Abstract
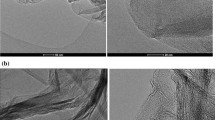
A novel three-dimension (3D) graphene/MgO composite was synthesized through self-assembly and embedding MgO nanoparticle in reduced graphene in situ. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), powder X-raydiffraction (XRD) and X-rayphotoelectron spectroscopy(XPS) were employed to characterize the prepared 3D graphene/MgO composite. The adsorption performance of some metal ions on 3D graphene/MgO was investigated. The results showed that the adsorption capacity was greater than 3D graphene and the maximum adsorption capacity at 25 °C was found to be 358.96 mg/g, 388.4 mg/g and 169.8 mg/g for Pb2+, Cd2+ and Cu2+, respectively. The adsorption kinetic conformed to the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and the adsorption isotherm was well described by Langmuir model. The thermodynamic constants revealed that the sorption process was endothermic and spontaneous in nature. Based on the results of the removal of heavy metal ions from metal smelting wastewater, it can be concluded that the prepared 3D graphene/MgO composite is an effective and potential adsorbent.
摘要
通过水热法在石墨烯自组装和原位还原的过程中嵌入MgO 制备了一种新的三维石墨烯/MgO 复 合物。采用 FT-IR, TGA, SEM, TEM, XRD 和 XPS 等测试手段对制备的材料进行了表征。研究了 三维石墨烯/MgO 复合物对一些金属离子的吸附性能。研究结果表明复合物材料的吸附性能优于三 维石墨烯, 25°C 时对 Pb2+, Cd2+, Cu2+ 的最大吸附量分别为 358.96 mg/g, 388.4 mg/g 和 169.8 mg/g, 吸附过程符合准二级动力学和 Langmuir 等温吸附模型。热力学参数表明吸附过程是一个吸热自发的 过程。将三维石墨烯/MgO 复合物用于冶炼厂废水样中重金属离子的去除, 结果显示材料具有很好的 去除效果。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WANG Jun-ping, MA Xiao-xing, FANG Guo-zhen, PAN Ming-fei, YE Xiao-ke, WANG Shuo. Preparation of iminodiacetic acid functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and its application as sorbent for separation and preconcentration of heavy metal ions [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(2): 1985–1992. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.087.
BARAKAT M. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater [J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2011, 4(4): 361–377. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.07.019.
CHAN B, DUDENEY A. Reverse osmosis removal of arsenic residues from bioleaching of refractory gold concentrates [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2008, 21(4): 272–278. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2007.10.003.
YUAN Yang, ZHANG Guang-hui, LI Yang, ZHANG Guo-liang, ZHANG Feng-bao, FAN Xiao-bin. Poly (amidoamine) modified graphene oxide as an efficient adsorbent for heavy metal ions [J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2013, 4(6): 2164–2167. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C3PY21128B.
ATALAYA J, ISACSSON A, KINARET J M. Continuum elastic modeling of graphene resonators [J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 8(12): 4196–4200. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/nl801733d.
KUMAR A S K, JIANGS J. Chitosan-functionalized graphene oxide: A novel adsorbent an efficient adsorption of arsenic from aqueous solution [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2016, 4(2): 1698–1713. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.02.035.
KU Y, JUNG I L. Photocatalytic reduction of Cr (VI) in aqueous solutions by UV irradiation with the presence of titanium dioxide [J]. Water Research, 2001, 35(1): 135–142. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00098-1.
GAO Ting-ting, YU Jin-gang, ZHOU Ying, JIANG Xin-yu. The synthesis of graphene oxide functionalized with dithiocarbamate group and its prominent performance on adsorption of lead ions [J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2017, 71: 426–432. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.11.033.
WANG Zhian, ZHANG Xiumei, WU Xiongwei, YU Jin-gang, JIANG Xin-yu, WU Zhi-liang, HAO Xin. Soluble starch functionalized graphene oxide as an efficient adsorbent for aqueous removal of Cd(II): The adsorption thermodynamic, kinetics and isotherms [J]. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2017, 82: 440–449. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4313-3.
ZHOU Ying, YU Jin-gang, JIANG Xin-yu. Removing lead ions from aqueous solutions by the thiosemicarbazide grafted multi-walled carbon nanotubes [J]. Water Science and Technology, 2017, 76(2): 302–310. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.198.
FU Feng-lian, WANG Qi. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2011, 92(3): 407–418. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.011.
CHEN Na, TENG Jie, JIAO Fei-peng, JIANG Xin-yu, HAO Xin, YU Jin-gang. Preparation of triethanolamine functionalized carbon nanotube for aqueous removal of Pb(II) [J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2017, 71: 191–200. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.20551.
RAY P Z, SHIPLEY H J. Inorganic nano-adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals and arsenic: A review [J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(38): 29885–29907. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA02714D.
SHEELA T, NAYAKA Y A, VISWANATHA R, BASAVANNA S, VENKATESHA T. Kinetics and thermodynamics studies on the adsorption of Zn (II), Cd (II) and Hg (II) from aqueous solution using zinc oxide nanoparticles [J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 217: 163–170. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2011.10.023.
FUTALAN C M, KAN C C, DALIDA M L, HSIEN K J, PASCUA C, WAN Meng-Wei. Comparative and competitive adsorption of copper, lead, and nickel using chitosan immobilized on bentonite [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2011, 83(2): 528–536. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.08.013.
YUE Bao-yu, YU Lin-yan, JIAO Fei-peng, JIANG Xin-yu, YU Jin-gang. The fabrication of pentaerythritol pillared graphene oxide composite and its adsorption performance towards metal ions from aqueous solutions [J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2018, 102: 124–133. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2018.21805.
ZHOU Fang, YU Jin-gang, JIANG Xin-yu. Green synthesis of 3D porous graphene/lignin composites with improved adsorption capacity for heavy metal ions in aqueous solution [J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2018, 103: 175–181. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2018.21899.
ATALAYA J, ISACSSON A, KINARET J M. Continuum elastic modeling of graphene resonators [J]. Nano Letters, 2008, 8(12): 4196–4200. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/nl801733d.
VARSHNEY V, PATNAIK S S, ROY A K, FROUDAKIS G, FARMER B L. Modeling of thermal transport in pillared-graphene architectures [J]. ACS Nano, 2010, 4(2): 1153–1161. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/nn901341r.
HUANG Ke-Jing, YU Sheng, LI Jing, WU Zhi-Wei, WEI Cai-Yun. Extraction of neurotransmitters from rat brain using graphene as a solid-phase sorbent, and their fluorescent detection by HPLC [J]. Microchimica Acta, 2012, 176(3): 327–335. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0719-8.
HAN Qiang, WANG Zong-hua, XIA Jian-fei, ZHANG Xiao-qiong, WANG Hong-wu, DING Ming-yu. Application of graphene for the SPE clean-up of organophosphorus pesticides residues from apple juices [J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2014, 37(1, 2): 99–105. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201301005.
ZHOU Fang, YU Jin-gang, JIANG Xin-yu. 3D porous graphene synthesised using different hydrothermal treatment times for the removal of lead ions from an aqueous solution [J]. Micro & Nano Letters, 2017, 12(5): 308–311. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1049/mnl.2016.0618.
KABIRI S, TRAN D N, ALTALHI T, LOSIC D. Outstanding adsorption performance of graphene-carbon nanotube aerogels for continuous oil removal [J]. Carbon, 2014, 80: 523–533. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.08.092.
ZHOU Fang, FENG Xue-zhen, YU Jin-gang, JIANG Xin-yu. High performance of 3D porous graphene/lignin/sodium alginate composite for adsorption of Cd(II) and Pb(II) [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25: 15651–15661. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1733-8.
GAO Chao, YU Xin-yao, XU Ren-xia, LIU Jin-huai, HUANG Xing-jiu. AlOOH-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites: One-pot hydrothermal synthesis and their enhanced electrochemical activity for heavy metal ions [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2012, 4(9): 4672–4682. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/am3010434.
CHEN Wu-feng, LI Si-rong, CHEN Chun-hua, YAN Li-feng. Self-assembly and embedding of nanoparticles by in situ reduced graphene for preparation of a 3d graphene/nanoparticle aerogel [J]. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(47): 5679–5683. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201102838.
ZHANG Zhe-ye, XIAO Fei, GUO Yun-long, WANG Shuai, LIU Yun-qi. One-pot self-assembled three-dimensional TiO2-graphene hydrogel with improved adsorption capacities and photocatalytic and electrochemical activities [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(6): 2227–2233. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/am303299r.
MENG Jing-ke, CAO Yuan, SUO Yang, LIU Yu-shan, ZHANG Jian-min, ZHENG Xiu-cheng. Facile fabrication of 3D SiO2@graphene aerogel composites as anode material for lithium ion batteries [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 176: 1001–1009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.07.141.
LIU Jun-tao, GE Xiao, YE Xin-xin, WANG Guo-zhong, ZHANG Hai-min, ZHOU Hong-jian, ZHANG Yun-xia, ZHAO Hui-ju. 3D graphene/δ5-MnO2 aerogels for highly efficient and reversible removal of heavy metal ions [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(5): 1970–1979. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA08106H.
GAO Cui-ling, ZHANG Wen-li, LI Hong-bian, LANG Lei-ming, XU Zheng. Controllable fabrication of mesoporous MgO with various morphologies and their absorption performance for toxic pollutants in water [J]. Crystal Growth and Design, 2008, 8(10): 3785–3790. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cg8004147.
LERF A, HE He-yong, FORSTER M, KLINOWSKI J. Structure of graphite oxide revisited [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 1998, 102(23): 4477–4482. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9731821.
VUKOVIĆ G D, MARINKOVIĆ A D, ŠKAPIN S D, RISTIĆ M Ɖ, ALEKSIĆ R, PERIĆ-GRUJIĆ A A, USKOKOVIĆ P S. Removal of lead from water by amino modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 173(3): 855–865. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.08.036.
ZHAO Gui-xia, REN Xue-mei, GAO Xing, TAN Xiao-li, LI Jia-xing, CHEN Chang-lun, HUANG Yu-ying, WANG Xiang-ke. Removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions on few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets [J]. Dalton Transactions, 2011, 40(41): 10945–10952. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C1DT11005E.
PENG Wei-jun, LI Hong-qiang, LIU Yan-yan, SONG Shao-xian. Comparison of Pb(II) adsorption onto graphene oxide prepared from natural graphites: Diagramming the Pb(II) adsorption sites [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 364: 620–627. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.12.208.
CAO Chang-yan, QU Jin, WEI Fang, LIU Hua, SONG Wei-guo. Superb adsorption capacity and mechanism of flowerlike magnesium oxide nanostructures for lead and cadmium ions [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2012, 4(8): 4283–4287. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/am300972z.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(21571191, 51674292) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2016JJ1023) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China; Project(2018TP1003) supported by the Key Laboratory of Hunan Province for Water Environment and Agriculture Product Safety, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Liang, Cy., Yu, Jg. et al. Adsorption properties of a novel 3D graphene/MgO composite for heavy metal ions. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 813–823 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4051-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4051-5