Abstract
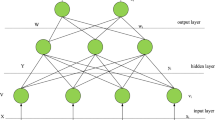
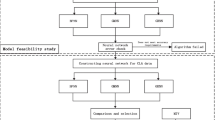
In this paper, the artificial neural network (ANN) model was used to evaluate the degree of intensive urban land use in Nanjing City, China. The construction and application of the ANN model took into account the comprehensive, spatial and complex nature of urban land use. Through a preliminary calculation of the degree of intensive land use of the sample area, representative sample area selection and using the back propagation neural network model to train, the intensive land use level of each evaluation unit is finally determined in the study area. Results show that the method can effectively correct the errors caused by the limitations of the model itself and the determination of the ideal value and weights when the multifactor comprehensive evaluation is used alone. The ANN model can make the evaluation results more objective and practical. The evaluation results show a tendency of decreasing land use intensity from the core urban area to the periphery and the industrial functional area has relatively low land use intensity compared with other functional areas. Based on the evaluation results, some suggestions are put forward, such as transforming the mode of urban spatial expansion, strengthening the integration and potential exploitation of the land in the urban built-up area, and strengthening the control of the construction intensity of protected areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn B S, Cho S S, Kim C Y, 2000. The integrated methodology of rough set theory and artificial neural network for business failure prediction. Expert Systems with Applications, 18(2): 65–74. doi: 10.1016/S0957-4174(99)00053-6
Almeida C M, Gleriani J M, Castejon E F et al., 2008. Using neural networks and cellular automata for modelling intra-urban land-use dynamics. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 22(9): 943–963. doi: 10.1080/13658810701731168
Bai X M, Shi P J, Liu Y S, 2014. Society: Realizing China's urban dream. Nature, 509(7499): 158–160. doi:10.1038/509158a
Di Xianghong, Hou Xiyong, Wang Yuandong et al., 2015. Spatial-temporal characteristics of land use intensity of coastal zone in China during 2000–2010. Chinese geographical science, 25(1): 51–61. doi: 10.1007/s11769-014-0707-0
Erb K H, Haberl H, Jepsen M R et al., 2013. A conceptual framework for analysing and measuring land-use intensity. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 5(5): 464–470. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2013.07.010
Estoque R C, Murayama Y, 2015. Intensity and spatial pattern of urban land changes in the megacities of Southeast Asia. Land Use Policy, 48: 213–222. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2015.05. 017
Ferdous N, Bhat R C, 2013. A spatial panel ordered-response model with application to the analysis of urban land-use development intensity patterns. Journal of Geographical Systems, 15(1): 1–29. doi: 10.1007/s10109-012-0165-0
Gevrey M, Dimopoulos I, Lek S, 2003. Review and comparison of methods to study the contribution of variables in artificial neural network models. Ecological Modelling, 160(3): 249–264. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3800(02)00257-0
Gong J Z, Chen W L, Liu Y S, 2014. The intensity change of urban development land: Implications for the city master plan of Guangzhou, China. Land Use Policy, 40: 91–100. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2013.05.001
Guresen E, Kayakutlu G, Daim T U, 2011. Using artificial neural network models in stock market index prediction. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(8): 10389–10397. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2011.02.068
Hui E C M, Wu Y Z, Deng L J et al., 2015. Analysis on coupling relationship of urban scale and intensive use of land in China. Cities, 42: 63–69. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2014.09.002
Jiang Hai, Qu Futian, Ou Minghao et al., 2008. Evaluation methods and application of regional Land-use intensity. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 24(1): 117–123. (in Chinese)
Khan J, Wei J S, Ringner M et al., 2001. Classification and diagnostic prediction of cancers using gene expression profiling and artificial neural networks. Nature Medicine, 7(6): 673–679. doi: 10.1038/89044
Kuemmerle T, Erb K, Meyfroidt P et al., 2013. Challenges and opportunities in mapping land use intensity globally. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 5(5): 484–493. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2013.06.002
Levers C, Butsic V, Verburg P, 2016. Drivers of changes in agricultural intensity in Europe. Land Use Policy, 58(15): 380–393. doi. 10.1016/j.landusepol.2016.08.013
Li Guangdong, Fang Chuanglin, Pang Bo, 2014. Quantitative measuring and influencing mechanism of urban and rural land intensive use in China. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 24(5): 858–874. doi: 10.1007/s11442-014-1125-z
Li Kongqing, Chen Yinrong, 2013. Evaluation on the intensity of urban land use based on low-carbon concept: a case study of Nanjing City. China Land Sciences, 27(1): 61–66. (in Chinese)
Li X, Yeh A G O, 2002. Neural-network-based cellular automata for simulating multiple land use changes using GIS. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 16(4): 323–343. doi: 10.1080/13658810210137004
Liu X D, Gao J, 2011. Discussion on the index system of intensive land use evaluation in development area. Asian Agricultural Research, 3(2): 91–96
Luo H C, Li X M, Zheng S J et al., 2012. Study on synthesis evaluation of intensive land use and growth pattern transfor mation of towns. Journal of Computers, 7(8): 1959–1966. doi: 10.4304/jcp.7. 8.1959–1966
Meng Y, Zhang F R, An P L et al., 2008. Industrial land-use efficiency and planning in Shunyi, Beijing. Landscape and Urban Planning, 85(1): 40–48. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2007.09.004
Pijanowski B C, Brown D G, Shellito B A et al., 2002. Using neural networks and GIS to forecast land use changes: a land transformation model. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 26(6): 553–575. doi: 10.1016/S0198-9715(01)00015-1
Pradhan B, Lee S, 2009. Landslide risk analysis using artificial neural network model focussing on different training sites. International Journal of Physical Sciences, 4(1): 1–15
Pradhan B, Lee S, 2010. Delineation of landslide hazard areas on Penang Island, Malaysia, by using frequency ratio, logistic regression, and artificial neural network models. Environmental Earth Sciences, 60(5): 1037–1054. doi: 10.1007/s12665-009-0245-8
Qiao Weifeng, 2013. Study on Urban Spatial Multidimensional Expansion of Nanjing Based on Land Use Perspective. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University. (in Chinese)
Recknagel F, 1997. ANNA: Artificial Neural Network model for predicting species abundance and succession of blue-green algae. Hydrobiologia, 349(1): 47–57. doi: 10.1023/A:100304142 7672
Salomon R, Hemmen J, 1996. Accelerating back propagation through dynamic self-adaptation. Neural Networks, 9(4), 589–601. doi: 10.1016/0893-6080(95)00144-1
Shao Xiaomei, Wang Jing, 2008. Appraisal of intensive land use of development zones in small towns: a case study of Cixi in Zhejiang Province. Progress in Geography, 27(1): 75–81. (in Chinese)
Shi Y S, Huang Y C, 2013. Relationship between morphological characteristics and land-use intensity: empirical analysis of shanghai development zones. Journal of Urban Planning and Development, 139(1): 49–61. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)UP.1943-5444.0000134
Sluisa T, Pedrolia B, Kristensen S, 2016. Changing land use intensity in Europe: recent processes in selected case studies. Land Use Policy, 57(30): 777–785. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol. 2014.12.005
Taleai M, Sharifi A, Sliuzas R, 2007. Evaluating the compatibility of multi-functional and intensive urban land uses. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 9(4): 375–391. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2006.12.002
Temme A J A M, Verburg P H, 2011. Mapping and modeling of changes in agricultural intensity in Europe. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 140(1–2): 46–56. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2010.11.010
Wang F, Antipova A, Porta S, 2011. Street centrality and land use intensity in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. Journal of Transport Geography, 19(2): 285–293. doi:10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2010.01. 004
Wang J, Chen Y, Shao X et al., 2012. Land-use changes and policy dimension driving forces in China: present, trend and future. Land Use Policy, 29(4): 737–749. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol. 2011.11.010
Wang Mingshu, Zhu Ming, 2012. Evaluating intensive land use situation of development zone based on cloud models. Transaction of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 28(10): 247–252. (in Chinese)
Xie Hualin, He Yafen, Zou Jinlang et al., 2016. Spatio-temporal difference analysis of cultivated land use intensity based on emergy in the Poyang Lake Eco-economic Zone of China. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 26(10): 1412–1430. doi: 10.1007/s11442-016-1335-7
Yang J Y, Yang Y, Tang W, 2012. Development of evaluation model for intensive land use in urban centers. Frontiers of Architectural Research, 1(4): 405–410. doi: 10.1016/j.foar. 2012.07.006
Zhang Y D, Wu L N, 2009. Stock market prediction of S&P 500 via combination of improved BCO approach and BP neural network. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(5): 8849–8854. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2008.11.028
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of Special Financial Grant and General Financial Grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2015T80127, 2014M561040), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41371172, 41401171, 41471143), A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (No. 164320H101)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, W., Gao, J., Liu, Y. et al. Evaluation of intensive urban land use based on an artificial neural network model: A case study of Nanjing City, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 27, 735–746 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-017-0905-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-017-0905-7