Abstract
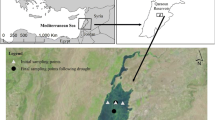
This study applied a multivariate model based on three simulated sensors to estimating water quality variables in Shitoukoumen Reservoir, Changchun City, Jilin Province, China, including concentration of total suspended matter, concentration of chlorophyll-a and non-pigment matter absorption. Two field campaigns for spectra measurements with a total of 40 samples were carried out on June 13 and September 23, 2008. The in-situ spectra were recalculated to the spectral bands and sensitivities of the instruments applied in this paper, i.e. Landsat TM, Alos and P6, by using the average method. And the recalculated spectra were used for estimating water quality variables by the single model and multivariate model. The results show that the multivariate model is superior to the single model as the multivariate model takes the combined effects of water components into consideration and can estimate water quality variables simultaneously. According to R 2 and RMSE, Alos is superior to other sensors for water quality variables estimation although the precision of non-pigment matter absorption inversion performed the second.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alison B B, James N K, 2005. The relative importance of chlorophyll and colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) to the prediction of the diffuse attenuation coefficient in shallow estuaries. Estuaries and Coasts, 28(5): 643–652. DOI: 10.1007/BF02732903
Bricaud A, Morel A, Prieur L, 1981. Absorption by dissolved organic matter of the sea (yellow substance) in the UV and visible domain. Limnology and Oceanography, 26(1): 43–53.
Carpenter D J, Carpenter S M, 1983. Modeling inland water quality using Landsat Data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 13:345–352. DOI: 10.1016/0034-4257(83)90035-4
David Doxaran, Samantha J L, Jean-Marie Froidefond, 2004. Mapping tidal and seasonal movements of the maximum turbidity zone in estuarine waters from remotely sensed (SPOT, LANDSAT) data. A semi-empirical approach. EARSeL eProceedings, 3(1): 54–68.
Dekker A G, Vos R J, Peters S W M, 2001. Comparison of remote sensing data, model results and in situ data for total suspended matter (TSM) in the southern Frisian lakes. The Science of the Total Environment, 268: 197–214. DOI: 10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00679-3
Giardino C, Pepe M, Brivio P A et al., 2001. Detecting chlorophyll, Secchi disk depth and surface temperature in a sub-alpine lake using Landsat imagery. The Science of the Total Environment, 268: 19–29. DOI: 10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00692-6
Giulietta S F, James L M, 2000. Ocean optics protocols for satellite ocean color sensor validation, Revision 2. NASA/TM-2000-209966, Goddard Space Flight Space Center.
Hellweger F L, Schlosser P, Lall U et al., 2004. Use of satellite imagery for water quality studies in New York Harbor. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 61(3): 437–448. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecss.2004.06.019
Kabbara N, Benkhelil J, Awad M et al., 2008. Monitoring water quality in the coastal area of Tripoli (Lebanon) using high-resolution satellite data. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 63(5): 488–495. DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.20-08.01.004
Le Chengfeng, Li Yunmei, Zha Yong et al., 2008. Seasonal variation of in water constituents’ absorption properties in Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake. Environmental Science, 9: 2448–2455. (in Chinese)
Liu Dianwei, Zhang Bai, Song Kaishan et al., 2006. Study on Regional Landscape Information of Remote Sensing. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese)
Ma R H, Tang J W, Dai J F, 2006. Bio-optical model with optimal parameter suitable for Taihu Lake in wager colour remote sensing. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 27(19):4305–4327. DOI: 10.1080/01431160600857428
Moed J R and Hallegraeff G M, 1978. Some problems in the estimation of chlorophyll-a and phaeopigments pre- and post-acidification spectrophotometric measurements. International Review of Hydrobiology, 63(6): 787–800. DOI: 10.1002/iroh.197-80630610
Pan Delu, Ma Ronghua, 2008. Several key problems of lake water quality remote sensing. Journal of Lake Sciences, 20(2):139–144. (in Chinese)
Prieur L, Sathyendranath S, 1981. An optical classification of coastal and oceanic waters based on the specific spectral absorption curves of phytoplankton pigments, dissolved organic matter, and other particulate materials. Limnology and Oceanography, 26: 671–689.
Su Y F, Liou J J, Hou J C et al., 2008. A multivariate model for coastal water quality mapping using satellite remote sensing images. Sensors, 8: 6321–6339. DOI: 10.3390/s8106321
Tang Junwu, Tian Guoliang, Wang Xiaoyong et al., 2004. The methods of water spectra measurement and analysis I: Above-Water Method. Journal of Remote Sensing, 8(1): 37–44. (in Chinese)
Xu Jingping, Zhang Bai, Lin Yu et al., 2007a. Estimating total suspended sediments concentrations and transparency with hyper-spectral reflectance in Shitoukoumen Reservoir, Jilin Province. Journal of Lake Sciences, 19(3): 269–274. (in Chinese)
Xu J P, Zhang B, Song K S et al., 2007b. Simplified bio-optical modelling of concentrations of total suspended matter in a turbid inland water condition. SPIE. 6752: 67521J1–67521J9. DOI: 10.1117/12.760493
Yang Yipeng, Wang Qiao, Wang Wenjie et al., 2004. Application and advances of remote sensing techniques in determining water quality. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 20(6): 6–12. (in Chinese)
Zepp R G, Callaghan T V, Erickson D J, 1998. Effects of enhanced solar ultraviolet radiation on biogeochemical cycles. Journal of Protochemistry Photobiology B: Biology, 46: 69–82. DOI: 10.1016/S1011-1344(98)00196-9
Zhang Yunlin, Qin Boqiang, Yang Longyuan, 2006. Spectral absorption coefficients of particulate matter and chromophoric dissolved organic matter in Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26(12): 3969–3979. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of Knowledge Innovation Programs of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KZCX2-YW-340, KZCX2-YW-341), Key Project of Jilin Province Scientific and Technological Development Program (No. 20080425)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, G., Liu, D., Song, K. et al. Application of multivariate model based on three simulated sensors for water quality variables estimation in Shitoukoumen Reservoir, Jilin Province, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 20, 337–344 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-010-0406-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-010-0406-4