Abstract
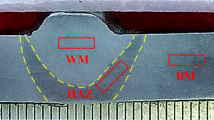
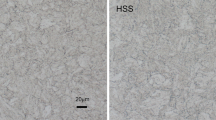
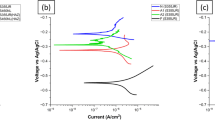
The high strength low-alloy steels are welded by underwater wet welding with stainless steel electrodes. The micro-structural and electrochemical corrosion study of base metal (BM), weld zone (WZ) and heat affected zone (HAZ) are carried out to understand the influence of the corrosion product layer generated on the high strength low-alloy steels welded by underwater wet welding with stainless steel electrodes, methods used including, potentiodynamic polarization, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The results indicate that the WZ acts as a cathode and there is no corrosion product on it throughout the immersion period in seawater. The HAZ and BM acts as anodes. The corrosion rates of the HAZ and BM change with the immersion time increasing. In the initial immersion period, the HAZ has the highest corrosion rate because it has a coarse tempered martensite structure and the BM exhibites a microstructure with very fine grains of ferrite and pearlite. After a period of immersion, the BM has the highest corrosion rate. The reason is that the corrosion product layer on the HAZ is dense and has a better protective property while that on the BM is loose and can not inhibit the diffusion of oxygen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basak, A. K., Diomidis, N., Celis, J. P., Masquelier, C., and Warichet, D., 2008. Chemical reactivity of thermo-hardenable steel weld joints investigated by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochimica Acta, 53: 7575–7582.
Bordbar, S., Alizadeh, M., and Hashemi, S. H., 2013. Effects of microstructure alteration on corrosion behavior of welded joint in API X70 pipeline steel. Materials and Design, 45: 597–604.
Cui, Y., and Lundin, C. D., 2007. Austenite-preferential corrosion attack in 316 austenitic stainless steel weld metals. Materials and Design, 28: 324–328.
Deen, K. M., Ahmad, R., Khan, I. H., and Farahat, Z., 2010. Microstructural study and electrochemical behavior of low alloy steel weldment. Materials and Design, 31: 3051–3055.
Du, C., Li, X., Liang, P., Liu, Z., Jia, G., and Cheng, Y., 2009. Effects of microstructure on corrosion of X70 pipe steel in an alkaline soil. Journal of Materials Engineering and Perfomance, 18: 216–220.
Fushimi, K., Naganuma, A., Azumi, K., and Kawahara, Y., 2008. Current distribution during galvanic corrosion of carbon steel welded with type-309 stainless steel in NaCl solution. Corrosion Science, 50: 903–911.
Ito, S., Kihira, H., and Murat, T., 1988. A new method to monitor in-situ protective properties of rust on weathering steel. In: American Society for Testing and Materials. Dean, S. W., and Lee, T. S., eds., ASTM STP 965, Philadelphia PA, 366–373.
Lananowski, J., 2008. Development of under-water welding techniques. Welding International, 25: 933–937.
Maksimov, S. Y., 2010. Underwater arc welding of higher strength low-alloy steels. Welding International, 24: 449–454.
Padilla, E., Chawla, N., Silva, L. F., dos Santos, V. R., and Paciornik, S., 2013. Image analysis of cracks in the weld metal of a wet welded steel joint by three dimensional (3D) X-ray microtomography. Materials Characterization, 83: 139–144.
Sadeghian, M., Shamanian, M., and Shafyei, A., 2014. Effect of heat input on microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar joints between super duplex stainless steel and high strength low alloy steel. Materials and Design, 60: 678–684.
Torkamany, M. J., Sabbaghzadeh, J., and Hamedi, M. J., 2012. Effect of laser welding mode on the microstructure and mechanical performance of dissimilar laser spot welds between low carbon and austenitic stainless steels. Materials and Design, 34: 666–672.
Wang, H., Wei, F. I., Chang, Y. S., and Shih, H. C., 1997. The corrosion mechanisms of carbon steel and weathering steel in SO2 polluted atmospheres. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 47: 1–8.
Wu, W. Y., Hu, S. S., and Shen, J. Q., 2015. Microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of laser welded dissimilar joints between ferritic stainless steel and carbon steel. Materials and Design, 65: 855–861.
Yamaguchi, S., Yoshida, T., and Saito, T., 1994. Improvement in descaling of hot strip by hydrochloric acid. Isij International, 34: 670–678.
Zhang, G., and Cheng, Y., 2009. Micro-electrochemical characterization of corrosion of welded X70 pipeline steel in near-neutral pH solution. Corrosion Science, 51: 1714–1724.
Zou, Y., Wang, J., and Zheng, Y. Y., 2010. Characteristics of the electrode process for rusted carbon steel. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 26: 2361–2368.
Zou, Y., Wang, J., and Zheng, Y. Y., 2011. Electrochemical techniques for determining corrosion rate of rusted steel in seawater. Corrosion Science, 53: 208–216.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 5120 9129 and 21203034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Q., Zou, Y., Kong, X. et al. The influence of the corrosion product layer generated on the high strength low-alloy steels welded by underwater wet welding with stainless steel electrodes in seawater. J. Ocean Univ. China 16, 49–56 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-017-3057-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-017-3057-6