Abstract
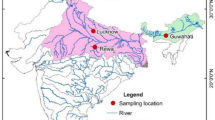
Pholis fangi is an ecologically important fish species inhabiting Chinese coastal waters of Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea. To investigate the genetic diversity and population genetic structure of P. fangi, a fragment of 487 bp in the first hypervariable region (HVR-1) of the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) control region was sequenced for 181 individuals collected from Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea. A total of 18 polymorphic sites were detected, which defined 25 haplotypes. A moderate level of haplotype diversity (h = 0.7052) and a low level of nucleotide diversity (π = 0.0028) were detected. Both the phylogenetic tree and the haplotype network showed no significant genealogical structure difference among sampling locations. Pairwise FST comparison and hierarchical molecular variance analysis (AMOVA) revealed that no significant genetic structure difference existed throughout the investigated regions, suggesting a high gene exchange among different populations. The results of neutrality test and mismatch distribution analysis indicated that a late Pleistocene population expansion (38000–127000 years ago) happened. Seasonal schooling migration may contribute to the genetically homogeneous population structure of the species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi, Y. P., 2005. Biology and its fishery of Fang’s blenny Enedrias fangi Wang et Wang in offshore in Liaoning Province. Fisheries Science, 24: 27–28 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Bonin, A., Nicole, F., Pompanon, F., Miaud, C., and Taberlet, P., 2007. Population adaptive index: A new method to help measure intraspecific genetic diversity and prioritize populations for conservation. Conservation Biology, 21: 697.
Englbrecht, C. C., Freyhof, J., Nolte, A., Rassmann, K., Schliewen, U., and Tautz, D., 2000. Phylogeography of the bullhead Cottus gobio (Pisces: Teleostei: Cottidae) suggests a pre-Pleistocene origin of the major central European populations. Molecular Evolution, 9: 709–722.
Excoffier, L., and Lischer, H. E. L., 2010. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Molecular Ecology Resources, 10: 564–567.
Excoffier, L., Smouse, P. E., and Quattro, J. M., 1992. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics, 131: 479–491.
Excoffier, L., 2004. Patterns of DNA sequence diversity and genetic structure after a range expansion: Lessons from the infinite-island model. Molecular Ecology, 13: 853–864.
Felsenstein, J., 1985. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution, 39: 783–791.
Fernándeziriarte, P. J., Alonso, M. P., Sabadin, D. E., Arauz, P. A., and Iudica, C., 2011. Phylogeography of weakfish Cynoscion guatucupa (Perciformes: Sciaenidae) from the southwestern Atlantic. Scientia Marina, 75: 701–706.
Frankham, R., Ballou, J. D., and Briscoe, D. A., 2002. An Introduction to Conservation Genetics. Cambridge University Press, New York, 617pp.
Fu, Y. X., 1997. Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics, 147: 915–925.
Grant, W. S., and Bowen, B. W., 1998. Shallow population histories in deep evolutionary lineages of marine fishes: Insights from sardines and anchovies and lessons for conservation. Journal of Heredity, 89: 415–426.
Han, Z. Q., Yanagimoto, T., Zhang, Y. P., and Gao, T. X., 2012. Phylogeography study of Ammodytes personatus in Northwestern Pacific: Pleistocene isolation, temperature and current conducted secondary contact. PLoS One, 7: e37425.
Hedgecock, D., Chow, V., and Waples, R. S., 1992. Effective population number of shellfish broodstock estimated from temporal variance in allelic frequencies. Aquaculture, 88: 215–232.
Hewitt, G. M., 2000. The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages. Nature, 405: 907–913.
Huang, X. X., Zeng, X. Q., and Zhang, C., 2010. The reproductive biology of Enedrias fangi in the inshore waters of Qingdao. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 40: 55–59 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hwang, S. D., Lee, T. W., and Hwang, S. W., 2008. Age, growth and life history of gunnel, Pholis fangi, in the Yellow Sea. Fisheries Research, 93: 72–76.
Jiang, Z. Q., and Qin, K. J., 1995. Age and growth of Enedrias fangi in Dalian. Journal of Dalian Fisheries College, 50 (1): 33–41 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang, Z. Q., Meng, Q. J., and Miao, Z. O., 1997. The reproductive biology of Enedrias fangi in Dalian. Journal of Dalian Fisheries College, 12: 1–6.
Klimova, A., Phillips, C. D., Fietz, K., Olsen, M. T., Harwood, J., Amos, W., and Hoffman, J. I., 2014. Global population structure and demographic history of the grey seal. Molecular Ecology, 23: 3999–4017.
Kuhner, M. K., 2006. LAMARC 2.0: Maximum likelihood and Bayesian estimation of population parameters. Bioinformatics, 22: 768–770.
Lambeck, K., Esat, T. M., and Potter, E. K., 2002. Links between climate and sea levels for the past three million years. Nature, 419: 199–206.
Li, L., 2013. Study on morphology and genetics of Pholis fangi and P. nebulosa. Master thesis. Ocean University of China (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, L., Zhang, H., Sun, D. R., and Gao, T. X., 2014. Structure of mitochondrial DNA control region of Pholis fangi and its phylogenetic implication. Journal of Ocean University of China, 13: 491–496.
Li, M., Li, Z. G., Xu, B. D., Wang, X. H., and Shi, Q., 2015. Effects of spatiotemporal and environmental factors on the distribution and abundance of Pholis fangi in Haizhou Bay using a generalized additive model. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 22: 812–819 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, T., Zhang, X. M., Zhang, P. D., and Huang, G. Q., 2011. Seasonal variation on community structure of fishery resources in the coastal waters of Southern Shangdong Peninsular. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 41: 41–50 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, J., Chen, Y. X., and Ma, L., 2015. Fishes of the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea. Science Press, Beijing, 211pp (in Chinese).
Liu, J. X., Gao, T. X., Wu, S. F., and Zhang, Y. P., 2007. Pleistocene isolation in the Northwestern Pacific marginal seas and limited dispersal in a marine fish, Chelon haematocheilus (Temminck and Schlegel, 1845). Molecular Ecology, 16: 275–288.
Luan, J., Xu, B. D., Xue, Y., Ren, Y. P., and Zhang, C. L., 2017. Size distribution and length-weight relationships in Pholis fangi in Haizhou Bay. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 24: 1323–1331 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lynch, M., 1996. A quantitative-genetic perspective on conservation issues. In: Conservation Genetics: Case Histories from Nature. Avise, J., and Hamrick, J., eds., Chapman and Hall, New York, 471–501.
Posada, D., and Crandall, K. A., 1998. Modeltest: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics, 14: 817–818.
Rogers, A. R., and Harpending, H., 1992. Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic differences. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 9: 552–569.
Song, N., Gao, T. X., Ying, Y. P., Yanagimoto, T., and Han, Z. Q., 2017. Is the Kuroshio Current a strong barrier for the dispersal of the gizzard shad (Konosirus punctatus) in the East China Sea? Marine and Freshwater Research, 68: 810–820.
Tajima, F., 1989. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics, 123: 585–595.
Tamura, K., Peterson, D., Peterson, N., Stecher, G., Nei, M., and Kumar, S., 2011. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28: 2731–2739.
Whitehead, A., Anderson, S. L., Kuivila, K. M., Roach, J. L., and May, B., 2003. Genetic variation among interconnected populations of Catostomus occidentalis: Implications for distinguishing impacts of contaminants from biogeographical structuring. Molecular Ecology, 12: 2817–2833.
Zhao, L. L., Yi, D., Li, C. H., Sun, D. R., and Gao, T. X., 2017. Phylogeography and population structure of Johnius grypotus (Richardson, 1846) as revealed by mitochondrial control region sequences. ZooKeys, 705: 143–158.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Prof. Xiaoqi Zeng, Dr. Xiaodong Bian and Dr. Zhongxin Wu for collecting the samples. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41776171).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, T., Li, L., Fang, R. et al. Shallow Genetic Structure of Pholis fangi in Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea Inferred from mtDNA Control Region. J. Ocean Univ. China 18, 947–952 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-019-3991-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-019-3991-6