Abstract
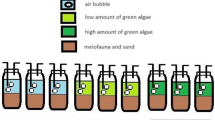
Meiofauna samples from intertidal sediments of Qingdao No.2 Bathing Beach, China, were collected for field study, and subjected to organic enrichment in a laboratory microcosm experiment for 21 d. There were three different treatments including non-organic addition as the control, low-organic enrichment (2 g DW green algae per 150 mL) and high-organic enrichment (10 g DW green algae per 150 mL). After 21 d, the meiofauna richness decreased in both organic enrichment treatments. Among the three treatments, total meiofauna abundance was significantly different, and the control groups had higher abundance than the other two treatment groups. However, the responses of the meiofauna abundance in the two organic enrichment treatments were non-significantly different. The relationship of meiofaunal abundance and nematode/copepod ratios to organic matter and oxygen level in the microcosm experiments were discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armenteros, M., Pérez-Garcí, J. A., Ruiz-Abierno, A., Díaz-Asencio, L., Helguera, Y., Vincx, M., and Decraemer, W., 2010. Effects of organic enrichment on nematode assemblages in a microcosm experiment. Marine Environmental Research, 70: 374–382.
Armonies, W. and Reise, K., 2000. Faunal diversity across a sandy shore. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 196: 49–57.
Austen, M. C., and Widdicombe, S., 2006. Comparison of the response of meio- and macrobenthos to disturbance and organic enrichment. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 330: 96–104.
Boucher, G., and Lambshead, P. J. D., 1995. Ecological biodiversity of marine nematodes in samples from temperate, tropical and deep-sea regions. Conservation Biology, 9: 1594–1604.
Bouwman, L. A., Romeijn, K., and Admiraal, W., 1984. On the ecology of meiofauna in an organically polluted estuarine mudflat. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Sciences, 19: 633–653.
Coull, B. C., Ellison, R. L., Fleeger, J. W., Higgins, R. P., Hope, W. D., Hummon, W. D., Rieger, R. M., Sterrer, W. E., Thiel, H., and Tietjen, J. H., 1977. Quantitative estimates of the meiofauna from the deep sea of North Carolina, U.S.A. Marine Biology, 39: 233–240.
Creutzberg, F., Wapenaar, P., Duineveld, G., and Lopez, N., 1984. Distribution and density of the benthic fauna in the southern North Sea in relation to bottom characteristics and hydrographic conditions. Rapport et Proces-verbaux des Reunions, Conseil International pour l’Exploration de la Mer, 183: 101–110.
Dang, H. Y., Huang, B., and Zhang, Z. N., 1996. Study on marine benthos in an organically polluted intertidal beach of Qingdao Bay II: The pollution ecology of meiobenthos. Studia Marina Sinica, 37: 91–101.
Edgar, G. J., 1999. Experimental analysis of structural versus trophic importance of seagrass beds. I: Effects on macrofaunal and meiofaunal invertebrates. Vie Milieu, 49: 239–248.
Freckman, D. W., 1988. Bacterivorous nematodes and organic-matter decomposition. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 24: 195–217.
Giere, O., 1993. Meiobenthology: The Microscopic Motile Fauna of Aquatic Sediments. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 528pp.
Giere, O., 2009. Meiobenthology: The Microscopic Motile Fauna of Aquatic Sediments. 2nd edition. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 527pp. ISBN: 978-3-540-68657-6.
Gyedu-Ababio, T. K., and Baird, D., 2006. Response of meiofauna and nematode communities to increased levels of contaminants in a laboratory microcosm experiment. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 63: 443–450.
Heip, C. H. R., Herman, R., and Vincx, M., 1984. Variability and productivity of meiobenthos in the Southern Bight of the North Sea. Rapport et Proces-verbaux des Reunions, Conseil International pour l’Exploration de la Mer, 183: 51–56.
Higgins, R. P., and Thiel, H., 1988. Introduction to the Study of Meiofauna. Smithsonian Institute Press, Washington D. C., 376pp.
Hopper, B. E., Fell, J. W., and Cefalu, R. C., 1973. Effect of temperature on life cycles of nematodes associated with the mangrove (Rhizophora mangle) detrital system. Marine Biology, 23: 293–296.
Huston, M., 1979. A general hypothesis of species diversity. American Naturalist, 113: 81–101.
Huys, R., Herman, P. M. J., Heip, C. H. R., and Soetaert, K., 1992. The meiobenthos of the North Sea: density, biomass trends and distribution of copepod communities. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 49: 23–44.
James, W. N., and Mark, D. B., 2004. Marine Biology: An Ecological Approach. 6th edition. Benjamin-Cummings Publishing Company, Hardcover, 342–343.
Juario, J. V., 1975. Nematode species composition and seasonal fluctuation of a sublittoral meiofauna community in the German Bight, 15: 283–337.
Lambshead, P. J. D., 1984. The nematode/copepod ratio. Some anomalous results from the firth of clyde. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 15: 256–259.
McLachlan, A., Woolridge, T., and Dye, A. H., 1981. The ecology of sandy beaches in southern Africa. South African Journal of Zoology, 16: 219–231.
Mclntyre, A. D., 1969. Ecology of the marine meiobenthos. Biological Reviews, 44: 245–290.
Montagna, P. A., Bauer, J. E., Harind, D., and Spies, R. B., 1995. Meiofaunal and microbial trophic interactions in a natural submarine hydrocarbon seep. Vie et milieu, 45: 17–25.
Moreno, M., Ferrero, T. J., Granelli, V., Marin, V., Albertelli, G., and Fabiano, M., 2006. Across-shore variability and trophodynamic features of meiofauna in a microtidal beach of the NW Mediterranean. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 66: 357–367.
Neiraa, C., Sellanesb, J., Levinc, L. A., and Arntzd, W. E., 2001. Meiofaunal distributions on the Peru margin: relationship to oxygen and organic matter availability. Deep-Sea Research I, 48: 2453–2472.
O’lafsson, E., 1992. Small-scale spatial distribution of marine meiobenthos: the effects of decaying macrofauna. Oecologica, 90: 37–42.
Ott, J., 1972. Studies on the diversity of the nematode fauna in intertidal sediments. 5 th European Marine Biology Symposium. Piccin, Padua, 275–285.
Pascal, P. Y., Dupuy, C., Richard, P., Rzeznik-Orignac, J., and Niquil, N., 2008. Bacterivory of a mudflat nematode community under different environmental conditions. Marine Biology, 154: 671–682.
Pinn, E. H., and Rodgers, M., 2005. The influence of visitors on intertidal biodiversity. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 85: 263–268.
Raffaelii, D. G., and Mason, C. F., 1981. Pollution monitoring with meiofauna, using the ratio of nematodes to copepods. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 12: 158–163.
Rieper-Kirchner, M., 1989. Microbial degradation of North Sea macroalgae: field and laboratory studies. Botanica Marina, 32: 241–252.
Sandulli, R., and Giudici, M. D. N, 1989. Effects of organic enrichment on meiofauna: a laboratory study. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 20: 223–227.
Schratzberger, M., Warr, K., and Rogers, S. I., 2007. Functional diversity of nematode community in the southwestern North Sea. Marine Environmental Resource, 63: 368–389.
Shaalan, I. M., 2005. Sustainable tourism development in the Red Sea of Egypt: threats and opportunities. Journal of Cleaner Production, 13: 83–87.
Short, A. D., 1999. Handbook of beach and shoreface morphodynamics. John Wiley, New York, 379pp.
Sundbäck, K., Jonsson, B., Nilsson, P., and Lindström, I., 1990. Impact of accumulating drifting macroalgae on a shallow-water sediment system: an experimental study. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 58: 261–274.
Sutherland, T. F., Levings, C. D., Petersen, S. A., Poon, P., and Piercey, B., 2007. The use of meiofauna as an indicator of benthic organic enrichment associated with salmonid aquaculture. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 54: 1249–1261.
Tenore, K. R., 1977. Utilization of aged detritus derived from different sources by the polychaete Capitella capitata. Marine Biology, 44: 51–55.
Tratalos, J. A., and Austin, T. J., 2001. Impacts of recreational SCUBA diving oil on coral communities of the Caribbean island of Grand Cayman. Biological Conservation, 102: 67–75.
Vanreusel, A., 1990. Ecology of the free-living marine nematodes from the Voordelta (Southern Bight of the North Sea). I. Species composition and structure of the nematode communities. Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 31: 439–462.
Vanreusel, A., 1991. Ecology of the free-living marine nematodes from the Voordelta (Southern Bight of the North Sea). II. Habitat preferences of the dominant species. Nematologica. Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 37: 343–359.
Warwick, R. M., and Price, R., 1979. Ecological and metabolic studies on free living nematodes from an estuarine mudflat. Estuaries and Coastal Marine Science, 9: 257–271.
Webb, D. G., 1996. Response of macro- and meiobenthos from a carbon-poor sand to phytodetrital sedimentation. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 203: 259–271.
Widbom, B., 1984. Determination of average individual dry weight and ashfree dry weight in different sieve fractions of marine meiofauna. Marine Biology, 84: 101–108.
Woodin, S. A., and Jackson, J. B. C, 1979b. Interphyletic competition among marine benthos. Journal of Marine Resource, 34: 25–41.
Woodin, S. A., and Jackson, J. B. C., 1979a. Facilitative and inhibitory interactions among estuarine meiobenthic harpacticoid copepods. Ecology, 68: 1906–1919.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhou, H., Zhang, Z. et al. Effects of organic enrichment on sandy beach meiofauna: A laboratory microcosm experiment. J. Ocean Univ. China 10, 246–254 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-011-1831-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-011-1831-4