Abstract
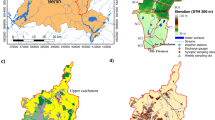
The deteriorating water quality in the Taihu Lake Basin has attracted widespread attention for many years, and is correlated with a sharp increase in the quantity of pollutant discharge such as agricultural fertilizers and industrial wastewater. In this study, several factors were selected for evaluating and regionalizing the water environmental capacity by ArcGIS spatial analysis, including geomorphologic characteristics, water quality goals, water body accessibility, water-dilution channels, and current water quality. Then, the spatial optimization of agriculture and industry was adjusted through overlay analysis, based on the balance between industrial space and water environmental capacity. The results show that the water environmental capacity gradually decreases from the west to the east, in contrast, the pollution caused by industrial and agricultural clustering is distributes along Taihu Lake, Gehu Lake and urban districts. The analysis of the agricultural space focuses on optimizing key protected areas of the Taihu Lake Basin, and the shores of Gehu Lake, optimally adjusting the second protected areas of the Taihu Lake Basin, and generally adjusting the urban areas of Changzhou and Wuxi cities. The analysis of industrial space focuses on optimizing the downtowns of Changzhou and Wuxi cities, optimally adjusting key protected areas and second protected areas of the Taihu Lake Basin, and generally adjusting the south and southwest of Gehu Lake. Lastly, some schemes of industrial and agricultural layouts and policies for the direction of industrial and agricultural development were proposed, reflecting a correlation between industry and agriculture and the water environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao Quansheng, Jiang Wenlai, 1998. Relationship between spatial differentiation of water environment capacity of rivers in China and macrolayout of industrial productivity. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 18(3): 205–211. (in Chinese)
Bao Quansheng, Wang Huadong, Cao Lijun, 1996. Research for division into districts of China’ s river water environmental capacity. China Environmental Science, 16(2): 87–91. (in Chinese)
Cao Lijun, Bao Quansheng, 1998. The coordination of the contradiction between the regional economic development and the shortage of the water environmental capacity-the macro layout of industrial productivity and the strategy of industrial structure adjustment. Economic Geography, 18(4): 54–61. (in Chinese)
Chen Wen, Zhuo Zhengkun, Zhao Haixia et al., 2008. Regionalization of water environmental risk and spatial development guidance: A case study of Wuxi City. Journal of Lake Sciences, 20(1): 129–134. (in Chinese)
Coyle R, 1997. The management of environmental problems for the large industrial zone: Issues and initiatives of Central and Eastern Europe and the Former Soviet Union. Industry and Environment, 19(4): 45–47. (in Chinese)
Deng Wei, He Yan, 1999. Water resource: One of the most important resource problems to be paid more attention to in the world in 21st century. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 12(2): 97–101. (in Chinese)
Duc T A, Vachaud G. Bonnet M P et al., 2007. Experimental investigation and modeling approach of the impact of urban wastewater on a tropical river: A case study of the Nhue River, Hanoi, Viet Nam. Journal of Hydrology, 334(3–4): 347–358. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.10.022
Freeman A M, 1993. The Measurement of Environmental and Resource Values: Theory and Methods. Washington, DC: Resources for the Future.
Gibert C S, Wendy A T, 2003. Watershed scale assessment of nitrogen and phosphorus loadings in the Indian River Lagoon Basin, Florida. Journal of Environmental Management, 67(4): 363–372. doi: 10.1016/S0301-4797(02)00220-7
Han Bingbing, Wang Dong, 2005. Research on object control of water environment capacity base on city classification. China Water Resources, (13): 145–149. (in Chinese)
Hu W P, Zhai Sh J, Zhu Z C et al., 2008. Impacts of the Yangtze River water transfer on the restoration of Lake Taihu. Ecology Engineering, 34: 30–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2008.05.018
Huang Yi, Cai Jialiang, Zheng Weishuang et al., 2009. Research progress in water ecological function regionalization and its approach at watershed scale. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 28(3): 542–548. (in Chinese)
Jiang Wen, 2005. Discussion on environmental problems and management in high-tech development zones. Environmental Science and Technology, 28(1): 67–68. (in Chinese)
Jin Xiangcan, Hu Xiaozhen, 2001. Control Technology of Eutrophical Lake in China. Specialist Dissertation of International Learning Workshop About Eutrophical Lake and Its Control Technology in China. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. (in Chinese)
Kunwar P S, Amrita M, Sarita S, 2005. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti River (India) using multivariate statistical techniques— A case study. Analytica Chimica Acta, 538(1–2): 355–374. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2005.02.006
Li Changfeng, Gao Junfeng, Cao Hui, 2002. Research status and rends on land use change impacts on water resources. Soil, 34(4): 191–196, 205. (in Chinese)
Li Ronggang, Xia Yuanling, Wu Anzhi et al., 2000. Pollutants sources and their discharging amount in Taihu Lake area of Jiangsu Province. Journal of Lake Science, 12(2): 147–153. (in Chinese)
Li Xin, 2005. Environmental characteristics during the process of urbanization in south Jiangsu with concentrated population. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 14(5): 595–599. (in Chinese)
Lin Xueqin, Fang Chuanglin, 2008. Research progress on the eco-environmental effect of industry agglomeration in city group. Progress in Geography, 27(3): 110–118. (in Chinese)
Ottaviano G I P, Tabuchi T, Thisse J F, 2002. Agglomeration and trade revisited. International Economic Review, 43(1): 409–436.
Qin Boqiang, Hu Weiping, Chen Weimin, 2004. Water Environment Evolution Process and Mechanism of Taihu Lake. Beijing: Science Press.
Ren W, Zhong Y, Meligrana J et al., 2003. Urbanization, land use and water quality in Shanghai: 1947–1996. Environment International, 29: 649–659. doi: 10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00051-5
Stone R, 2011. China Aims to Turn Tide against Toxic Lake Pollution. Science, 333(2): 1210–1211. doi: 10.1126/science.333.6047.1210
Sun W, Chen W, Chen C et al., 2011. Constraint regionalization of water environment and the guidance for industrial layout: A case study of Jiangsu Province. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 21(5): 937–948. doi: 10.1007/s11442-011-0891-0
Sun Wei, Chen Wen, Dun Xuejun et al., 2007. The feasible development regionalization of land use based on the ecological-economic analysis approach in lakeshore city area: Taking Wuxi as a case. Journal of Lake Sciences, 19(2): 190–196. (in Chinese)
Tian Wei, Yu Muqing, Liu Guiqin, 1998. Study on water environmental capacity and its influence on regional exploitation in the Tumen River region. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 18(2): 169–175. (in Chinese)
Verhoef E T, Nijkamp P, 2002. Externalities in urban sustainability environmental versus localization-type agglomeration externalities in a general spatial equilibrium model of a single-sector monocentric industrial city. Ecological Economics, 40(2): 157–179. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8009(01)00253-1
Virkanen J, 1998. Effect of urbanization on metal deposition in the bay of Töölönlahti, Southern Finland, Marine Pollution Bulletin, 36(9): 729–738. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(98)00053-8
Wang M, Webber M, Finlayson B et al., 2008. Rural industries and water pollution in China. Journal of Environmental Management, 86(4): 648–659. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.12.019
Wang Nianqi, Liang Tao, 1995. Study on the model of the environment evaluation of Beijing industrial layout. Environmental protection, (2): 33–34. (in Chinese)
Wang Shugong, Zhou Yongzhang, Mai Zhiqin, 2003. Study on the Programming framework of the ecological environment protection strategic of the urban agglomeration (Circle): A case study of cities group in the Pearl River Delta. China Population Resource and Environment, 13(4): 51–55. (in Chinese)
Webber M, Barnett J, Wang M et al., 2008. The Yellow River in transition. Environment Science Policy, 11(5): 422–429. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2008.02.002
Wilson K B, 1995. Water used to be scattered in the landscape: local understandings of soil erosion and land use planning in Southern Zimbabwe. Environment and History, 1(3): 281–296.
Xia Qing, 1989. Regionalization of the Water Environmental Protect Function Areas. Beijing: China Ocean Press. (in Chinese)
Yang Guishan, 2004. Introduction of the Basin Comprehensive Management. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese)
Zeng Yong, Wang Xiqin, 2010. Water environmental capacity model and its parameters sensitivity analysis for Xitiaoxi River in Zhejiang Province, China. China Environmental Science, 30(12): 1627–1632. (in Chinese)
Zhao Haixia, Wang Mei, Duan Xuejun, 2012. Spatial optimization of industrial clustering under the constraint of water environmental capacity in Taihu Lake Basin. China Environmental Science, 32(6): 647–652. (in Chinese)
Zhao N, Liu Y, Chen J N, 2009. Regional industrial production’s spatial distribution and water pollution control: A plant-level aggregation method for the case of a small region in China. Science of the Total Environment, 407(17): 4946–4953. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.05.023
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41130750, 70703033), ‘135’ Strategic Development Planning Project of Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. 2012135006)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, H., You, B., Duan, X. et al. Industrial and agricultural effects on water environment and its optimization in heavily polluted area in Taihu Lake Basin, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 23, 203–215 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-013-0593-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-013-0593-x