y. B., and Wang, Z., 2019. Screening of a high bioflocculant-producing bacterial strain from an intensive fish pond and comparison of the bioflocculation effects with Rhodococcus erythropolis. Aquaculture Research, 50(4): 1047–1056.
Jensen, P. R., Erin, G., Chrisy, M., Tracy, J. M., and William, F., 2005. Culturable marine actinomycete diversity from tropical Pacific Ocean sediments. Environmental Microbiology, 7(7): 1039–1048.
Kunle, O., Uchechukwu, U. N., Arinze, S. O., Leonard, V. M., and Anthony, I. O., 2016. Studies on bioflocculant production by Bacillus sp. AEMREG7. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 25(1): 236–245.
Levesque, L., Mizzen, C. A., Mclachlan, D. R., and Fraser, P. E., 2000. Ligand specific effects on aluminium incorporation and toxicity in neurons and astrocytes. Brain Research, 877(2): 191–202.
Li, Y., He, N., Guan, H., Du, G., and Chen, J., 2003. A novel polygalacturonic acid bioflocculant REA-11 produced by Corynebacterium glutamicum: A proposed biosynthetic pathway and experimental confirmation. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 63(2): 200–206.
Li, Z., Zhong, S., Lei, H. Y., Chen, R. W., Yu, Q., and Li, H. L., 2009. Production of a novel bioflocculant by Bacillus licheniformis X14 and its application to low temperature drinking water treatment. Bioresource Technology, 100(4): 3650–3656.
Lian, B., Chen, Y., Zhao, J., Teng, H. H., Zhu, L., and Yuan, S., 2008. Microbial flocculation by Bacillus mucilaginosus: Applications and mechanisms. Bioresource Technology, 99(11): 4825–4831.
Liu, C., Wang, K., Jiang, J. H., Liu, W. J., and Wang, J. Y., 2015a. A novel bioflocculant produced by a salt-tolerant, alkaliphilic and biofilm-forming strain Bacillus agaradhaerens C9 and its application in harvesting Chlorella minutissima UTEX2341. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 93: 166–172.
Liu, H., Chen, G., and Wang, G., 2015b. Characteristics for production of hydrogen and bioflocculant by Bacillus sp. XF-56 from marine intertidal sludge. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 40(3): 1414–1419.
Liu, J. W., Ma, J. W., Liu, Y. Z., Yang, Y., Yue, D. B., and Wang, H. T., 2014. Optimized cultivation of a bioflocculant M-C11 produced by Klebsiella pneumoniae and its application in sludge dewatering. Environmental Science, 35(3): 1183–1189.
Liu, W. J., Wang, K., Li, B. Z., Yuan, H. L., and Yang, J. S., 2010. Production and characterization of an intracellular bioflocculant by Chryseobacterium daeguense W6 cultured in low nutrition medium. Bioresource Technology, 101(3): 1044–1048.
Lu, W. Y., Zhang, T., Zhang, D. Y., Li, C. H., Wen, J. P., and Du, L. X., 2005. A bioflocculant produced by Enterobacter aerogenes and its use in defecating the trona suspension. Biochemical Engineering, 27(1): 1–7.
Luo, Y., Li, C., Abbasi, A. M., Hou, Y., and Fu, X., 2016. Screening of bioflocculant-producing bacteria and its application in clarification process of sugarcane juice. International Sugar Journal, 118: 34–40.
Mabinya, L. V., Cosa, S., Nwodo, U., and Okoh, A. I., 2012. Studies on bioflocculant production by Arthrobacter sp. Raats, a fresh water bacteria isolated from Tyume River, South Africa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13: 1054–1065.
Nontembiso, P., Sekelwa, C., Leonard, M. V., and Anth, O. I., 2011. Assessment of bioflocculant production by Bacillus sp. Gilbert, a marine bacterium isolated from the bottom sediment of Algoa Bay. Journal of Marine Drugs, 9(7): 1232–1242.
Nwod, U. U., Agunbiade, M. O., Green, E., Nwamadi, M., Rumbold, H., and Okoh, A. I., 2013. Characterization of an exopolymeric flocculant produced by a Brachybacterium sp.. Materials, 6(4): 1237–1254.
Okaiyeto, K., Nwodo, U. U., Mabinya, L. V., and Okoh, A. I., 2014. Evaluation of the flocculation potential and characterization of bioflocculant produced by Micrococcus sp. Leo. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 50(6): 601–608.
Okaiyeto, K., Nwodo, U. U., Mabinya, L. V., Okoli, A. S., and Okoh, A. I., 2016. Evaluation of flocculating performance of a thermostable bioflocculant produced by marine Bacillus sp. Environmental Technology, 138(2): 1–34.
Patil, S. V., Salunkhe, R. B., Patil, C. D., Patil, D. M., and Salunke, B. K., 2010. Bioflocculant exopolysaccharide production by Azotobacter indicus using flower extract of Madhuca latifolia L. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 162(4): 1095–1108.
Polizzi, S., Pira, E., Ferrara, M., Buginani, M., Papaleo, A., Albera, R., et al., 2002. Neurotoxic effects of aluminum among foundry workers and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotoxicology, 23: 761–774.
Salehizadeh, H., and Shojaosadati, S. A., 2001. Extracellular biopolymeric flocculants recent trends and biotechnological importance. Biotechnology Advances, 19(5): 371–385.
Sharma, B. R., Dhuldhoya, N. C., and Merchant, U. C., 2006. Flocculants-ecofriendly approach. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 14(2): 195–202.
Shih, I. L., Van, Y. T., Yeh, L. C., Lin, H. G., and Chang, Y. N., 2001. Production of a biopolymer flocculant from Bacillus licheniformis and its flocculation properties. Bioresource Technology, 78(3): 267–272.
Su, X., Shen, X., Ding, L., and Yokota, A., 2012. Study on the flocculability of the Arthrobacter sp., an actinomycete resuscitated from the VBNC state. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 28(1): 91–97.
Tang, J. Y., Qi, S. J., Li, Z. G., An, Q., Xie, M. Q., Yang, B., et al., 2014. Production, purification and application of polysaccharide-based bioflocculant by Paenibacillus mucilaginosus. Carbohydrate Polymers, 113C: 463–470.
Tawila, Z., Ismail, S., Amrc, S. A., and Elkhairb, E. A., 2019. A novel efficient bioflocculant QZ-7 for the removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewater. RSC Advances, 15: 27825–27834.
Ugbenyen, A., Sekelwa, C., Mabinya, L. V., Olubukola, O. B., Farhad, A., and Okoh, A. I., 2012. Thermostable bacterial bioflocculant produced by Cobetia sp. isolated from Algoa Bay (South Africa). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 9(6): 2108–2120.
Ugbenyen, A. M., Cosa, S., Mabinya, L. V., and Okoh, A. I., 2014. Bioflocculant production by Bacillus sp. Gilbert isolated from a marine environment in South Africa. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 50(1): 49–54.
Wang, L., Ma, F., Qu, Y., Sun, D., Li, A., Guo, J., et al., 2011. Characterization of a compound bioflocculant produced by mixed culture of Rhizobium radiobacter F2 and Bacillus sphaeicus F6. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 27(11): 2559–2565.
Wang, S. G., Gong, W. X., Liu, X. W., Tian, L., Yue, Q. Y., and Gao, B. Y., 2007. Production of a novel bioflocculant by culture of Klebsiella mobilis using dairy wastewater. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 36(2): 1–6.
Wu, H., Li, Q., Lu, R., Wang, Y., Zhuang, X., and He, N., 2010. Fed-batch production of a bioflocculant from Corynebacterium glutamicum. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 37(11): 1203–1209.
Xia, S., Zhang, Z., Wang, X., Yang, A., Chen, L., Zhao, J., et al., 2008. Production and characterization of bioflocculant by Proteus mirabilis TJ-1. Bioresource Technology, 99(14): 6520–6527.
Yang, M., Liang, Y., Dou, Y, Jia X, Che, H., 2015. Isolation and identification of a bioflocculant-producing strain and optimisation of cultural conditions via a response surface model. Chemistry and Ecology, 31(7): 650–660.
Yim, J. H., Kim, S. J., Ahn, S. H., and Hong, K. L., 2007. Characterization of novel bioflocculant, p-KG03, from a marine dinoflagellate, Gyrodium impudicum KG03. Bioresource Technology, 98(2): 361–367.
Yin, Y. J., Tian, Z. M., Tang, W., Li, L., and Song, L. Y., 2014. Production and characterization of high efficiency bioflocculant isolated from Klebsiella sp. ZZ-3. Bioresource Technology, 171: 336–342.
Yu, G. H., He, P. J., and Shao, L. M., 2009. Characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) fractions from excess sludges and their effects on bioflocculability. Bioresource Technology, 100(13): 3193–3198.
Zaki, S. A., Elkady, M. F., Farag, S., and Abdelhaleem, D., 2013. Characterization and flocculation properties of a carbohydrate bioflocculant from a newly isolated Bacillus velezensis 40B. Journal of Environmental Biology, 34(1): 51–58.
Zhang, Z. Q., Lin, B., Xia, S. Q., Wang, X. J., and Yang, A. M., 2007. Production and application of a novel bio-flocculant by multiple microorganism consortia using brewery wastewater as carbon source. Journal of Environmental Science, 19(6): 242–243.
Zheng, Y., Ye, Z. L., Fang, X. L., Li, Y. H., and Cai, W. M., 2008. Production and characteristics of a bioflocculant produced by Bacillus sp. F19. Bioresource Technology, 99(16): 7686–7691.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Public Welfare Projects in Zhejiang Province (No. LGN21C200001), the Public Welfare Projects in Zhoushan city (Nos. 2021C 41005 and 2021C41007) and the Natural Science Foundation of Marine Fishery Institute of Zhejiang Province (No. 2020KF 010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, W., Liao, M., Zhang, D. et al. Studies on Bioflocculant Production by Pseudoalteromonas sp. NUM8, a Marine Bacteria Isolated from the Circulating Seawater. J. Ocean Univ. China 20, 1276–1284 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4747-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4747-7