Abstract
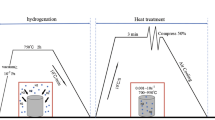
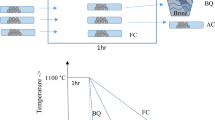
The effects of rapid heating cyclic heat treatment on mechanical properties of a TiAl-based alloy (Ti-33Al-3Cr) were studied by means of an induction heating machine. The results show that: 1) fine fully-lamellar microstructure with colony size of about 50 µm and lamellar spacing of about 0.12 µm can be obtained; 2) the compression mechanical properties can be improved to a large extent and the best comprehensive compression mechanical properties can reach the yield stress 745 MPa, the large flow stress 1 672 MPa and the compression ratio 19.4%; and 3) the compression fracture at room temperature after induction heat treatment and aging is still typical cleavage fracture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grange R A, Shackelford E R. Method of producing ultrafine-grained steel[P]. US3178324, 1965.
ZHANG Ji, MA Wan-qing, ZOU Dun-xu, et al. The heat treatment process and mechanisms of obtaining the NG microstructure from a cast TiAl alloy[J]. Transactions of Metal Heat Treatment(in Chinese), 1996, 17(3): 17.
ZHANG Ji, ZHANG Jian-wei, ZOU Dun-xu, et al. The generating kinetics and mechanisms of the cast TiAl intermetallic alloy FFL microstructure [J]. Transactions of Metal Heat Treatment (in Chinese), 1996, 17(4): 12.
ZHANG Ji, ZHANG Zhi-hong, ZOU Dun-xu, et al. Refinement of cast TiAl alloy FL microstructure [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research (in Chinese), 1997, 9(S1): 162.
WANG Jian-nong. New processing technology and microstructure control of TiAl-based alloys[R]. In: Key Fundamental Problems Research of High-Performanced Intermetallic Structural Materials (in Chinese), 2000.
XIE Kun, WANG Jian-nong, TANG Jian-cheng, et al. Refining TiAl grains by cyclic heat treatment[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 1999, 28(4): 248.
PENG Chao-qun, HUANG Bai-yun, HE Yue-hui, et al. Microstructural refinement of as-cast TiAl-based alloy by cyclic heat treatment[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology(in Chinese), 1999, 30(1): 52–54.
PENG Chao-qun. Effects of Cyclic Heat Treatment on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of TiAl-based Alloy[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2001.
Dao M, Kad B K, Asaro R J. Deformation and fracture under compressive loading in lamellar TiAl microstructures[J] Phil Mag A, 1996, 74(3): 569–591.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Advanced Materials Committee of China(No. 715-005-0040)
Biography of the first author: PENG Chao-qun, associate professor, born in 1966, majoring in TiAl-based intermetallics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Cq., Huang, By. & He, Yh. Effects of induction heat treatment on mechanical properties of TiAl-based alloy. J Cent. South Univ. Technol. 9, 5–10 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-002-0002-6
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-002-0002-6