Abstract
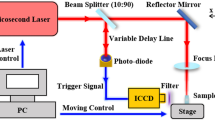
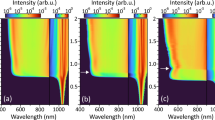
The influence of the picosecond (ps) pulsed burst with a nanosecond scale of temporal separation (50 ns) on filamentary traces in sapphire substrate is investigated. The spatiotemporal evolution of the filamentary plasma string induced by sub-pulses of the burst-mode is revealed according to the analysis of the instantaneous photoluminescence images. Due to the presence of residual plasma, the energy loss of sub-pulse during the balancing of self-focusing effect is reduced, and thus refreshes the plasma via refocusing. The refreshed plasma peak generated by the subsequent subpulse appears at relatively low density positions in the formed filamentary plasma string, which results in more uniform densities and less spatial overlap among the plasma peaks. The continuity and uniformity of the filamentary trace in sapphire are enhanced by the burst-mode. Besides, the burst filamentary propagation can also remain effective when the sub-pulse energy is below the self-focusing threshold. Based on this uniform and precise energy propagation mode, the feasibility of its use for the laser lift-off (LLO) process is verified.
摘要
研究了蓝宝石衬底中皮秒脉冲序列诱发等离子体串的时空演变。残余等离子体的存在,降低了子脉冲在自聚焦效应平衡过程的能量损失,使得后续子脉冲可以通过再聚焦刷新等离子体。刷新后的等离子体峰移动至丝状等离子体串密度相对较低的位置,有效地降低了等离子体峰之间的空间重叠并匀化了等离子体串的密度,最终使得丝状线迹的连续性和均匀性得到增强。基于这种均匀而精确的能量传播模式,验证了其用于激光剥离工艺的可行性。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BIAN Jing, ZHOU L, WAN Xiao-dong, et al. Laser transfer, printing, and assembly techniques for flexible electronics [J]. Advanced Electronic Materials, 2019, 5(7): 1800900. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/aelm.201800900.
WASISTO H S, PRADES J D, GÜLINK J, et al. Beyond solid-state lighting: Miniaturization, hybrid integration, and applications of GaN nano- and micro-LEDs [J]. Applied Physics Reviews, 2019, 6(4): 041315. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5096322.
PARK K I, SON J H, HWANG G T, et al. Highly-efficient, flexible piezoelectric PZT thin film nanogenerator on plastic substrates [J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(16): 2514–2520. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201305659.
SUN Wei-gao, JI Ling-fei, LIN Zhen-yuan, et al. Low-energy UV ultrafast laser controlled lift-off for high-quality flexible GaN-based device [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(8): 2111920. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202111920.
HORNG R H, CHIANG C C, HSIAO H Y, et al. Improved thermal management of GaN/sapphire light-emitting diodes embedded in reflective heat spreaders [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93(11): 111907. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2983740.
KIM Y, PARK S, KIM B K, et al. Laser lift-off of polyimide thin-film from glass carrier using DPSS laser pulses of top-hat square profiles [J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021, 142: 107245. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107245.
SERRA P, PIQUÉ A. Laser-induced forward transfer: Fundamentals and applications [J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2019, 4(1): 1800099. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.201800099.
BIAN J, CHEN F, YANG B, et al. Laser-induced interfacial spallation for controllable and versatile delamination of flexible electronics [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 48(12): 54230–54240. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c18951.
HUNEUS F, LINGEL C, ZELLER T, et al. Compact line focus system for laser-based debonding of flexible electronic components [C]//SPIE LASE. Proc SPIE 10906, Laser-Based Micro- and Nanoprocessing XIII. San Francisco, California, USA. 2019, 10906: 42–48. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2513763.
JIA Yue-chen, WANG Shi-xiang, CHEN Feng. Femtosecond laser direct writing of flexibly configured waveguide geometries in optical crystals: Fabrication and application [J]. Opto-Electronic Advances, 2020, 3(10): 190042. DOI: https://doi.org/10.29026/oea.2020.190042.
COUAIRON A, MYSYROWICZ A. Femtosecond filamentation in transparent media [J]. Physics Reports, 2007, 441(2–4): 47–189. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2006.12.005.
AMINA, JI Ling-fei, YAN Tian-yang, et al. Ionization behavior and dynamics of picosecond laser filamentation in sapphire [J]. Opto-Electronic Advances, 2019, 2(6): 19000301–19000307. DOI: https://doi.org/10.29026/oea.2019.190003.
BERGÉ L, SKUPIN S, NUTER R, et al. Ultrashort filaments of light in weakly ionized, optically transparent media [J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2007, 70(10): 1633–1713. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/70/10/r03.
YAN Tian-yang, JI Ling-fei, SUN Wei-gao. Characteristics and formation mechanism of filamentary plasma string induced by single picosecond laser pulse in sapphire [J]. Applied Physics A, 2021, 128(1): 1–8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05147-8.
LIU Jiang-wei, ZENG Ping-wang, RAO Zheng-hua, et al. Transport phenomena and keyhole evolution process in laser welding of stainless steel [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(8): 2088–2099. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4156-x.
FINNEY L A, LIN J, SKRODZKI P J, et al. Filament-induced breakdown spectroscopy signal enhancement using optical wavefront control [J]. Optics Communications, 2021, 490: 126902. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2021.126902.
MAYERHOFER R. Ultrashort-pulsed laser material processing with high repetition rate burst pulses [C]//SPIE LASE. Proc SPIE 10091, Laser Applications in Microelectronic and Optoelectronic Manufacturing (LAMOM) XXII. San Francisco, California, USA. 2017, 10091: 192–201. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2255184.
LI Jian-zhao, ERTORER E, HERMAN P R. Ultrafast laser burst-train filamentation for non-contact scribing of optical glasses [J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(18): 25078–25090. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.27.025078.
BRODEUR A, CHIN S L. Ultrafast white-light continuum generation and self-focusing in transparent condensed media [J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 1999, 16(4): 637. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1364/josab.16.000637.
HOUARD A, JUKNA V, POINT G, et al. Study of filamentation with a high power high repetition rate ps laser at 1.03 urn [J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(7): 7437–7448. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.24.007437.
SKUPIN S, NUTER R, BERGÉ L. Optical femtosecond filaments in condensed media [J]. Physical Review A, 2006, 74(4): 043813. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/physreva.74.043813.
FEIT M D, FLECK J A. Effect of refraction on spot-size dependence of laser-induced breakdown [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1974, 24(4): 169–172. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1655139.
COLLINO F, JOLY P, MILLOT F. Fictitious domain method for unsteady problems [J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1997, 138(2): 907–938. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jcph.1997.5849.
LEE K T, LEE Y C, TU Sheng-han, et al. Mechanism underlying damage induced in gallium nitride epilayer during laser lift-off process [J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 47(2): 930–932. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1143/jjap.47.930.
Funding
Project(51975017) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(KZ202110005012) supported by the Scientific Research Project of Beijing Educational Committee, China; Project(2018YFB1107500) supported by the National Key R&D Program of China
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contributors
JI Ling-fei developed the overarching research goals and reviewed the writing of the final manuscript. SUN Wei-gao conducted the literature review and wrote the manuscript. YAN Tian-yang validated the proposed method with practical experiments and edited the manuscript. WANG Yu-heng provided numerical simulations to examine and edited the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
SUN Wei-gao, YAN Tian-yang, WANG Yu-heng, and JI Ling-fei declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Wg., Yan, Ty., Wang, Yh. et al. Spatiotemporal evolution of high-aspect-ratio filamentary trace in sapphire of picosecond pulse burst-mode for laser lift-off. J. Cent. South Univ. 29, 3304–3311 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-5141-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-5141-3