Abstract
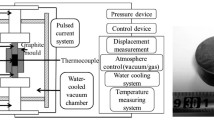
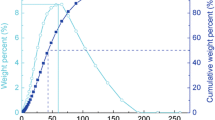
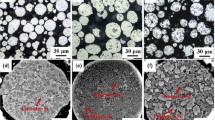
Hypereutectic Al-40 wt.% Si alloys were fabricated by the combination of gas atomization and spark plasma sintering (SPS) technology. The effects of holding time (15–60 min) on phase composition, microstructure, density, mechanical properties of Al-Si alloys were investigated by XRD, SEM, a hydrostatic balance, an automatic micro hardness tester and a universal tensile testing machine. The results showed that homogenous distribution of ultrafine primary Si and high density of alloys can be obtained at holding time of 30 min. Compared with primary Si (3.7 µm) fabricated by gas atomization, the average size increased from 5.17 to 7.72 µm with the increase of holding time during SPS process. Overall, the relative density, maximum tensile strength and Vickers hardness of 94.9%, 205 MPa and HV0.2 196.86 were achieved at holding time of 30 min, respectively. In addition, all the diffraction peaks were corresponded to α-Al or β-Si and no other phase can be detected. Finally, the densification process of SPS was also discussed.
摘要
本文采用气体雾化和放电等离子烧结相结合的工艺制备过共晶Al-40 wt.%Si合金. 采用XRD、 SEM、 静水压天平、 显微硬度计和万能拉伸试验机研究保温时间对Al-Si合金相组成、 显微组织、 致密度和力学性能的影响. 结果表明, 保温时间30 min时可获得均匀分布在铝基体上的超细初生硅和高密度的合金组织; 与气雾化制备的3.7 μm的初生硅相比, 随着保温时间的延长, 初生硅的平均粒径由5.17 μm增大到7.72 μm; 在保温时间为30 min时, 相对密度, 抗拉强度和维氏硬度分别达到最大值94.9%, 205 MPa和HV0.2 196.86; 此外, 所有的衍射峰都属于α-Al或β-Si, 检测到没有其他相; 另外, 对放电等离子烧结致密化过程进行了讨论.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SARASWAT E, MAHARANA H S, NARAYANA MURTY S V S, et al. Fabrication of Al-Si controlled expansion alloys by unique combination of pressureless sintering and hot forging [J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2020, 31(7): 2820–2832. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.05.007.
LI Jin-pin. Microstructure and mechanical properties of hypereutectic Al-23Si alloy fabricated by powder metallurgy [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2014: 1–4. (in Chinese)
WANG Jian-hua, YANG Wei, TU Hao, et al. Effect of complex modification of Al-5Ti and Al-3P on hypereutectic Al-18Si alloys [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(10): 2651–2660. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4202-8.
HAQUE A, SHEKHAR S, NARAYANA MURTY S V S, et al. Fabrication of controlled expansion Al-Si composites by pressureless and spark plasma sintering [J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2018, 29(12): 3427–3439. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2018.09.024.
CHIEN C W, LEE S L, LIN J C, et al. Effects of sip size and volume fraction on properties of Al/Sip composites [J]. Materials Letters, 2002, 52(4, 5): 334–341. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(01)00418-9.
CHEN Ye-gao, ZHONG Yi, YIN Jiang-cheng, et al. Microstructure and properties of 7075Al alloy fabricated by directly combined of spray forming and continuous extrusion forming under different atomization gas pressures [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2016, 29(9): 804–812. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-016-0454-6.
YANG Wen-tao, HE Peng-fei, LIU Ming, et al. A review on microstructure and tribological behavior of fast solidfied hypereutectic Al-Si alloys [J]. Materials Reports, 2021 (11): 1–26. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11896/cldb.19120187.
LV Pin-hui, WANG Xiao-feng, DONG Cui-ge, et al. Preparation and characterization of different surface modified SiCp reinforced Al-matrix composites [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(9): 2567–2577. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4482-z.
SI Chao-run, TANG Xing-ling, ZHANG Xian-jie, et al. Characteristics of 7055Al alloy powders manufactured by gas-solid two-phase atomization: A comparison with gas atomization process [J]. Materials & Design, 2017, 118: 66–74. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.01.028.
CIFTCI N, ELLENDT N, COULTHARD G, et al. Novel cooling rate correlations in molten metal gas atomization [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2019, 50(2): 666–677. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-019-01508-0.
LI Yun-zhe, LIU Shi-feng, ZHANG Guang-xi, et al. Effects of sintering temperature and holding time on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-1Al-8V-5Fe prepared by spark plasma sintering [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(4): 1183–1194. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4689-7.
ZHANG Zhao-hui, LIU Zhen-feng, LU Ji-fang, et al. The sintering mechanism in spark plasma sintering-Proof of the occurrence of spark discharge [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2014, 81: 56–59. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2014.03.011.
RUDINSKY S, AGUIRRE J M, SWEET G, et al. Spark plasma sintering of an Al-based powder blend [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 621: 18–27. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.10.056.
ZHANG Xiao dong, CHI Y, ZHAO Zhan-kui. Genetic characteristics and mechanical properties of high-siliconaluminum alloy by rapid solidification and spark plasma sintering [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2016, 850: 835–840. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net%2FMSF.850.835.
SARAVANAN T T, KAMARAJ M, SHARMA S C, et al. On characteristic eutectic free microstructural evolution in hypereutectic Al-Si processed through spark plasma sintering [J]. Materials Letters, 2020, 275: 128150. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128150.
CAI Zhi-yong, WANG Ri-chu, PENG Chao-qun, et al. Morphology and microstructure of gas-atomized hypereutectic Al-Si alloy powders [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2016, 45(4): 1018–1023.
ZHAO Heng-xian, CHEN Run-hui. Progress in refinement modification of hypereutectic Al-Si alloys [J]. Light Metals, 1992 (2): 61–64+60. DOI: https://doi.org/10.13662/j.cnki.qjs.1992.02.014.
CAI Zhi-yong, WANG Ri-chu, ZHANG Chun, et al. Microstructure and thermal stability of rapidly solidified hypereutectic Al-Si alloys [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(3): 618–625. DOI: https://doi.org/10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2015.03.010. (in Chinese)
MURUGASAMI R, VIVEKANANDHAN P, KUMARAN S, et al. Densification and alloying of ball milled silicongermanium powder mixture during spark plasma sintering [J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2017, 28(2): 506–513. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2016.11.010.
HU Zheng-yang, ZHANG Zhao-hui, CHENG Xing-wang, et al. A review of multi-physical fields induced phenomena and effects in spark plasma sintering: Fundamentals and applications [J]. Materials & Design, 2020, 191: 108662. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108662.
MARDER R, ESTOURNÈS C, CHEVALLIER G, et al. Plasma in spark plasma sintering of ceramic particle compacts [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2014, 82: 57–60. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2014.03.023.
SONG Xiao-yan, LIU Xue-mei, ZHANG Jiu-xing. The microstructure evolution and mechanism of conductive powder during SPS process [J]. Science in China Ser. E: Engineering and Materials Science, 2005(5): 459–469. DOI: https://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:JEXK.0.2005-05-001.
OGUNBIYI O F, JAMIRU T, SADIKU E R, et al. Spark plasma sintering of nickel and nickel based alloys: A Review [J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2019, 35: 1324–1329. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2019.05.022.
JIA Jian-bo, YANG Yue, SUN Wei, et al. Preparation and densification mechanism of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy prepared by spark plasma sintering [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2019(7): 1399–1407. (in Chinese)
FENG H K, YU S R, LI Y L, et al. Microstructure and properties of Sip/Al-Si surface composites prepared by ultrasonic method [J]. Materials & Design, 2009, 30(7): 2420–2424. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2008.10.016.
YU Hui-hui, XIN Yun-chang, WANG Mao-yin, et al. Hall-Petch relationship in Mg alloys: A review [J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2018, 34(2): 248–256. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2017.07.022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The overarching research goals were finished by AN Yu-jiao, NIU Li-bin, GAO Chong, HU Yu-yang, LI Yu-hua, LIU Jin-song. AN Yu-jiao provided the concept and edited the draft of the manuscript. GAO Chong and HU Yu-yang conducted the experiment and analyzed the measured data. LI Yu-hua organized the full text references. The initial draft of the manuscript was written by NIU Li-bin and LIU Jin-song. All authors replied to the reviewers’ comments and revised the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(18JS060) supported by the Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Nano-materials and Technology, China; Project (2018JQ5087) supported by Natural Science Basic Research Plan of Shaanxi Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, Yj., Niu, Lb., Gao, C. et al. Effect of holding time on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-40 wt.%Si alloys fabricated by combination of gas atomization and spark plasma sintering. J. Cent. South Univ. 29, 860–870 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-4975-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-4975-z