Abstract
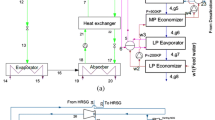
A simplified dual-pressure ammonia-water absorption power cycle (DPAPC-a) using low grade energy resources is presented and analyzed. This cycle uses turbine exhaust heat to distill the basic solution for desorption. The structure of the cycle is simple which comprises evaporator, turbine, regenerator (desorber), absorber, pump and throttle valves for both diluted solution and vapor. And it is of high efficiency, because the working medium has large temperature difference in evaporation and small temperature difference in absorptive condensation, which can match the sensible exothermal heat resource and the cooling water simultaneously. Orthogonal calculation was made to investigate the influence of the working concentration, the basic concentration and the circulation multiple on the cycle performance, with 85–110 °C heat resource and 20–32°C cooling water. An optimum scheme was given in the condition of 110 °C sensitive heat resource and 20 °C cooling water, with the working concentration of 0.6, basic concentration of 0.385, and circulation multiple of 5. The thermal efficiency and the power recovery efficiency are 8.06 % and 6.66%, respectively. The power recovery efficiency of the DPAPC-a is 28.8% higher than that of the steam Rankine cycle (SRC) and 12.7% higher than that of ORC (R134a) under the optimized situation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
RADERMACHER R. Thermodynamic and heat transfer implications of working fluid mixtures in Rankine cycles [J]. Int J Heat Fluid Flow, 1989, 10(2): 90–102.
MAGO P J, CHAMRA L M, SOMAYAJI C. Performance analysis of different working fluids for use in organic Rankine cycles [C]// Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part A: Journal of Power and Energy, 2007: 255–263.
BORSUKIEWICZ G A, NOWAK W. Maximizing the working fluid flow as away of increasing power output of geothermal power plant [J]. Appl Therm Eng, 2007, 27(11/12): 2074–2078.
RAYEGAN R, TAO Y X. A procedure to select working fluids for solar organic Rankine cycles (ORCs) [J]. Renew Energy, 2011, 3(6): 659–670.
KALINA A I. Combined-cycle system with novel bottoming cycle [J]. J Eng Gas Turbines Power, 1984, 106(10): 737–742.
GOSWAMI D Y, XU F. Analysis of a new thermodynamic cycle for combined power and cooling using low and mid temperature solar collectors [J]. Solar Energy Engineering, 1999, 121(2): 91–97.
INFANTE FERREIRA C A, ZAMFIRESCU C, ZAVTSEV D. Twin screw oil-free wet compressor for a compression-absorption cycle [J]. Refrigeration, 2006, 29(4): 556–565.
ROY P, DESILETS M, GALANIS N, NESREDDINE H, CAYER E. Thermodynamic analysis of a power cycle using a low-temperature source and a binary NH3-H2O mixture as working fluid [J]. Int J Thermal Sci, 2010, 49(1): 48–58.
ZAMFIRESCU C, DINCER I. Thermodynamic analysis of a novel ammonia-water trilateral Rankine cycle [J]. Thermochim Acta, 2008, 477(1/2): 7–15.
PADILLA R V, DEMIRKAYA G, GOSWAMI D Y, STEFANAKOS E, RAHMAN M. Analysis of power and cooling cogeneration using ammonia-water mixture [J]. Energy, 2010, 35(12): 1–9.
LUO Chen-ding, ZHANG Na, CAI Rui-xian, LIU M. Sensitivity analysis of ammonia absorption power/refrigeration combined cycle [J]. Journal of Chinese Electrical Engineering Science, 2008, 28(17): 1–7. (in Chinese)
WAGAR W R, ZAMFIRESCU C, DINCER Z. Thermodynamic performance assessment of an ammonia-water Rankine cycle for power and heat production [J]. Energy Conversation Manage, 2010, 51(12): 2501–2509.
CHEN Ya-ping. Thermodynamic analysis of a modified Kalina cycle [J]. Journal of Southeast University, 1989, 19(4): 52–58. (in Chinese)
CHEN Ya-ping. Thermodynamic analysis of a simplified Kalina cycle [J]. Thermal Power Generation, 1997, 47(4): 20–23. (in Chinese)
LIU Hua-jin. Study on a modified ammonia-water absorption power cycle system for utilization of low-grade waste heat [D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2011. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(50976022) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(BY2011155) supported by Science and Technology Innovation and Transformation of Achievements of Special Fund of Jiangsu Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, Jy., Chen, Yp., Liu, Hj. et al. Thermodynamic analysis of simplified dual-pressure ammonia-water absorption power cycle. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 19, 797–802 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-012-1074-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-012-1074-6