Abstract
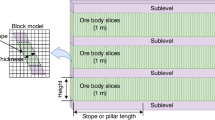
Underground mines require complex construction activities including the shaft, levels, raises, winzes and ore passes. In an underground mine based on stoping method, orebody part(s) maximizing profit should be determined. This process is called stope layout optimization (SLO) and implemented under site-specific geotechnical, operational and economic constraints. For practical purpose, the design obtained by SLO shows consecutive stopes in one path, which assists in defining the mining direction of these stopes. However, this direction may not accommodate the spatial distribution of the ore grade: if the orebody orientation and mining direction differ, the value of the mining operation may decrease. This paper proposes an approach whereby paths in the SLO are defined as decision variables to avoid the cost of mining in the wrong direction. Furthermore, in the genetic-based formulation, which accounts for orebody uncertainty, a robust cluster average design process is proposed to improve SLO’s performance regarding metal content. A case study in narrow gold vein deposit shows that the profit of an underground mining operation could be underestimated by 25%–48% if the algorithm ignores stope layout orientation.
摘要
地下矿山需要复杂的基建工作, 包括竖井、中段、提升、盲井和溜井. 使用空场法开采地下矿 山时, 要确定能使利润最大化的矿体部分, 该过程称为采场布局优化(SLO), 需要在特定场地的岩土 工程、运营和经济约束下实施. 在实际应用中, 通过采场布局优化得到的设计图显示了一条路径上的 连续采场, 这有助于确定这些采场的开采方向. 但是, 该方向可能无法适应矿石品位的空间分布: 如 果矿体走向和开采方向不同, 开采作业的价值可能会降低. 本文提出了一种把采场布局优化中的路径 定义为决策变量的方法, 以避免在错误方向上开采造成损失. 此外, 在考虑矿体不确定性的遗传算法 中, 提出了一种鲁棒聚类平均设计方法, 以提高采场布局优化在金属含量方面的性能. 对薄金矿脉的 实例研究表明, 如果算法中忽略采场布局方向, 地下采矿作业的利润可能会被低估25%~48%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
STADLER H. A framework for collaborative planning and state-of-the-art [M]// Supply Chain Planning. Springer, 2009: 1–26.
ATAEE-POUR M. Optimisation of stope limits using a heuristic approach [J]. Mining Technology, 2004, 113(2): 123–128. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1179/037178404225004959.
ATAEE-POUR M. A critical survey of the existing stope layout optimization techniques [J]. Journal of Mining Science, 2005, 41(5): 447–466. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10913-006-0008-9.
SANDANAYAKE D S, TOPAL E, ASAD M W A. A heuristic approach to optimal design of an underground mine stope layout [J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 30: 595–603. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.01.060.
VILLALBA M E, KUMRAL M. Heuristic stope layout optimization accounting for variable stope dimensions and dilution management [J]. International Journal of Mining and Mineral Engineering, 2017, 8(1): 1–18. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMME.2017.10003210.
RUSSELL S, NORVIG P. Artificial intelligence: A modern approach [M]. 3rd ed. Pearson Education, Inc., 1995.
TOPAL E, SENS J. A new algorithm for stope boundary optimization [J]. Journal of Coal Science & Engineering (China), 2010, 16(2): 113–119. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12404-010-0201-y.
SANDANAYAKE D S, TOPAL E, ASAD M W A. Designing an optimal stope layout for underground mining based on a heuristic algorithm [J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2015, 25(5): 767–772. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2015.07.011.
ERDOGAN G, CIGLA M, TOPAL E, YAVUZ M. Implementation and comparison of four stope boundary optimization algorithms in an existing underground mine [J]. International Journal of Mining, Reclamation and Environment, 2017, 31(6): 389–403. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/17480930.2017.1331083.
OVANIC J, YOUNG D S. Economic optimization of stope geometry using separable programming with special branch and bound techniques [C]// MITRI H S. The 3rd Canadian Conference on Computer Applications in the Mineral Industry. Montreal, 1995: 129–135.
VOß S. Meta-heuristics: The state of the art [M]// NAREYEK A. Workshop on Local Search for Planning and Scheduling. Springer, 2000: 1–23.
MANCHUK J, DEUTSCH C V. Optimizing stope designs and sequences in underground mines [J]. SME Transactions, 2008, 324: 67–75.
ALFORD C, HALL B. Stope optimisation tools for selection of optimum cut-off grade in underground mine design [C]// Project Evaluation Conference. Melbourne, 2009: 137–144.
NIKBIN V, ATAEE-POUR M, SHAHRIAR K, POURRAHIMIAN Y. A 3D approximate hybrid algorithm for stope boundary optimization [J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2018.05.012.
GRIECO N, DIMITRAKOPOULOS R. Managing grade risk in stope design optimisation: probabilistic mathematical programming model and application in sublevel stoping [J]. Mining Technology, 2007, 116(2): 49–57. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1179/174328607X191038.
VILLALBA M E, KUMRAL M. Underground mine planning: Stope layout optimization under uncertainty using genetic algorithms [J]. International Journal of Mining, Reclamation and Environment 2019, 33(5): 353–370. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/17480930.2018.1486692.
MORIN M A. Underground hardrock mine design and planning: A system’s perspective [D]. Kingston, Ontario: Queen’s University, 2001.
GLIGORIC Z, BELJIC C, SIMEUNOVIC V. Shaft location selection at deep multiple orebody deposit by using fuzzy TOPSIS method and network optimization [J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2010, 37(2): 1408–1418. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2009.06.108.
BRAZIL M, THOMAS D A, WENG J F, RUBINSTEIN J H, LEE D H. Cost optimisation for underground mining networks [J]. Optimization and Engineering, 2005, 6(2): 241–256. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-005-6797-x.
JOURNEL A G, HUIJBREGTS C J. Mining geostatistics [M]. Academic Press, 1978.
DEUTSCH C V, JOURNEL A G. Geostatistical software library and user’s guide [M]. New York: Oxford University Press, 1998.
DIMITRAKOPOULOS R. Conditional simulation algorithms for modelling orebody uncertainty in open pit optimisation [J]. International Journal of Surface Mining, Reclamation and Environment, 1998, 12(4): 173–179. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/09208118908944041.
DEUTSCH C V. Geostatistical reservoir modeling [M]. New York: Oxford University Press, 2002.
JOURNEL A G, KYRIAKIDIS P C. Evaluation of mineral reserves: A simulation approach [M]. New York: Oxford University Press, Inc., 2004.
DIMITRAKOPOULOS R, RAMAZAN S. Stochastic integer programming for optimising long term production schedules of open pit mines: methods, application and value of stochastic solutions [J]. Mining Technology, 2008, 117(4): 155–160. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1179/174328609X417279.
DIMITRAKOPOULOS R. Stochastic optimization for strategic mine planning: A decade of developments [J]. Journal of Mining Science, 2011, 47(2): 138–150. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062739147020018.
BENNDORF J, DIMITRAKOPOULOS R. Stochastic long-term production scheduling of iron ore deposits: Integrating joint multi-element geological uncertainty [J]. Journal of Mining Science, 2013, 49(1): 68–81. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-69320-0_12.
VILLALBA M E, DIMITRAKOPOULOS R. Stochastic short-term mine production schedule accounting for fleet allocation, operational considerations and blending restrictions [J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2016, 255(3): 911–921. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2016.05.050.
CUBA M A, BOISVERT J B, DEUTSCH C V. Simulated learning model for mineable reserves evaluation in surface mining projects [J]. SME Transactions, 2013, 334: 527–534.
JORC. Australaisian code for reporting of exploration results, mineral resources and ore reserves [M]. AusIMM and AIG. 2012: 44.
MITCHELL M. An introduction to genetic algorithms [M]. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1999.
GOLDBERG D E. Genetic algorithms in search, optimization, and machine learning [M]. New York: Addison Wesley Longman, 1989.
BAWDEN J W, NANTEL J, SPROTT D. Practical rock engineering in the optimization of stope dimensions-application and cost-effectiveness [J]. CIM Bulletin, 1989, 82(926): 63–70.
WU A X, HUANG M Q, HAN B, WANG Y M, YU S F, MIAO X X. Orthogonal design and numerical simulation of room and pillar configurations in fractured stopes [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014, 21(8): 3338–3344. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2307-7.
HEIDARZADEH S, SAEIDI A, ROULEAU A. Evaluation of the effect of geometrical parameters on stope probability of failure in the open stoping method using numerical modeling [J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2018, 29(3): 399–408. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2018.05.011.
GU X W, WANG Q, CHU D Z, ZHANG B. Dynamic optimization of cutoff grade in underground metal mining [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2010, 17(3): 492–497. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-010-0512-6.
SALAMA A, NEHRING M, GREBERG J. Evaluation of the impact of commodity price change on mine plan of underground mining [J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2015, 25(3): 375–382. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2015.03.008.
REEVES C. Genetic algorithms [M]// Handbook of Metaheuristics. New York: Kluwer Academic, 2003: 55–82.
VILLALBA M E, KUMRAL M. Calibration of genetic algorithm parameters for mining-related optimization problems [J]. Natural Resources Research, 2019, 28(2): 443–456. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-018-9395-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(488262-15) supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villalba Matamoros, M.E., Kumral, M. A value adding approach to hard-rock underground mining operations: Balancing orebody orientation and mining direction through meta-heuristic optimization. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 3126–3139 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4241-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4241-1
Key words
- underground mine planning
- orebody uncertainty
- orebody orientation
- mining direction
- stope layout optimization