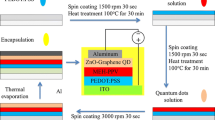
Abstract
Compared to conventional quantum dot light-emitting diodes, tandem quantum dot light-emitting diodes (TQLEDs) possess higher device efficiency and more applications in the field of flat panel display and solid-state lighting in the future. The TQLED is a multilayer structure device which connects two or more light-emitting units by using an interconnection layer (ICL), which plays an extremely important role in the TQLED. Therefore, realizing an effective ICL is the key to obtain high-efficiency TQLEDs. In this work, the p-type materials polys (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene), poly (styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT: PSS) and the n-type material zinc magnesium oxide (ZnMgO), were used, and an effective hybrid ICL, the PEDOT: PSS-GO/ZnMgO, was obtained by doping graphene oxide (GO) into PEDOT:PSS. The effect of GO additive on the ICL was systematically investigated. It exhibits that the GO additive brought the fine charge carrier generation and injection capacity simultaneously. Thus, the all solution-processed red TQLEDs were prepared and characterized for the first time. The maximum luminance of 40877 cd/m2 and the highest current efficiency of 19.6 cd/A were achieved, respectively, showing a 21% growth and a 51% increase when compared with those of the reference device without GO. The encouraging results suggest that our investigation paves the way for efficient all solution-processed TQLEDs.
摘要
串联量子点发光二极管(TQLEDs)相较于传统QLEDs而言, 在相同的发光亮度下具有更高的器 件效率, 因而, 在未来显示和照明领域中具有极高的应用价值。TQLEDs是利用连接层(ICL)将两个或 多个发光单元连接起来的多层结构器件, 其中的连接层起着极为重要的作用。因此, 实现有效的连接 层是获得高效率TQLEDs的关键。为获得高效率溶液加工TQLEDs, 本文采用可溶液加工的P 型材料 聚(3, 4-亚乙基二氧噻吩):聚苯乙烯磺酸盐(PEDOT:PSS)和n 型材料氧化锌镁(ZnMgO), 并在 PEDOT:PSS 中掺杂无机氧化物-氧化石墨烯(GO) (体积比为5:1), 形成PEDOT:PSS-GO/ZnMgO 掺 杂ICL 以增强其在下层有机薄膜上的浸润性, 增加了连接层的有效沉积, 提高了连接层的载流子注入 和产生。利用该ICL 制备了溶液加工倒置红光TQLEDs: ITO/ZnO/QDs/PVK/PEDOT: PSS-GO/ZnMgO/QDs/PVK/PEDOT:PSS/Al, 其最大发光强度为40877 cd/m2, 最大电流效率高达19.6 cd/A, 相 比于未掺杂GO的参考器件(最大亮度为33868 cd/m2, 最大电流效率为13 cd/A), 其发光强度增加了 21%, 最大电流效率增加了51%。结果表明, 无机氧化物掺杂是一种可实现有效ICL 的简单且有效的 方法, 能有效提升溶液加工TQLEDs的性能, 进而推动QLEDs的实际生产应用。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
JI Wen-yu, SHEN Huai-bin, ZHANG Han, KANG Zhi-hui, ZHANG Han-zhuang. Over 800% efficiency enhancement of all-inorganic quantum-dot light emitting diodes with an ultrathinalumina passivating layer [J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10: 11103–11109. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR01460D.
CHEN Li-xiang, LEE M H, WANG Yi-wen, SYED A A, ZHU Fu-rong. Interface dipole for remarkable efficiency enhancement in all-solution-processable transparent inverted quantum dot light-emitting diodes [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, 6: 2596. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TC00303C.
DAI Xing-liang, ZHANG Zhen-xing, JIN Yi-zheng, NIU Yuan, CAO Xiao-yong, CHEN Li-wei, WANG Jian-pu, PENG Xiao-gang. Solution-processed, high-performance light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots [J]. Nature, 2014, 515: 96–99. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13829.
MASHFORD B S, STEVENSON M, POPVIC Z, HAMILTON C, ZHOU Zhao-qun, BREEN C, STECKEL J, BULOVIC V, BAWENDI M, COE-SULLIVAN S, KAZLAS T P. High-efficiency quantum-dot light-emitting devices with enhanced charge injection [J]. Nature Photonics, 2013, 7: 407–412. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.70.
BAE W K, LIM J, LEE D, PARK M J, LEE H, KWAK J, CHAR K, LEE C, LEE S. R/G/B/Natural white light thin colloidal quantum dot-based light-emitting devices [J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(37): 6387–6393. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201400139.
YANG Yi-xing, ZHENG Ying, CAO W, TITOV A, HYVONEN J, MANDERS R J, XUE Jian-geng, HOLLOWAY H P, QIAN Lei. High-efficiency light-emitting devices based on quantum dots with tailored nanostructures [J]. Nature Photonics, 2015, 9: 259–266. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/NPHOTON.2015.36.
RAMASAMY P, KIM N, KANG Y S, RAMIRES O, LEE J S. Tunable, bright, and narrow-band luminescence from colloidal indium phosphide quantum dots [J]. Chem Mater, 2017, 29(16): 6893–6899. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b02204.
WANG Fu-zhi, SUN Wen-da, LIU Pai, WANG Zhi-bin, ZHANG Jin, WEI Jiang-liu, LI Yang, HAYAT T, ALSAEDI A, TAN Zhao-ao. Achieving balanced charge injection of blue quantum dot light-emitting diodes through transport layer doping strategies [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2019, 10(5): 960–965. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b00189.
ZHAO Yong-shuang, CHEN Li-xiang, WU Jia-lin, TAN Xing-wen, XIONG Zhu-hong, LEI Yan-lian. Composite hole transport layer consisting of high-mobility polymer and small molecule with deep-lying HOMO level for efficient quantum dot light-emitting diodes [J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2020, 41(1): 80–83. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2019.2953088.
LIU Yu, JIANG Cong-biao, WANG Juan-hong, MU Lan, HE Zhi-wei, ZHONG Zhen-ji, CUN Yang-ke, MAI Chao-huang, WANG Jian, PENG Jun-biao, CAO Yong. Highly efficient all-solution processed inverted quantum dots based light-emitting diodes [J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(2): 1564–1570. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b08129.
JI Wen-yu, LV Ying, JING Peng-tao, ZHANG Han, WANG Jia, ZHANG Han-zhuang, ZHAO Jia-long. Highly efficient and low turn-on voltage quantum dot light-emitting diodes by using a stepwise hole-transport layer [J]. ACS Appled Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7: 15955–15960. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b04050.
ZHANG Heng, SUN Xiao-wei, CHEN Shu-ming. Over 100 cd-A−1 efficient quantum dot light-emitting diodes with inverted tandem structure [J]. Advnceo Functonal Materials, 2017, 27: 1700610. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201700610.
JIANG Cong-biao, ZOU Jian-hua, LIU Yu, SONG Chen, HE Zhi-wei, ZHONG Zhen-ji, WANG Jian, YIP H L, PENG Jun-biao, CAO Yong. Fully solution-processed tandem white quantum-dot light-emitting diode with an external quantum efficiency exceeding 25% [J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(6): 6040–6049. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b02289.
ZHENG Heng, FENG Yuan-xiang, CHEN Shu-ming. Improved efficiency and enhanced color quality of light-emitting diodes with quantum dot and organic hybrid tandem structure [J]. ACS Appled Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(40): 26982–26988. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b07303.
ZHANG Heng, CHEN Shu-ming, SUN Xiao-wei. Efficient red/green/blue tandem quantum-dot light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 21% [J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(1): 697–704. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b07867.
SHEN Huai-bin, GAO Qiang, ZHANG Yan-bin, LIN Yue, LIN Qing-li, LI Zhao-han, CHEN Ling, ZENG Zai-ping, LI Xiao-guang, JIA Yu, WANG Shu-jie, DU Zu-liang, LI Lin-song, ZHANG Zheng-yu. Visible quantum dot light-emitting diodes with simultaneous high brightness and efficiency [J]. Nature Photonics, 2019, 13: 192–197. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-019-0364-z.
CHIBA T, PU Y J, KIDO J. Solution-processed white phosphorescent tandem organic light-emitting devices [J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(32): 4681–4687. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201501866.
KIM J H, HAN C Y, LEE K H, AN K S, SONG W, KIM J, OH M S, DO Y R, YANG H. Performance improvement of quantum dot-light-emitting diodes enabled by an alloyed ZnMgO nanoparticle electron transport layer [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2015, 27(1): 197–204. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cm503756q.
SCHNIEPP H C, LI J L, MCALLISTER M J, SAI H, HERRERA-ALONSO M, ADAMSON D H, PRUD’HOMME R, CAR R, SAVILLE D A, AKSAY L A. Functionalized single graphene sheets derived from splitting graphite oxide [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2006, 110(17): 8535–8539. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp060936f.
CHEN Shan, YU Xiao-wen, ZHANG Miao, CAO Jia-min, LI Ying-ru, DING Li-ming, SHI Ge. A graphene oxide/oxygen deficient molybdenum oxide nanosheet bilayer as a hole transport layer for efficient polymer solar cells [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3: 18380–18383. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta04823k.
BAE S, LEE J U, PARK H, JUN E H, JUN J W, JO W H. Enhanced performance of polymer solar cells with PSSA-g-PANI/Graphene oxide composite as hole transport layer [J]. Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells, 2014, 130: 599–604. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2014.08.006.
GAO Yang, YIP H L, HAU S K, O’MALLEY K M. Anode modification of inverted polymer solar cells using graphene oxide [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 97(20): 203306. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3507388.
ZHOU Ying, LIANG Chun-yan, YU Jin-gang, JIANG Xin-yu. Adsorption properties of a novel 3D graphene/MgO composite for heavy metal ions [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(4): 813–823. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4051-5.
YUAN Xu, YUE Wen-bo, ZHANG Jin. Electrochemically exfoliated graphene as high-performance catalyst support to promote electrocatalytic oxidation of methanol on Pt catalysts [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(9): 2515–2529. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4477-9.
SONG D H, SONG S H, SHEN T Z, LEE J S, PARK W H, KING S S, SONG J K. Quantum dot light-emitting diodes using a graphene oxide/PEDOT:PSS bilayer as hole injection layer [J]. Rsc Advances, 2017, 7(69): 43396–43402. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA07948F.
XIANG Quan-jun, YU jia-guo. JARONIEC M Graphene-based semiconductor photocatalysts [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(2): 782–796. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cs15172j.
PARK Y, CHOI K S, KIM S Y. Graphene oxide/PEDOT:PSS and reduced graphene oxide/PEDOT: PSS hole extraction layers in organic photovoltaic cells [J]. Physica Status Solidi, 2012, 209(7): 1363–1368. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201228040.
WANG Yi-shan, WANG Hao-wei, XU Jun-feng, HE Bo, LI Wei-le, WANG Qi, YANG Sheng-yi, ZOU Bing-suo. PEDOT: PSS modification by blending graphene oxide to improve the efficiency of organic solar cells [J]. Polymer Composites, 2018, 39(9): 3066–3072. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.24311.
WU Xin-kai, LIAN Lu-poh, YANG Shuai, HE Gu-feng. Highly conductive PEDOT: PSS and graphene oxide hybrid film with the dipping treatment by hydroiodic acid for organic light emitting diodes [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2016, 4(36): 8528–8534. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c6tc02424f.
CHEN Jing, PAN Jiang-yong, HUANG Qian-qian, XU Feng, NATHAN A. Graphene oxide/PEDOT: PSS as injection layer for quantum dot light emitting diode [J]. Physica Status Solidi (A) Applications and Materials, 2015, 212(12): 2856–2861. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201532430.
WU Jia-lin, CHEN Li-xiang, TAN Xing-wen, ZHANG Qiao-ming, LEI Yan-lian. Large performance enhancement in all-solution-processed, full-color, inverted quantum dot light-emitting diodes by using graphene oxide-doped hole injection layer [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020, 124: 11617–11624. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c02277.
LEI Yan-lian, ZHAO Yong-shuang, ZHANG Qiao-ming, XIONG Zu-hong, CHEN Li-xiang. Highly efficient and bright red quantum dot light-emitting diodes with balanced charge injection [J]. Organic Electronics, 2020, 81: 105683. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2020.105683.
Funding
Project(11904298) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0586) supported by Chongqing Natural Science Foundation, China; Project(S202010635001) supported by Chongqing Municipal Training Program of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates, China
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Hh., Su, H., Chen, Lx. et al. GO-induced effective interconnection layer for all solution-processed tandem quantum dot light-emitting diodes. J. Cent. South Univ. 28, 3737–3746 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4850-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4850-3
Key words
- tandem quantum dot light-emitting diodes
- all solution-processed
- interconnection layer
- graphene oxide
- current efficiency