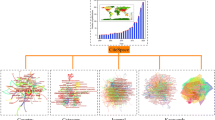
Abstract
In total, 9,552 documents were extracted from the Web of Science Core Collection and subjected to knowledge mapping and visualization analysis for the field of phytoremediation of HM-contaminated soil (PHMCS) with CiteSpace 5.7 R3 software. The results showed that (1) the number of publications increased linearly over the studied period. The top 10 countries/regions, institutions and authors contributing to this field were exhibited. (2) Keyword co-occurrence cluster analysis revealed a total of 8 clusters, including “Bioremediation,” “Arsenic,” “Biochar,” “Oxidative stress,” “Hyperaccumulation,” “EDTA,” “Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi,” and “Environmental pollution” clusters (3) In total, 334 keyword bursts were obtained, and the 25 strongest, longest duration, and newest keyboard bursts were analyzed in depth. The strongest keyword burst test showed that the hottest keywords could be divided into 7 groups, i.e., “Plant bioremediation materials,” “HM types,” “Chelating amendments,” “Other improved strategies,” “Technical terminology,” “Risk assessment,” and “Other.” Almost half of the newest topics had emerged in the past 3 years, including “biochar,” “drought,” “health risk assessment,” “electrokinetic remediation,” “nanoparticle,” and “intercropping.” (4) In total, 9 knowledge base clusters were obtained in this study. The studies of Ali et al. (2013), Blaylock et al. (1997), Huang et al. (1997), van der Ent et al. (2013), Salt et al. (1995), and Salt (1998), which had both high frequencies and the strongest burst scores, have had the most profound effects on PHMCS research. Finally, future research directions were proposed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Zia-Ur-Rehman M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Qayyum M F, Irshad M K (2015). Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: A review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 119: 186–197
Ahmad M, Rajapaksha A U, Lim J E, Zhang M, Bolan N, Mohan D, Vithanage M, Lee S S, Ok Y S (2014). Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere, 99: 19–33
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad M A (2013). Phytoremediation of heavy metals-concepts and applications. Chemosphere, 91(7): 869–881
Anning A K, Akoto R (2018). Assisted phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil from a mined site with Typha latifolia and Chrysopogon zizanioides. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 148: 97–104
Asad S A, Farooq M, Afzal A, West H (2019). Integrated phytobial heavy metal remediation strategies for a sustainable clean environment: A review. Chemosphere, 217: 925–941
Bai Y, Zhou Y, Gong J (2021). Physiological mechanisms of the tolerance response to manganese stress exhibited by Pinus massoniana, a candidate plant for the phytoremediation of Mn-contaminated soil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 1–12
Baker A J M, Brooks R R (1989). Terrestrial higher plants which hyperaccumulate metallic elements: A review of their distribution, ecology and phytochemistry. Biorecovery, 1: 81–126
Biederman L A, Harpole W S (2013). Biochar and its effects on plant productivity and nutrient cycling: A meta-analysis. Global Change Biology. Bioenergy, 5(2): 202–214
Blaylock M J, Salt D E, Dushenkov S, Zakharova O, Gussman C, Kapulnik Y, Ensley B D, Raskin I (1997). Enhanced accumulation of Pb in Indian mustard by soil-applied chelating agents. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(3): 860–865
Brooks R R, Lee J, Reeves R D, Jaffré T (1977). Detection of nickeliferous rocks by analysis of herbarium specimens of indicator plants. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 7: 49–57
Bukhat S, Imran A, Javaid S, Shahid M, Majeed A, Naqqash T (2020). Communication of plants with microbial world: Exploring the regulatory networks for PGPR mediated defense signaling. Microbiological Research, 238: 126486
Cappa J J, Pilon-Smit E A H (2013). Evolutionary aspects of elemental hyperaccumulation. Planta 238: 1–9
Carvalho C F M, Viana D G, Pires F R, Egreja Filho F B, Bonomo R, Martins L F, Cruz L B S, Nascimento M C P, Cargnelutti Filho A, Rocha Júnior P R D (2019). Phytoremediation of barium-affected flooded soils using single and intercropping cultivation of aquatic macrophytes. Chemosphere, 214: 10–16
Chaudhry H, Nisar N, Mehmood S, Iqbal M, Nazir A, Yasir M (2020). Indian Mustard Brassica juncea efficiency for the accumulation, tolerance and translocation of zinc from metal contaminated soil. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 23: 101489
Chen C (2004). Searching for intellectual turning points: Progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(Suppl 1): 5303–5310
Chen C, Dubin R, Kim M C (2014). Emerging trends and new developments in regenerative medicine: A scientometric update (2000–2014). Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 14(9): 1295–1317
Chen C, Hu Z, Liu S, Tseng H (2012). Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: A scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 12(5): 593–608
Chen C M (2017). Science mapping: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of Data and Information Science, 2(2): 1–40
Chen D, Liu X, Bian R, Cheng K, Zhang X, Zheng J, Joseph S, Crowley D, Pan G, Li L (2018). Effects of biochar on availability and plant uptake of heavy metals: A meta-analysis. Journal of Environmental Management, 222: 76–85
Cui X, Guo X, Wang Y, Wang X, Zhu W, Shi J, Lin C, Gao X (2019). Application of remote sensing to water environmental processes under a changing climate. Journal of Hydrology (Amsterdam), 574: 892–902
de Castilhos Ghisi N, Zuanazzi N R, Fabrin T M C, Oliveira E C (2020). Glyphosate and its toxicology: A scientometric review. Science of the Total Environment, 733: 139359
El-Bahr S M, Shousha S, Albokhadaim I, Shehab A, Khattab W, Ahmed-Farid O, El-Garhy O, Abdelgawad A, El-Naggar M, Moustafa M, Badr O, Shathele M (2020). Impact of dietary zinc oxide nanoparticles on selected serum biomarkers, lipid peroxidation and tissue gene expression of antioxidant enzymes and cytokines in Japanese quail. BMC Veterinary Research, 16: 349
Emamverdian A, Ding Y L, Mokhberdoran F, Xie Y F, Zheng X, Wang Y J (2020). Silicon dioxide nanoparticles improve plant growth by enhancing antioxidant enzyme capacity in bamboo (Pleioblastus pygmaeus) under lead toxicity. Trees (Berlin), 34(2): 469–481
Ernst W H O (2006). Evolution of metal tolerance in higher plants. Forest Snow and Landscape Research, 80(3): 251–274
Fayiga A O, Ma L Q (2006). Using phosphate rock to immobilize metals in soil and increase arsenic uptake by hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata. Science of the Total Environment, 359(1–3): 17–25
Gong X, Huang D, Liu Y, Zou D, Hu X, Zhou L, Wu Z, Yang Y, Xiao Z (2021). Nanoscale zerovalent iron, carbon nanotubes and biochar facilitated the phytoremediation of cadmium contaminated sediments by changing cadmium fractions, sediments properties and bacterial community structure. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 208: 111510
Guan X J, Zhao K Y, Liu S L, Li Y, Yu F M, Li C M, Liu K H (2021). The Global Trends and Hot Topics in the Field of Phytoremediation of Manganese-Contaminated Environment over the Past Three Decades-A Review Based on Citespace Visualization. Journal of Guangxi Normal University (Natural Sicence Edition): 1–17 (in Chinese)
Guedes F R C M, Maia C F, Silva B R S d, Batista B L, Alyemeni M N, Ahmad P, Lobato A K d S ((2021). Exogenous 24-epibrassinolide stimulates root protection, and leaf antioxidant enzymes in rice plants lead stressed: central roles to minimize Pb content and oxidative stress. Environmental Pollution, 280(1): 116992
Guo J, Lv X, Jia H, Hua L, Ren X, Muhammad H, Wei T, Ding Y (2020). Effects of EDTA and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on plant growth and heavy metal uptake of hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii Hance. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 88: 361–369
Hassan Z, Aarts M G M (2011). Opportunities and feasibilities for biotechnological improvement of Zn, Cd or Ni tolerance and accumulation in plants. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 72(1): 53–63
Hu Y M, Zhang P, Yang M, Liu Y Q, Zhang X, Feng S S, Guo D W, Dang X L (2020). Biochar is an effective amendment to remediate Cd-contaminated soils—A meta-analysis. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 20(11): 3884–3895
Huang H, Zhao Y, Xu Z, Zhang W, Jiang K (2019). Physiological responses of Broussonetia papyrifera to manganese stress, a candidate plant for phytoremediation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 181: 18–25
Huang J W W, Chen J J, Berti W R, Cunningham S D (1997). Phytoremediation of Lead-Contaminated Soils: Role of Synthetic Chelates in Lead Phytoextraction. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(3): 800–805
Huang L, Zhou M, Lv J, Chen K (2020). Trends in global research in forest carbon sequestration: A bibliometric analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 252: 119908
Jaffré T, Brooks R R, Lee J, Reeves R D (1976). Sebertia acuminata: A hyperaccumulator of nickel from New Caledonia. Science, 193 (4253): 579–580
Ji Z, Pei Y (2019). Bibliographic and visualized analysis of geopolymer research and its application in heavy metal immobilization: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 231: 256–267
Kamali M, Jahaninafard D, Mostafaie A, Davarazar M, Gomes A P D, Tarelho L A C, Dewil R, Aminabhavi T M (2020). Scientometric analysis and scientific trends on biochar application as soil amendment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 395: 125128
Kim Y H, Khan A L, Waqas M, Lee I J (2017). Silicon regulates antioxidant activities of crop plants under abiotic-induced oxidative stress: A review. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8: 510
Kofroňová M, Hrdinová A, Mašková P, Soudek P, Tremlová J, Pinkas D, Lipavská H (2019). Strong antioxidant capacity of horseradish hairy root cultures under arsenic stress indicates the possible use of Armoracia rusticana plants for phytoremediation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 174: 295–304
Lee R B (1982). Selectivity and kinetics of ion uptake by barley plants following nutrient deficiency. Annals of Botany, 50(4): 429–449
Lessl J T, Ma L Q (2013). Sparingly-soluble phosphate rock induced significant plant growth and arsenic uptake by Pteris vittata from three contaminated soils. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(10): 5311–5318
Li K, Rollins J, Yan E (2018). Web of Science use in published research and review papers 1997–2017: A selective, dynamic, cross-domain, content-based analysis. Scientometrics, 115(1): 1–20
Li M S, Luo Y P, Su Z Y (2007). Heavy metal concentrations in soils and plant accumulation in a restored manganese mineland in Guangxi, South China. Environmental pollution, 147(1): 168–175
Li N N, Wang J C, Song W Y (2015). Arsenic uptake and translocation in plants. Plant & Cell Physiology, 57(1): 4–13
Li Y, Lin J M, Huang Y Y, Yao Y W, Wang X R, Liu C Z, Liang Y, Liu K H, Yu F M (2020). Bioaugmentation-assisted phytoremediation of manganese and cadmium co-contaminated soil by Polygonaceae plants (Polygonum hydropiper L. and Polygonum lapathifolium L.) and Enterobacter sp. FM-1. Plant and Soil, 448(1–2): 439–453
Liang J Y, Wang Y S, Duan M, Li Y, Chen Z, Yu F M, Liu K H (2021). Effects of Biochar on Soil Available Cadmium and Cadmium Uptake by Plants—A Meta Analysis. Journal of Guangxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition): 1–14 (in Chinese)
Liu K H, Fan L Q, Li Y, Zhou Z M, Chen C S, Chen B, Yu F M (2018). Concentrations and health risks of heavy metals in soils and crops around the Pingle manganese (Mn) mine area in Guangxi Province, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 25(30): 30180–30190
Liu K H, Li C M, Tang S Q, Shang G D, Yu F M, Li Y (2020b). Heavy metal concentration, potential ecological risk assessment and enzyme activity in soils affected by a lead-zinc tailing spill in Guangxi, China. Chemosphere, 251: 126415
Liu K H, Yu F M, Chen M L, Zhou Z M, Chen C S, Li M S, Zhu J (2016a). A newly found manganese hyperaccumulator: Polygonum lapathifolium Linn. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 18(4): 348–353
Liu K H, Zhang H C, Liu Y, Li Y, Yu F M (2020d). Investigation of plant species and their heavy metal accumulation in manganese mine tailings in Pingle Mn mine, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 27(16): 19933–19945
Liu K H, Liang X L, Li C M, Yu F M, Li Y (2020c). Nutrient status and pollution levels in five areas around a manganese mine in southern China. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering: 14(6): 100
Liu K H, Xu J, Dai C L, Li C M, Li Y, Ma J M, Yu F M (2021). Exogenously applied oxalic acid assists in the phytoremediation of Mn by Polygonum pubescens Blume cultivated in three Mn-contaminated soils. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 15(5): 86
Liu K H, Zhou Z M, Yu F M, Chen M L, Chen C S, Zhu J, Jiang Y R (2016b). A newly found cadmium hyperaccumulatior: Centella asiatica Linn. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin and Advances in Food Sciences, 25: 2668–2675
Lu J, Lu H, Li J, Liu J, Feng S, Guan Y (2019). Multi-criteria decision analysis of optimal planting for enhancing phytoremediation of trace heavy metals in mining sites under interval residual contaminant concentrations. Environmental pollution, 255(Pt 2): 113255
Ma C, Ci K, Zhu J, Sun Z, Liu Z, Li X, Zhu Y, Tang C, Wang P, Liu Z (2021). Impacts of exogenous mineral silicon on cadmium migration and transformation in the soil-rice system and on soil health. Science of the Total Environment, 759: 143501
Ma L Q, Komar K M, Tu C, Zhang W, Cai Y, Kennelley E D (2001). A fern that hyperaccumulates arsenic. Nature, 409: 579
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Moreno A, Zhang C, Freitas H (2017). Serpentine endophytic bacterium Pseudomonas azotoformans ASS1 accelerates phytoremediation of soil metals under drought stress. Chemosphere, 185: 75–85
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Zhang C, Freitas H (2016). Inoculation of Brassica oxyrrhina with plant growth promoting bacteria for the improvement of heavy metal phytoremediation under drought conditions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 320: 36–44
Mahar A, Wang P, Ali A, Awasthi M K, Lahori A H, Wang Q, Li R, Zhang Z (2016). Challenges and opportunities in the phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: A review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 126: 111–121
Meena V S, Meena S K, Verma J P, Kumar A, Aeron A, Mishra P K, Bisht J K, Pattanayak A, Naveed M, Dotaniya M L (2017). Plant beneficial rhizospheric microorganism (PBRM) strategies to improve nutrients use efficiency: A review. Ecological Engineering, 107: 8–32
Ministry of environmental protection and Ministry of land and resources of China (2014). Bulletin of national soil pollution survey. [2021-03-21]. http://www.zhb.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/qt/201404/W020140417558995804588.pdf
Nie L, Shah S, Rashid A, Burd G I, George Dixon D, Glick B R (2002). Phytoremediation of arsenate contaminated soil by transgenic canola and the plant growth-promoting bacterium Enterobacter cloacae CAL2. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 40(4): 355–361
Norini M P, Thouin H, Miard F, Battaglia-Brunet F, Gautret P, Guégan R, Le Forestier L, Morabito D, Bourgerie S, Motelica-Heino M (2019). Mobility of Pb, Zn, Ba, As and Cd toward soil pore water and plants (willow and ryegrass) from a mine soil amended with biochar. Journal of Environmental Management, 232: 117–130
Ouyang W, Wang Y, Lin C, He M, Hao F, Liu H, Zhu W (2018). Heavy metal loss from agricultural watershed to aquatic system: A scientometrics review. Science of the Total Environment, 637–638: 208–220
Pan P, Lei M, Qiao P W, Zhou G D, Wan X M, Chen T B (2019). Potential of indigenous plant species for phytoremediation of metal (loid)-contaminated soil in the Baoshan mining area, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 26 (23): 23583–23592
Pollard A J, Powell K D, Harper F A, Smith J A C (2002). The Genetic Basis of Metal Hyperaccumulation in Plants. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 21(6): 539–566
Racchi M L (2013). Antioxidant defenses in plants with attention to Prunus and Citrus spp. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland), 2(4): 340–369
Rajkumar M, Prasad M N V, Swaminathan S, Freitas H (2013). Climate change driven plant-metal-microbe interactions. Environment International, 53: 74–86
Reeves R D, Baker A J M (1984). Studies on metal uptake by plants from serpentine and non-serpentine polulations of Thlaspi goesingense Hálácsy (cruciferae). New Phytologist, 28(1): 191–204
Robinson W O, Edgington G (1945). Minor elements in plants, and some accumulator plants. Soil Science, 60(1): 15–28
Sachs J (1865). Handbuch der Experimental-Physiologie der Pflanzen. Leipzig, Germany: Verlag von Wilhelm Engelmann. 153–154
Salt D E, Blaylock M, Kumar N P B A, Dushenkov V, Ensley B D, Chet I, Raskin I (1995). Phytoremediation: A novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Bio/ technology (Nature Publishing Company), 13(5): 468–474
Salt D E, Smith R D, Raskin I (1998). Phytoremediation. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 49(1): 643–668
Schat H (1999). Plant responses to inadequate and toxic micro-nutrient availability: General and nutrient-specific mechanisms. In: Gissel-Nielsen G, Jensen A, eds. Plant Nutrition Molecular Biology and Genetics. Amsterdam: Kluwer, 311–326
Schützendübel A, Polle A (2002). Plant responses to abiotic stresses: Heavy metal-induced oxidative stress and protection by mycorrhization. Journal of Experimental Botany, 53(372): 1351–1365
Sharifi P, Bidabadi S S, Zaid A, Abdel Latef A A H (2021). Efficacy of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in regulating growth performance, total glutathione and redox state of Calendula officinalis L. cultivated on Pb and Cd polluted soil. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 213: 112051
Sharples J M, Meharg A A, Chambers S M, Cairney J W G (2000). Symbiotic solution to arsenic contamination. Nature, 404(6781): 951–952
Shoji R, Yajima R, Yano Y (2008). Arsenic speciation for the phytoremediation by the Chinese brake fern, Pteris vittata. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 20(12): 1463–1468
Simiele M, Lebrun M, Miard F, Trupiano D, Poupart P, Forestier O, Scippa G S, Bourgerie S, Morabito D (2020). Assisted phytoremediation of a former mine soil using biochar and iron sulphate: Effects on As soil immobilization and accumulation in three Salicaceae species. Science of the Total Environment, 710: 136203
Siyar R, Doulati Ardejani F, Farahbakhsh M, Norouzi P, Yavarzadeh M, Maghsoudy S (2020). Potential of Vetiver grass for the phytoremediation of a real multi-contaminated soil, assisted by electrokinetic. Chemosphere, 246: 125802
Speiser A, Silbermann M, Dong Y, Haberland S, Uslu V V, Wang S, Bangash S A K, Reichelt M, Meyer A J, Wirtz M, Hell R (2018). Sulfur partitioning between glutathione and protein synthesis determines plant growth. Plant Physiology, 177(3): 927–937
Straker C J, Mitchell D T (1986). The activity and characterization of acid phosphatases in endomycorrhizal fungi of the Ericaeae. New Phytologist, 104(2): 243–256
Syukor A R A, Sulaiman S, Siddique M N I, Zularisam A W, Said M I M (2016). Integration of phytogreen for heavy metal removal from wastewater. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112(Pt. 4): 3124–3131
Tariq S R, Ashraf A (2016). Comparative evaluation of phytoremediation of metal contaminated soil of firing range by four different plant species. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 9(6): 806–814
van der Ent A, Baker A J M, Reeves R D, Pollard A J, Schat H (2013). Hyperaccumulators of metal and metalloid trace elements: Facts and fiction. Plant and Soil, 362(1–2): 319–334
Vieira L A J, Alves R D F B, Menezes-Silva P E, Mendonca M A C, Silva M L F, Silva M C A P, Sousa L F, Loram-Lourenco L, Alves da Silva A, Costa A C, Silva F G, Farnese F S (2021). Water contamination with atrazine: Is nitric oxide able to improve Pistia stratiotes phytoremediation capacity? Environmental Pollution, 272: 115971
Visoottiviseth P, Francesconi K, Sridokchan W (2002). The potential of Thai indigenous plant species for the phytoremediation of arsenic contaminated land. Environmental Pollution, 118(3): 453–461
Wang G, Zhang J S, Wang G F, Fan X Y, Sun X, Qin H L, Xu N, Zhong M Y, Qiao Z Y, Tang Y P, Song R T (2014). Proline responding1 plays a critical role in regulating general protein synthesis and the cell cycle in maize. Plant Cell, 26(6): 2582–2600
Wang L, Lin H, Dong Y B, He Y H (2018). Effects of cropping patterns of four plants on the phytoremediation of vanadium-containing synthetic wastewater. Ecological Engineering, 115: 27–34
Wieshammer G, Unterbrunner R, García T B, Zivkovic M F, Puschenreiter M, Wenzel W W(2007). Phytoextraction of Cd and Zn from agricultural soils by Salix spp. and intercropping of Salix caprea and Arabidopsis halleri. Plant and Soil, 298(1–2): 255–264
Xie M D, Chen W Q, Lai X C, Dai H B, Sun H, Zhou X Y, Chen T B (2019). Metabolic responses and their correlations with phytochelatins in Amaranthus hypochondriacus under cadmium stress. Environmental Pollution, 252(Pt B): 1791–1800
Xie X L, Yuan C, Zhu X L, Fu Y C, Gui J, Zhang Z X, Li P X, Liu D H (2018). In situ passivation remediation material in cadmium contaminated alkaline agricultural soil: A review. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 49: 1254–1260
Kumar Yadav K, Gupta N, Kumar A, Reece L M, Singh N, Rezania S, Ahmad Khan A (2018). Mechanistic understanding and holistic approach of phytoremediation: A review on application and future prospects. Ecological Engineering, 120: 274–298
Yang C, Ho Y N, Inoue C, Chien M F (2020a). Long-term effectiveness of microbe-assisted arsenic phytoremediation by Pteris vittata in field trials. Science of the Total Environment, 740: 140137
Yang C, Ho Y N, Makita R, Inoue C, Chien M F (2020b). A multifunctional rhizobacterial strain with wide application in different ferns facilitates arsenic phytoremediation. Science of the Total Environment, 712: 134504
Yang G M, Zhu L J, Santos J A G, Chen Y S, Li G, Guan D X (2017). Effect of phosphate minerals on phytoremediation of arsenic contaminated groundwater using an arsenic-hyperaccumulator. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 8: 366–372
Yang L P, Zhu J, Wang P, Zeng J, Tan R, Yang Y Z, Liu Z M (2018). Effect of Cd on growth, physiological response, Cd subcellular distribution and chemical forms of Koelreuteria paniculata. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 160: 10–18
Yang X J, Deng D M, Liu K H, Yu F M (2016). Response of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant defense systems of Polygonum hydropiper to Mn stress. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 23(4): 793–797
Yu F M, Li Y, Li F R, Li C M, Liu K H (2019). The effects of EDTA on plant growth and manganese (Mn) accumulation in Polygonum pubescens Blume cultured in unexplored soil, mining soil and tailing soil from the Pingle Mn mine, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 173: 235–242
Yu F M, Liu K H, Li M S, Zhou Z M, Deng H, Chen B (2013). Effects of cadmium on enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidative defences of rice (Oryza sativa L.). International Journal of Phytoremediation, 15 (6): 513–521
Yu F M, Li C M, Dai C L, Liu K H, Li Y (2020a). Phosphate: Coupling the functions of fertilization and passivation in phytoremediation of manganese-contaminated soil by Polygonum pubescens Blume. Chemoshere, 260: 127651
Yu F M, Yao Y W, Feng J P, Wang X R, Ma J M, Liu K H, Li Y (2020b). Enterobacter sp. FM-1 inoculation influenced heavy metal-induced oxidative stress in pakchoi (Brassica campestris L. spp. Chinensis Makino) and water spinach (Ipomoea aquatic F.) cultivated in cadmium and lead co-contaminated soils. Plant and Soil: 459(1): 155–171
Zaid A, Wani S H (2019). Reactive oxygen species generation, scavenging and signaling in plant defines responses. In: Jogaiah S, Abdelrahman M, eds. Bioactive Molecules in Plant Defense. Cham: Springer
Zhou W, Kou A Q, Chen J, Ding B Q (2018). A retrospective analysis with bibliometric of energy security in 2000–2017. Energy Reports, 4: 724–732
Zhu H H, Chen L, Xing W, Ran S M, Wei Z H, Amee M, Wassie M, Niu H, Tang D Y, Sun J, Du D Y, Yao J, Hou H B, Chen K, Sun J (2020). Phytohormones-induced senescence efficiently promotes the transport of cadmium from roots into shoots of plants: A novel strategy for strengthening of phytoremediation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 388: 122080
Zhu Y, Xu F, Liu Q, Chen M, Liu X, Wang Y, Sun Y, Zhang L (2019). Nanomaterials and plants: Positive effects, toxicity and the remediation of metal and metalloid pollution in soil. Science of the Total Environment, 662: 414–421
Zuanazzi N R, Ghisi N C, Oliveira E C (2020). Analysis of global trends and gaps for studies about 2,4-D herbicide toxicity: A scientometric review. Chemosphere, 241: 125016
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41967019) and the National Social Science Foundation Project of China (No. 16BTQ033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Highlights
• The overall global perspective of the PHMCS field was obtained.
• PHMCS research has flourished over the past two decades.
• In total, 8 clusters were obtained, and many new hot topics emerged.
• “Biochar,” “Drought,” “Nanoparticle,” etc., may be future hot topics.
• Five future directions are proposed.
Supplementary Files of
11783_2021_1507_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Global perspectives and future research directions for the phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil: A knowledge mapping analysis from 2001 to 2020
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, K., Guan, X., Li, C. et al. Global perspectives and future research directions for the phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil: A knowledge mapping analysis from 2001 to 2020. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 16, 73 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-021-1507-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-021-1507-2