Abstract
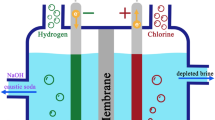
In order to develop an energy-saving electrodeposition process of copper, the electrodeposition of copper in copper sulfate solution by the ion-exchange membrane primary cell (IMPC) method has been studied. The experiments were carried out in an ion-exchange membrane primary cell with dimensions of 200 mm in length, 52 mm in width and 90 mm in height. The influences of temperature (294–323 K), interval between the anode and cathode (1.5–3.5 cm), mass concentrations of Cu2+ (6–40 g/L), H2SO4 (0–120 g/L) and Fe3+ (3–9 g/L) in catholyte and solution flow rate (0–8 cm/s) on current density and current efficiency were investigated experimentally. The current density increases with the increase of temperature and concentrations of Cu2+ and H2SO4 in catholyte. Cathode current efficiency decreases with the increase of concentration of Fe3+ in catholyte and anode current efficiency decreases with the increase of temperature. The high-quality cathodic copper can be obtained and the current density of membrane can be higher than 150 A/m2 and the current density of cathode can be higher than 300 A/m2. The experiment results show that IMPC method is effective for electrodeposition of copper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alan Toyer. Advance and developmental trend of copper’s hydrometallurgy [J]. Hydrometallurgy (in Chinese), 1997, 62(1): 52–56.
WU Xi. Some development of leaching-solvent extraction-electrowinning process of copper[J]. Hydrometallurgy (in Chinese), 1999, (2):45–47.
WANG Chen-yan, ZHAN Hui-fang, HU Hu-cheng, et al. Economical assessment of leaching-solvent extraction-electrowinning process for low-grade copper deposit in China[J]. Non-ferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy Part) (in Chinese), 1997, (4): 16–18.
FANG Jin-wei, LI Wei-zhong. Development and perspective of leaching-solvent extraction-electrowinning process of copper[J]. Non-ferrous Metals Metallurgy (in Chinese), 1999, (4): 15–18.
YAN Zhi-hua. Primary cell electrolysis and hydrometallurgy of copper[A]. Proceedings of the First Conference on Application of Membrane Separation Technology in Metallurgy (in Chinese) [C]. Changsha, 1999. 222–224.
LI Qing-gang, ZHU Kang-gen, ZHANG Qi-xiu, et al. Reduction of ferric iron in the titanium sulfate solution by the ion-exchange membrane primary cell method [J]. J of Central South University of Technology, 1999, 6(2): 90–96.
Bishiwash A K, Davenbert W G. Extraction metallurgy of copper (in Chinese)[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1980.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Foundation item: The Key Program of the 9th Five-year Plan of China(No.97-123-02-03-04)
Biography of the first author: ZHOU Kang-gen, doctor of engineering, professor, born in 1963, majoring in extractive metallurgy of rare metals and application of membrane separation technology to metallurgy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Kg., Li, Qg. & Zhang, Qx. Electrodeposition of copper by IMPC method. J Cent. South Univ. Technol. 7, 186–190 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-000-0050-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-000-0050-8