Abstract
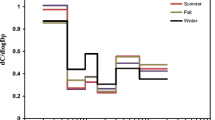
Mass concentrations of Total Suspended Particles (TSP) and size-segregated particles were obtained from July 2001 to June 2002 in Qingdao to characterize the seasonal variations of atmospheric aerosols and to show the impact of dust events on the air quality in Qingdao. Data on size-segregated aerosols show that 73.74% of the TSP mass concentration is contributed by particles with diameters less than 11µm. Particles with diameters less than 1.1µm have a higher concentration during the winter. In spring, larger particles tend to have higher mass concentrations. Bimodal particle size distributions have been observed, with maxima around 4.7–7µm and 0.43–0.65µm in the winter season, and 7–11µm and 0.65–1.lµm in the autumn season. Measurements made during the dust events in March 2002 show high concentrations of particles in the size range 2.1–7µm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arimoto, R., R. A. Duce, D. L. Savoie, J. M. Prospero, R. Talbot, et al, 1996. Relationships among aerosol constituents from Asia and the North Pacific during PEM-West. J. Geophys. Res., 101(D): 2011–2023.
Arimoto, R., 2001. Eolian dust and climate: relationships to sources, tropospheric chemistry, transport and deposition. Earth-Science Rev., 54: 29–42.
Davis, B. L., and J. X. Guo, 2000. Airborne particulate study in five cities of China. Atmos. Environ., 34(17): 2703–2711.
Duce, R.A., C.K. Unni, B.J. Ray, J.M. Prospero, and J. T. Merrill, 1980. Long range transport of soil dust from Asia to the tropical North Pacific: temporal variability. Science, 209: 1522–1524.
Fang, M., M. Zheng, F. Wang, K. S. Chim, and S. C. Kot, 1999. The long-range transport of aerosols from northern China to Hong Kong- a multi-technique study. Atmos. Environ., 33: 1803–1817.
Gao, Y., R. Arimoto, R. A. Duce, X.Y. Zhang, G.Y. Zhang, et al., 1997a. Temporal and spatial distributions of dust and its deposition to the China Sea. Tellus, 49B: 172–189.
Gao, Y., and R. A. Duce, 1997b. Air-sea chemical exchange in coastal oceans. Adv. Earth Sci., 12: 553–563.
Geng, M., 2005. On the characteristics and formation of sand-dust weather of Qingdao. Master dissertation. Ocean University of China.
Greaves, M.J., H. Elderfield, and E.R. Sholkovitz, 1999. Aeolian sources of rare earth elements to the Western Pacific Ocean. Marine Chem., 68: 31–38.
Husar, R. B., D. M. Tratt, B.A. Schichtel, S. R. Falke, F. Li, et al., 2001. The Asian dust eventsof April 1998. J. Geophys. Res., 106: 18317–18330.
Jaffe, D., I. Mckendry, T. Anderson, and H. Price, 2003. Six ‘new’ episodes of trans-Pacific transport of air pollutants. Atmos. Environ., 37: 391–404.
Kinne, S., and R. Pueschel, 2001. Aerosol radiative forcing for Asian continental outflow. Atmos. Environ., 35: 5019–5028.
Liu, Y., and M. Zhou, 1999. Atmospheric input of aerosols to the eastern seas of China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 21: 38–45.
Liu, Y., and M.Y. Zhou, 1999. The internal variation of mineral aerosols in the surface air over Beijing and the East China Sea. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 19: 642–647.
Martin, J.H., and R. M. Gordon, 1988. Northeast Pacific iron distributions in relation to phytoplankton productivity. Deep-Sea Res., 35: 177–196.
Mikami, M., O. Abe, M. Y. Du, O. Chiba, K. Fujita, et al., 2002. The impact of aeolian dust on climate: Sino-Japanese cooperative project ADEC. J. Arid Land Stud., 11(4): 211–222.
Morel, F. M.M., R.J. Hudson, and N. M. Price, 1991. Limitation of productivity by trace metals in the sea. Limnol. Oceanogr., 36: 1742–1755.
Murano, K., H. Mukai, S. Hatakeyama, E. S. Jang, and I. Uno, 2000. Trans-boundary air pollution over remote islands in Japan: observed data and estimates from a numerical model. Atmos. Environ., 34: 5139–5149.
Qin, Y., C. Chan Chak, and L. Y. Chan, 1997. Characteristics of chemical compositions of atmospheric aerosols in Hong Kong: spatial and seasonal distributions. Sci. Total Environ., 206: 25–37.
Sheng, L.F., M. Geng, Y. Wang, H.W. Gao, G.Y. Shi, et al., 2003. Effects of dust storms on atmospheric aerosols in Qingdao in spring 2002. Res. Environ. Sci., 16 (5): 11–13.
Sokolik, I. N., D. M. Winker, G. Bergametti, D. A. Gillette, G. Carmichael, et al., 2001. Introduction to special section: outstanding problems in quantifying the radiative impacts of mineral dust. J. Geophys. Res., 106: 18015–18027.
Song, C.H., and G.R. Carmichael, 1999. The aging process of naturally emitted aerosol (sea-salt and mineral aerosol) during long range transport. Atmos. Environ., 33: 2203–2218.
Yabuki, S., S. Kanayama, F. Fu, M. Honda, F. Yanagisawa, et al., 2002. Physical and chemical characteristics of aeolian dust collected over Asian dust source regions in China — Comparison with atmospheric aerosols in an urban area at Wako, Japan. J. Arid Land Stud., 11: 273–289.
Zhang, J., S. M. Liu, X. Lu, and W. W. Huang, 1993. Characterizing Asia wind-dust transport to the northwest Pacific Ocean: direct measurements of the dust flux for two years. Tellus, 45B: 335–345.
Zhang, J.L., Z.G. Yu, and J. Zhang, 1999. Wet and dry deposition and its influences on marine ecosystem. Marine Environ. Sci., 18: 70–76.
Zhou, M.Y., Z. Chen, R.H. Huang, Q. Wang, R. Arimoto, et al., 1994. Effects of two dust storms on solar radiation in the Beijing-Tianjin area. Geophy. Res. Lett., 21: 2697–2700.
Zhang, J., Y. Wu, C. L. Liu, Z. B. Shen, Z. G. Yu, et al., 2001. Aerosol characters from the desert region of Northwest China and the Yellow Sea in spring and summer: observations at Minqin, Qingdao, and Qianliyan in 1995–1996. Atmos. Environ., 35: 5007–5018.
Zhang, D. Z., and Y. Iwasaka, 1998. Morphology and chemical composition of individual dust particles collected over Wakasa Bay, Japan. J. Aerosol Sci., 29: s217-s218.
Zhang, D. Z., Y. S. Guang, Y. Iwasaka, and M. Hu, 2000. Mixture of sulfate and nitrate in coastal atmospheric aerosols: individual particle studies in Qingdao (36°04′ N, 120°21′E) China. Atmos. Environ., 34: 2669–2679.
Zhuang, G.S., and J.H. Guo, 2001. Composition, source, and size distribution of dust during dust storm in China in 2000 and its effect on global climate. Chin. Sci. Bull., 46: 191–197.
Wang, M., and M. Hu, 2001a. Mass concentration and major compositions of coastal aerosol in Qingdao. Environ. Sci., 22: 6–9 (in Chinese).
Wang, M., and M. Hu, 2001b. Major Inorganic compositions in fine and coarse particles of ambient aerosol at Qingdao. Environ. Sci., 22: 35–37 (in Chinese).
Xiao, H., G. R. Carmichael, and Y. Zhang, 1998. A Modeling evaluation of the Impact of mineral aerosols on the particulate sulfate formation in East Asia. Scientia Atmospherica Sinica, 22: 343–353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, L., Fu, Y., Qiu, M. et al. The seasonal variabilities in the concentration of atmospheric aerosols over Qingdao, China. J Ocean Univ. China 4, 383–390 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-005-0060-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-005-0060-0