Abstract
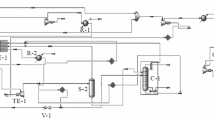
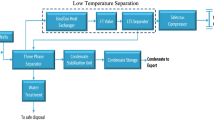
The occurrence of liquid condensation in natural gas accounts for new challenges during the interoperability between transmission networks, where condensation would lead to higher pressure drops, lower line capacity and may cause safety problem. A successful case of hydrocarbon dew point (HCDP) analysis is demonstrated during the mixing of natural gases in the transmission pipeline. Methods used to predict the HCDP are combined with equations of state (EOS) and characterization of C6+ heavy components. Predictions are compared with measured HCDP with different concentrations of mixed gases at a wide range of pressure and temperature scopes. Software named “PipeGasAnalysis” is developed and helps to systematic analyze the condensation problem, which will provide the guidance for the design and operation of the network.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BERGMAN D F, TECK M R, KATZ D L. Retrograde condensation in natural gas pipelines [R]. Washington DC: American Gas Association, 1975.
GEORGE D L, BARAJAS A M, BURKEY R C. The need for accurate hydrocarbon dew point determination [J]. Pipeline & Gas Journal, 2005 September.
GEORGE D L. Development of Accurate Methods for Predicting hydrocarbon dew points [R]. San Antonio: Southwest Research Institute, 2007.
VOULGARIS M E, PETERS C J, DE SWAN ARONS J, DERKS P A, JANSSEN R, SMIT A L C. Prediction of the potential hydrocarbon liquid content of lean natural gas comparison with field tests [C]// Proceedings of the 73rd Gas Processors Association Annual Convention, New Orleans, 1994: 40–48.
ERNEST K, DOUGLAS J P. Hydrocarbon dew point monitoring of natural gas using field-mounted, online gas chromatographs [J]. Pipeline & Gas Journal, 2005(7): 43.
ALFRADIQUE M F, CASTIER M. Calculation of phase equilibrium of natural gases with the Peng-Robinson and PC-SAFT equations of state [J]. Oil & Gas Science and Technology-Rev IFP, 2007, 62: 707–714.
ANDERSON B, DRISCOLL D. LNG interchangeability/gas quality: Results of the national energy Technology Laboratory’s research for FERC on natural gas quality and interchangeability [R]. Washington D C: US Department of Energy, 2007.
GONG J, SHI B H, WANG X P, WU Y. Study of calculating hydrocarbon dew point in gas pipeline [J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 2010, 28: 1643–1652.
WANG W A, ZHANG X P, LI M, GONG J. Investigation on phase behaviour of the pipelining natural gas [J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2011, 30: 423–426.
NIE Hai-kuan, ZHANG Jin-chuan. Control effect of fluid entry pressure on hydrocarbon accumulation [J]. J Cent South Univ Thechnol, 2010, 17: 1395–1402.
H S, CHUNG S M. Sayeed-Bin-Asad Berkah Fajar Y. H. Shin H. M. Jeong. Flow characteristics by particle image velocimetry in liquefied natural gas vaporizer model with several baffles [J]. J Cent South Univ Thechnol, 2011, 18: 1719–1725.
NISHIUMI H, ARAI T. Generalization of the binary interaction parameter of the Peng-Robinson equation of state by component family [J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 1988, 42: 43–62.
WANG W B, XIN P, ZHANG W W. Technical report of the HCDP analysis in Chinese natural gas network [R]. CPPE, 2011.
FAN S S, CHEN G J, MA Q L, et al. Experimental and modeling studies on the hydrate formation of CO2 and CO2-rich gas mixtures [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2000, 78: 173–178.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2011ZX05026-004-03) supported by the Key National Science and Technology Specific Program, China; Project(NCET-12-0969) supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University, China; Project(51104167) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(BJ-2011-02) supported by the Research Funds of China University of Petroleum-Beijing
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Duan, Jm., Li, M. et al. A successful case of hydrocarbon dew point analysis during mixing of natural gases in transmission pipeline. J. Cent. South Univ. 20, 2454–2458 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-013-1756-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-013-1756-8