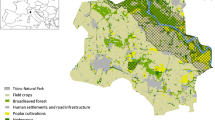
Abstract
The development of modern agriculture has resulted in much homogenization of the landscape consisting of large patches of farmland, so small remnant non-crop habitats especially linear corridors play an important role in the conservation of species and the maintenance of ecosystem functions. However, little attention has been paid to the effects of corridors structural characteristics on the plant species restricted to such habitats. In this study, we selected three types of corridors including ditch, hedgerow and road, and analyzed their structural characteristics. The plant species presented in these corridors were investigated, and the species diversity, abundance and frequency were estimated. Moreover, spatial arrangements of corridors were classified into different types to discuss whether there were significant effects of corridor network on plant distribution. The results show that three types of corridors have different effects on plant species composition and diversity. The one-one combined corridor networks and total network associated by three corridors have more complex structural features than each single type of corridor. However, there is no strong correlation between the corridor networks with their plant species. We suggest that carrying out a pointed vegetation survey at corridor intersections to further test the relationships between structural features of corridor and plants is necessary.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bianchi F J J A, Booij C J H, Tscharntke T, 2006. Sustainable pest regulation in agricultural landscapes: A review on landscape composition, biodiversity and natural pest control. Proceedings of the Royal Society, 273(1595): 1715–1727. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2006.3530
Corbit M, Marks P L, Gardescu S, 1999. Hedgerows as habitat corridors for forest herbs in central New York, USA. Journal of Ecology, 87(2): 220–232. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2745.1999.00339.x
Damschen E I, Haddad N M, Orrock J L et al., 2006. Corridors increase plant species richness at large scales. Science, 313(5791): 1284–1286. doi: 10.1126/science.1130098
Davies Z G, Pullin A S, 2007. Are hedgerows effective corridors between fragments of woodland habitat? An evidence-based approach. Landscape Ecology, 22(3): 333–351. doi: 10.1007/s10980-006-9064-4
Fahrig L, 2003. Effects of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 34: 487–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.34.011802.132419
Fischer J, Lindenmayer D B, 2007. Landscape modification and habitat fragmentation: A synthesis. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 16(3): 265–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1466-8238.2006.00287.x
Foley J A, DeFries R, Asner G P et al., 2005. Global consequences of land use. Science, 309(5734): 570–574. doi: 10.1126/science.1111772
Foley J A, Ramankutty N, Brauman K A et al., 2012. Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature, 478(7369): 337–342. doi: 10.1038/nature10452
Fu Bojie, Chen Liding, Ma Keming et al., 2011. Principles and Applications of Landscape Ecology (2nd edition). Beijing: Science Press, 79–81. (in Chinese)
Haas C A, 1995. Dispersal and use of corridors by birds in wooded patches on an agricultural landscape. Conservation Biology, 9(4): 845–854. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1739.1995.09040845.x
Haddad N M, Baum K A, 1999. An experimental test of corridor effects on butterfly densities. Ecological Applications, 9(2): 623–633. doi: 10.1890/1051-0761(1999)009[0623:AETOCE]2.0.CO;2
Haddad N M, Bowne D R, Cunningham A et al., 2003. Corridor use by diverse taxa. Ecology, 84(3): 609–615. doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2003)084[0609:CUBDT]2.0.CO;2
Haddad N, 1999. Corridor and distance effects on interpatch movements: A landscape experiment with butterflies. Ecological Applications, 9(2): 612–622. doi: 10.1890/1051-0761(1999)009[0612:CADEOI]2.0.CO;2
Haddad N, 2000. Corridor length and patch colonization by a butterfly, Junonia coenia. Conservation Biology, 14(3): 738–745. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1739.2000.99041.x
Kleijn D, Verbeek M, 2000. Factors affecting the species composition of arable field boundary vegetation. Journal of Applied Ecology, 37(2): 256–266. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2664.2000.00486.x
Lande R, 1996. Statistics and partitioning of species diversity, and similarity among multiple communities. Oikos, 76(1): 5–13.
Le Coeur D, Baudry J, Burel B et al., 2002. Why and how we should study field boundary biodiversity in an agrarian landscape context. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 89(1): 23–40.
Levey D J, Bolker B M, Tewksbury J J et al., 2005. Effects of landscape corridors on seed dispersal by birds. Science, 309(5731): 146–148. doi: 10.1126/science.1111479
Lu Tao, Ma Keming, Fu Bojie et al., 2008. Effects of ditch network structure on landscape pattern in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(6): 2746–2752. (in Chinese)
Marshall E J P, Moonen A C, 2002. Field margins in northern Europe: Their functions and interactions with agriculture. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 89(1): 5–21.
Matson P A, Parton W J, Power A G et al., 1997. Agricultural intensification and ecosystem properties. Science, 277(5325): 504–509. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5325.504
McCollin D, Jackson J I, Bunce R G H et al., 2000. Hedgerows as habitat for woodland plants. Journal of Environmental Management, 60(1): 77–90. doi: 10.1006/jema.2000.0363
Orrock J L, Damschen E I, 2005. Corridors cause differential seed predation. Ecological Applications, 15(3): 793–798. doi: 10.1890/04-1129
Resasco J, Levey D J, Damschen E I, 2012. Habitat corridors alter relative trophic position of fire ants. Ecosphere, 3(11): 1–9. doi: 10.1890/ES12-00266.1
Riffell S K, Gutzwiller K J, 1996. Plant-species richness in corridor intersections: Is intersection shape influential? Landscape Ecology, 11(3): 157–168. doi: 10.1007/BF02447514
Sitzia T, 2007. Hedgerows as corridors for woodland plants: A test on the Po Plain, northern Italy. Plant Ecology, 188(2): 235–252. doi: 10.1007/s11258-006-9159-7
Sullivan T P, Sullivan D S, Thistlewood H M A, 2012. Abundance and diversity of small mammals in response to various linear habitats in semi-arid agricultural landscapes. Journal of Arid Environments, 83: 54–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jaridenv.2012.03.003
Tewksbury J J, Levey D J, Haddad N M et al., 2002. Corridors affect plants, animals, and their interactions in fragmented landscapes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99(20): 12923–12926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.202242699
Townsend P A, Levey D J, 2005. An experimental test of whether habitat corridors affect pollen transfer. Ecology, 86(2): 466–475. doi: 10.1890/03-0607
Tscharntke T, Klein A M, Kruess A et al., 2005. Landscape perspectives on agricultural intensification and biodiversity-ecosystem service management. Ecology Letters, 8(8): 857–874. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00782.x
Tscharntke T, Tylianakis J M, Rand T A et al., 2012. Landscape moderation of biodiversity patterns and processes-eight hypotheses. Biological Reviews, 87(3): 661–685. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.2011.00216.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41071118)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Q., Liang, G., Lu, X. et al. Effects of corridor networks on plant species composition and diversity in an intensive agriculture landscape. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 24, 93–103 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-014-0659-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-014-0659-4