Abstract
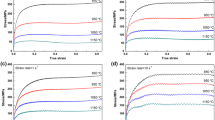
The basic factors relating to the rheological stress in the constitutive equations were introduced. Carbon constructional quality steels were regarded as a kind of elastic-viscoplastic materials under high temperature and the elastic-viscoplastic constitutive models were summarized. A series of tension experiments under the same temperature and different strain rates, and the same strain rate and different temperatures were done on 20 steel, 35 steel and 45 steel. 52 groups of rheological stress—strain curves were obtained. The experimental results were analyzed theoretically. The rheological stress constitutive models of carbon steels were built combining the strong points of the Perzyna model and Johnson-Cook model. Comparing the calculation results conducted from the model with the experiment results, the results proves that the model can reflect the temperature effect and strain rate effect of carbon constructional quality steels better.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CLAUSEN A H, BORVIK T, HOPPERSTAD O S, BENALLED A. Flow and fracture characteristics of aluminium alloy AA5083-H116 as function of strain rate, temperature and triaxiality [J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2004, 364(1/2): 260–272.
LEE W S, YEH G W. The plastic deformation behaviour of AISI 4340 alloy steel subjected to high temperature and high strain rate loading conditions [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1997, 71(2): 224–234.
KOZLOWSKI P F, ANAND L. Simple constitutive equations for steel at high temperature [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A 1992, 23: 903–918.
HUESPE A E, CARFONA A, NIGRO N, FACHINOTTI V. Visco-plastic constitutive models of steel at high temperature [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2000, 102(1/3): 143–152.
KHAN A S, LIANG Ri-qiang. Behaviors of three BCC metal over a wide range of strain rates and temperatures. Experiments and modeling [J]. Journal of Plasticity, 1999, 15(10): 1089–1109.
LUBARADA V A, BENSON D J, MEYERS M A. Strain-rate effects in rheological models of inelastic response [J]. Journal of Plasticity, 2003, 19(8): 1097–1118.
LUO Ying-she, TANG Xiao-di, WU Gang. Tensile rheological properties of sheet TC1 Ti-alloy [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 14(s1): 350–353.
YANG Liu, LUO Ying-she, TANG Xiao-di. Rheological properties of carbon constructional quality steels [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 14(s1): 285–288.
PERZYNA P. The constitutive equations for rate sensitive plastic materials [J]. Quarterly of Applied Mathematics, 1963, 20: 321–332.
JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. Fracture characteristics of three metals subjected to various strains, strain rates, temperatures and pressures [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1985, 21(1): 31–48.
LUO Ying-she, DONDA K, WANG Z, Experimental solution for viscocity coefficient of solid alloy material [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 8: 271–276.
YANG Liu. Research on the constitutive model depending upon temperature and strain rate of carbon constructional quality steels [D]. Xiangtan: Institute of Foundation Mechanics and Material Engineering, Xiangtan University, 2004. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2451002035) supported by Zhejiang Forestry University; Project(03JJY3007) supported by the Natural Science Foundations of Hunan Province; Project(02A008) supported by the Education Department of Hunan Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Luo, Ys. Constitutive model depending upon temperature and strain rate of carbon constructional quality steels. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 15 (Suppl 1), 43–46 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0311-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0311-5