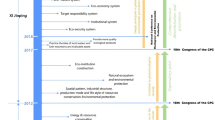
Abstract
High-quality development of ethnic minority areas is a key issue in China’s economic and social transformation. In order to explore the development trend and optimization path of high-quality development in ethnic minority areas, this study constructed a systematic evaluation index system of economic development, social development and government governance. The coupled coordination model was adopted to quantitatively analyze the spatio-temporal evolution characteristics of economic development, social development and government governance in Xinjiang from 2013 to 2020. The influencing factors of coupling coordination development of the three systems were identified by grey correlation analysis. The spatial-temporal pattern analysis results show that the coupling coordination degree of Xinjiang increased steadily, but the regional differences gradually expanded. The coupling coordination degree shows a stable structure with high center and low periphery, and a spatial pattern of low in southern Xinjiang and high in northern Xinjiang. The results of grey correlation analysis show that the grey correlation degree among economic development, social development and government governance in Xinjiang is above 0.78. The three systems of economic development, social development and government governance interact with each other, forming a complex system of high-quality development in ethnic minority areas. To promote high-quality development in Xinjiang, it should take social stability and long-term stability as the overall goal, improve the quality of the production and living environment on the basis of economic development, enhance regional economic competitiveness, and take government governance as a means to optimize the environment for regional development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An S, Zhang S L, Hou H P et al., 2022. Coupling coordination analysis of the ecology and economy in the Yellow River Basin under the background of high-quality development. Land, 11(8): 1235. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/1and11081235
Ariken M, Zhang F, Liu K et al., 2020. Coupling coordination analysis of urbanization and eco-environment in Yanqi Basin based on multi-source remote sensing data. Ecological Indicators, 114: 106331. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106331
Bahtebay J, Zhang F, Ariken M et al., 2021. Evaluation of the coordinated development of urbanization-resources-environment from the incremental perspective of Xinjiang, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 325: 129309. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129309
Chen L M, Huo C J, 2022. The measurement and influencing factors of high-quality economic development in China. Sustainability, 14(15): 9293. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159293
Chen Wenlie, Liang Siyu, 2022. Construction of modern economic system in ethnic regions under the guidance of ecological civilization. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Social Sciences), 22(2): 81–87. (in Chinese)
Chen Xiaohong, Zhang Mingxuan, Wang Ying et al., 2022. Coupling and coordination characteristics and influencing factors of the livable environment system for the elderly in China. Chinese Geographical Science, 32(6): 1052–1068. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-022-1283-3
Dang Xiuyun, Xin Fei, 2010. Issues and choices of the public service administration in ethnic minority areas in the new era. Journal of Minzu University of China (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition), 37(6): 34–38. (in Chinese)
Dong Q, Zhong K, Liao Y et al., 2023. Coupling coordination degree of environment, energy, and economic growth in resource-based provinces of China. Resources Policy, 81: 103308. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103308
Dong Suocheng, Zheng Ji, Li Yu et al., 2019. Quantitative analysis of the coupling coordination degree between urbanization and eco-environment in Mongolia. Chinese Geographical Science, 29(5): 861–871. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-019-1074-7
Fan Jie, 2020. High-quality development of national territory space governance and regional economic layout during 14th five-year plan in China. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 35(7): 796–805. (in Chinese)
Fan Jie, Wang Yafei, Wang Yixuan, 2020. High quality regional development research based on geographical units: discuss on the difference in development conditions and priorities of the Yellow River Basin compared to the Yangtze River Basin. Economic Geography, 40(1): 1–11. (in Chinese)
Guo Jiahang, Zuo Qiting, Li Donglin et al., 2021. Research on relationship between water resources utilization and industrial development in Xinjiang. Water Resources Protection, 37(2): 34–42. (in Chinese)
Hou C, Chen H, Long R, 2022. Coupling and coordination of China’s economy, ecological environment and health from a green production perspective. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 19(5): 4087–4106. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03329-8
Jin Bei, 2018. Study on the ‘High-Quality Development’ economics. China Industrial Economics, (4): 5–18. (in Chinese)
Li Junqing, 2014. Study on the modernization of public security governance system and capability in the frontier minority areas. Chinese Public Administration, (11): 52–55. (in Chinese)
Li Y, Zhang X T, Gao X X, 2022. An evaluation of the coupling coordination degree of an urban economy-society-environment system based on a multi-scenario analysis: the case of Chengde city in China. Sustainability, 14(11): 6790. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116790
Lin J Z, Kim H H, 2022. An empirical study on the high-quality development efficiency of the urban economy in China. International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences, 9(6): 119–124. doi: https://doi.org/10.21833/ijaas.2022.06.016
Lin T, Wang L J, Wu J B, 2022. Environmental regulations, green technology innovation, and high-quality economic development in China: application of mediation and threshold effects. Sustainability, 14(11): 6882. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116882
Liu Bo, Huang Qin, Yang Lizhen, 2021a. Evaluation on the coupling effect of the ‘Economy-Water-Land’ system in the Yangtze River economic belt under the background of high-quality development. Soft Science, 35(5): 27–34, 42. (in Chinese)
Liu Lin, Yu Qianghong, Li Guanghao, 2018. Can improving social public order help to reduce multidimensional poverty? Empirical evidence from the peasant households of Three Regions of Southern Xinjiang. East China Economic Management, 32(3): 96–102. (in Chinese)
Liu M K, Liu C X, Zhang S T et al., 2021b. Research on industry development path planning of resource-rich regions in china from the perspective of ‘resources, assets, capital’. Sustainability, 13(7): 3988. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073988
Liu W W, Wang J, 2021. Evaluation of coupling coordination degree between urban rail transit and land use. International Journal of Communication Systems, 34(2): e4015. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/dac.4015
Long X, Wu S, Wang J et al., 2022. Urban water environment carrying capacity based on VPOSR-coefficient of variation-grey correlation model: A case of Beijing, China. Ecological Indicators, 138: 108863. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108863
Liu Y, Yuan X, Li J et al., 2023. Trade-offs and synergistic relationships of ecosystem services under land use change in Xinjiang from 1990 to 2020: A Bayesian network analysis. Science of The Total Environment, 858: 160015. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160015
Ma Yan, 2020. Examining the coupling degree and interactive stress between urbanization and eco-environment in Yangtze River economic belt. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 29(2): 275–286. (in Chinese)
Mei Lirun, Cao Lihai, 2016. Eradication of extremism: a multidimensional analysis of Xinjiang’s governance dilemma in the perspective of good governance. Journal of Yunnan Minzu University (Social Sciences), 33(4): 21–26. (in Chinese)
Pan W, Wang J, Lu Z et al., 2021. High-quality development in China: Measurement system, spatial pattern, and improvement paths. Habitat International, 118: 102458. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2021.102458
Qin S, Han Z Y, Chen H et al., 2022. High-quality development of Chinese agriculture under factor misallocation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(16): 9804. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19169804
Salvia A L, Leal Filho W, Brandli L L et al., 2019. Assessing research trends related to Sustainable Development Goals: Local and global issues. Journal of Cleaner Production, 208: 841–849. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.242
Sun Y, Cui Y, Huang H X, 2016. An empirical analysis of the coupling coordination among decomposed effects of urban infrastructure environment benefit: case study of four Chinese autonomous municipalities. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2016: 8472703. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8472703
Tang Z, 2015. An integrated approach to evaluating the coupling coordination between tourism and the environment. Tourism Management, 46: 11–19. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2014.06.001
Tu J H, Zhang D P, 2020. Does tourism promote economic growth in Chinese ethnic minority areas? A nonlinear perspective. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 18: 100473. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdmm.2020.100473
Usman Umur, Rehemutula Turap, 2021. Study on the development of Xinjiang open industrial clusters driven by China-Europe railway express. Railway Freight Transport, 39(8): 54–58. (in Chinese)
Wang Shujia, Kong Wei, Ren Liang et al., 2021. Research on misuses and modification of coupling coordination degree model in China. Journal of Natural Resources, 36(3): 793–810. (in Chinese), doi: https://doi.org/10.31497/zrzyxb.20210319
Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Bureau of Statistics, 2014–2021. Xinjiang Statistical Yearbook. Beijing: China Statistics Press, (in Chinese)
Xu Wanting, Wang Heling, 2020. Empirical analysis of tertiary industry on county economic development in Xinjiang: spatial panel data model. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 50(11): 60–69. (in Chinese)
Yan B R, Dong Q L, Li Q et al., 2021. A study on the coupling and coordination between logistics industry and economy in the background of high-quality development. Sustainability, 13(18): 10360. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810360
Yan Renhua, Yang Ming, Xiong Heigang et al., 2015. The evolution of spatial-temporal pattern of industrial structure in Xinjiang at the county level. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 37(8): 117–124. (in Chinese)
Yang Minghong, 2021. The logic and transformation of the modernization of borderland governance in contemporary China. Journal of Yunnan Normal University (Humanities and Social Sciences Edition), 53(5): 11–20. (in Chinese)
Yangliu Qingqing, Li Xiaoping, 2020. Evaluation of high quality development in ethnic minority areas of China based on “Five Development Concepts”. Journal of Minzu University of China (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition), 47(1): 79–88. (in Chinese)
Yang Shengmin, 2015. How to understand the ethnic problems in current China: taking Xinjiang as a major case. Northwestern Journal of Ethnology, (3): 5–18. (in Chinese)
Ye S, Ge Y J, Xu S Y et al., 2022. Measurement and prediction of coupling coordination level of economic development, social stability and ecological environment in Qinghai-Thoughts on sustainable societal safety. Sustainability, 14(17): 10515. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710515
Yu Hailong, Liu Yuping, 2022. High-quality development in ethnic areas from perspective of total factor productivity. Journal of South-Central Minzu University (Humanities and Social Sciences), 42(9): 121–131. (in Chinese)
Zhao Hulan, Yang Zhaoping, Han Fang et al., 2020. Analysis and forecast of coupling situation among tourism industry-economic development-ecological environment in Xinjiang. Arid Land Geography, 43(4): 1146–1154. (in Chinese)
Zou Lijuan, Zhao Ling, 2020. Dialectical logic of realizing high-quality development and constructing the communal consciousness of the Chinese nation in the ethnic borderlands of China. Journal of Yunnan Minzu University (Social Sciences), 37(6): 12–17. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42230510), Key Project of Xinjiang Social Science Foundation (No. 22AZD006)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, H., Sun, Y., Zhao, H. et al. Spatial-temporal Coupling Analysis of Economic Development-Social Development-Government Governance in Xinjiang, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 33, 410–425 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-023-1351-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-023-1351-3