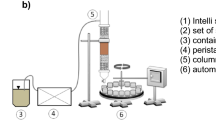
Abstract
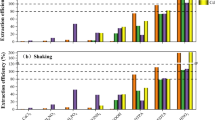
Some key factors on the heavy metals removal efficiencies were studied when soil washing technology was used in the remediation of soils contaminated by multiple heavy metals. The results show that the dissolubilities of Cu and Zn are promoted by humic acids, but Pb and Cd are inhibited by humic acids; heavy metals in the clay are more difficult to be extracted than silt; the strong acidic soils can cause the protonation of EDTA and weaken its extracting ability; EDTA is effective for extracting Pb and Cd, while oxalate (OX) is effective for extracting Cu and Zn; and biosurfactant can be used as additive to improve the removal of some particular heavy metals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CICCU R, GHIANI M, SERCI A, FADDA S, PERETTI R, ZUCC A. Heavy metal immobilization in the mining-contaminated soils using various industrial wastes [J]. Miner Eng, 2003, 16(3): 187–192.
LIU Yun-guo, ZHANG Hui-zhi, ZENG Guang-ming, HUANG Bao-rong, LI Xin, XU Wei-hua. Characteristics of tailings from the metal mines in Hunan Province, China [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2005, 12(2): 225–228.
LESTAN D, LUO C L, LI X D. The use of chelating agents in the remediation of metal-contaminated soils: A review [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2008, 153(1): 3–13.
ZHANG W H, TSANG D C W, LO I M C. Removal of Pb by EDTA—washing in the presence of hydrophobic organic contaminants or anionic surfactant [J] Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 155(3): 433–439.
BARONA A, ARANGUIZ I, ELIAS A. Metal associations in soils before and after EDTA extractive decontamination: Implications for the effectiveness of further clean-up procedures [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2001, 113(1): 79–85.
MAKKINA T, TAKANO H, KAMIYA T, ITOU T, SEKIYA N, INAHARA M, SAKURAI Y. Restoration of cadmium-contaminated paddy soils by washing with ferric chloride: Cd extraction mechanism and bench-scale verification. [J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 70(6): 1035–1043.
KEDZIOREK M A M, BOURG A C M. Solubilization of lead and cadmium during the percolation of EDTA through a soil polluted by smelting activities [J]. Contam Hydrol, 2000, 40(4): 381–392.
ELLIOTT H A, SHASTRI L. Extractive decontamination of metal-polluted soils using oxalate [J]. Water Air Soil Pollut, 1999, 110(3): 335–346.
XI Dan-li. Environment monitoring of China [M]. Beijing: Science and Environment Literature Press, 1992: 56–79. (in Chinese)
CHANG C S W, HUANG C C, WANG M C. Analytical and spectroscopic characteristics of refuse compost-derived humic substances [J]. International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 2003, 1(1): 62–71.
CLEMENTE R, WALKER D J, ROIG A, BERNAL M P. Heavy metal bioavailability in a soil affected by mineral sulphides contamination following the mine spillage at Aznalco’llar (Spain) [J]. Biodegradation, 2003, 14(3): 199–205.
LO I M C, YANG X Y. EDTA extraction of heavy metal from different soil fraction and synthetic soils [J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 1999, 109(1): 219–236.
ZHUANG J, YU G R, LIU X Y. Characteristics of lead sorption on clay minerals in relation to metal oxides [J]. Pedosphere, 2000, 10(1): 11–20.
NÚÑEZ-LÓPEZ R A, MEAS Y, GAMA S C, BORGES R O, OLGUIN E J. Leaching of lead by ammonium salts and EDTA from Salvinia minima biomass produced during aquatic phytoremediation [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 154(2): 623–632.
ORTEGA L M, LEBRUN R, BLAIS J F, HAUSLER R, DROGUI P. Effectiveness of soil washing, nanofiltration and electrochemical treatment for the recovery of metal ions coming from a contaminated soil [J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(8): 1943–1952.
LO I M C, ZHANG W. Study on the optimal conditions for the recovery of EDTA from soil washing effluents [J]. Environ Eng, 2005, 131(11): 1507–1513.
MULLIGAN C N, YONG R N, GIBBS B F, JAMES S, BENNETT H P J. Metal removal from contaminated soil and sediments by the biosurfactant surfactant [J]. Environment Science and Technology, 1999, 33(21): 3812–3820.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(20050532009) supported by the Doctoral Foundation of Ministry of Education of China; Projects(2006BAD03A1704, 2006BAD03A1706) supported by the National 11th-Five Technology Supporting Project
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Wb., Li, X., Gao, H. et al. Influence factors analysis of removing heavy metals from multiple metal-contaminated soils with different extractants. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 16, 108–111 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-009-0018-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-009-0018-2