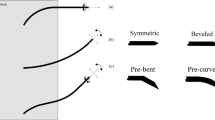
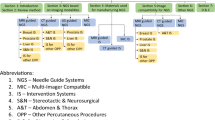
Abstract
Flexible needle systems showing multiple advantages in various medical scenarios, characterized by their flexibility, ease of operation, adaptable control and navigation capabilities. This paper presents a scientometric analysis of the research advancements in flexible needle systems. The paper reviews 498 articles with various perspectives from 1997 to 2023 and conducts a scientometric study including crucial institutions, journals, and article keywords. The analysis reveals that the knowledge domain of flexible needle systems is focused on signal processing, navigation, and control. Subsequently, a thorough examination of the current key research directions in the field of flexible needles is conducted, and an analysis of the challenges faced by this field is presented. The review also provides a comprehensive and integrated knowledge mind map to establish the flexible needle system’s information network. It offers valuable insights for researchers into future research directions and developments within the field of medical flexible needle systems in surgery.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable. No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Siegel, R.L., Miller, K.D., Jemal, A.: Cancer statistics, 2018. CA: Cancer J. Clin. 68(1), 7–30 (2018)
Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Dikshit, R., Eser, S., Mathers, C., Rebelo, M., Parkin, D.M., Forman, D., Bray, F.: Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in Globocan 2012. Int. J. Cancer 136(5), 359–386 (2015)
Jiang, W., Wu, D., Dong, W., Ding, J., Ye, Z., Zeng, P., Gao, Y.: Design and validation of a non-parasitic 2r1t parallel hand-held prostate biopsy robot with remote center of motion. J. Mech. Robot. 16(5), 051009 (2024)
Deb, S., Wijeysundera, H.C., Ko, D.T., Tsubota, H., Hill, S., Fremes, S.E.: Coronary artery bypass graft surgery vs percutaneous interventions in coronary revascularization: a systematic review. JAMA 310(19), 2086–2095 (2013)
Bravata, D.M., Gienger, A.L., McDonald, K.M., Sundaram, V., Perez, M.V., Varghese, R., Kapoor, J.R., Ardehali, R., Owens, D.K., Hlatky, M.A.: Systematic review: the comparative effectiveness of percutaneous coronary interventions and coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Ann. Intern. Med. 147(10), 703–716 (2007)
Kin, C., Snyder, K., Kiran, R.P., Remzi, F.H., Vogel, J.D.: Accidental puncture or laceration in colorectal surgery: a quality indicator or a complexity measure? Diseases Colon Rectum 56(2), 219–225 (2013)
Sandor, J., Ballagi, F., Nagy, A., Rákóczi, I.: A needle-puncture that helped to change the world of surgery. Surg. Endosc. 14(2), 201 (2000)
Robinson, S.R., Baird, R., Le, T., Wormald, P.J.: The incidence of complications after canine fossa puncture performed during endoscopic sinus surgery. Am. J. Rhinol. 19(2), 203–206 (2005)
Fu, C., Wang, N., Chen, B., Wang, P., Chen, H., Liu, W., Liu, L.: Surgical management of moderate basal ganglia intracerebral hemorrhage: comparison of safety and efficacy of endoscopic surgery, minimally invasive puncture and drainage, and craniotomy. World Neurosurg. 122, 995–1001 (2019)
Maria Joseph, F., Kumar, M., Hutapea, P., Dicker, A., Yu, Y., Podder, T.: Development of self-actuating flexible needle system for surgical procedures. J. Med. Devices 9(2), 020945 (2015)
Goksel, O., Dehghan, E., Salcudean, S.E.: Modeling and simulation of flexible needles. Med. Eng. Phys. 31(9), 1069–1078 (2009)
Engh, J.A., Podnar, G., Khoo, S.Y., Riviere, C.: Flexible needle steering system for percutaneous access to deep zones of the brain. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 32nd Annual Northeast Bioengineering Conference, pp. 103–104. IEEE (2006)
Van De Berg, N.J., Van Gerwen, D.J., Dankelman, J., Van Den Dobbelsteen, J.J.: Design choices in needle steering? A review. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 20(5), 2172–2183 (2014)
Scali, M., Pusch, T.P., Breedveld, P., Dodou, D.: Needle-like instruments for steering through solid organs: a review of the scientific and patent literature. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. [H] 231(3), 250–265 (2017)
Li, P., Yang, Z., Jiang, S.: Needle-tissue interactive mechanism and steering control in image-guided robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery: a review. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 56, 931–949 (2018)
Pacchierotti, C., Abayazid, M., Misra, S., Prattichizzo, D.: Teleoperation of steerable flexible needles by combining kinesthetic and vibratory feedback. IEEE Trans. Haptics 7(4), 551–556 (2014)
DiMaio, S.P., Salcudean, S.E.: Needle insertion modeling and simulation. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 19(5), 864–875 (2003)
Webster, R.J., III., Kim, J.S., Cowan, N.J., Chirikjian, G.S., Okamura, A.M.: Nonholonomic modeling of needle steering. Int. J. Robot. Res. 25(5–6), 509–525 (2006)
Minhas, D.S., Engh, J.A., Fenske, M.M., Riviere, C.N.: Modeling of needle steering via duty-cycled spinning. In: 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 2756–2759. IEEE (2007)
Goldenberg, S.L., Nir, G., Salcudean, S.E.: A new era: artificial intelligence and machine learning in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 16(7), 391–403 (2019)
Bharatha, A., Hirose, M., Hata, N., Warfield, S.K., Ferrant, M., Zou, K.H., Suarez-Santana, E., Ruiz-Alzola, J., D’amico, A., Cormack, R.A., et al.: Evaluation of three-dimensional finite element-based deformable registration of pre-and intraoperative prostate imaging. Med. Phys. 28(12), 2551–2560 (2001)
Gandia, R.M., Antonialli, F., Cavazza, B.H., Neto, A.M., Lima, D.A., Sugano, J.Y., Nicolai, I., Zambalde, A.L.: Autonomous vehicles: scientometric and bibliometric review. Transp. Rev. 39(1), 9–28 (2019)
Guo, G., Li, X.: A scientometric review of mobility-on-demand car-sharing systems. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 15(1), 212–229 (2022)
Misra, S., Reed, K.B., Schafer, B.W., Ramesh, K., Okamura, A.M.: Mechanics of flexible needles robotically steered through soft tissue. Int. J. Robot. Res. 29(13), 1640–1660 (2010)
Reed, K.B., Majewicz, A., Kallem, V., Alterovitz, R., Goldberg, K., Cowan, N.J., Okamura, A.M.: Robot-assisted needle steering. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 18(4), 35–46 (2011)
Alterovitz, R., Goldberg, K., Okamura, A.: Planning for steerable bevel-tip needle insertion through 2d soft tissue with obstacles. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1640–1645. IEEE (2005)
Park, W., Kim, J.S., Zhou, Y., Cowan, N.J., Okamura, A.M., Chirikjian, G.S.: Diffusion-based motion planning for a nonholonomic flexible needle model. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 4600–4605. IEEE (2005)
Patil, S., Burgner, J., Webster, R.J., Alterovitz, R.: Needle steering in 3-d via rapid replanning. IEEE Trans. Rob. 30(4), 853–864 (2014)
Abayazid, M., Roesthuis, R.J., Reilink, R., Misra, S.: Integrating deflection models and image feedback for real-time flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans. Rob. 29(2), 542–553 (2012)
Glozman, D., Shoham, M.: Image-guided robotic flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans. Rob. 23(3), 459–467 (2007)
Swaney, P.J., Burgner, J., Gilbert, H.B., Webster, R.J.: A flexure-based steerable needle: high curvature with reduced tissue damage. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60(4), 906–909 (2012)
Duindam, V., Alterovitz, R., Sastry, S., Goldberg, K.: Screw-based motion planning for bevel-tip flexible needles in 3d environments with obstacles. In: 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 2483–2488. IEEE (2008)
Ruggerio, C.A.: Sustainability and sustainable development: a review of principles and definitions. Sci. Total Environ. 786, 147481 (2021)
Tanaka, N., Higashimori, M., Kaneko, M., Kao, I.: Noncontact active sensing for viscoelastic parameters of tissue with coupling effect. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 58(3), 509–520 (2010)
Small, H.: Co-citation in the scientific literature: a new measure of the relationship between two documents. J. Am. Soc. Inform. Sci. 24(4), 265–269 (1973)
Olawumi, T.O., Chan, D.W.: A scientometric review of global research on sustainability and sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 183, 231–250 (2018)
Nishant, R., Kennedy, M., Corbett, J.: Artificial intelligence for sustainability: challenges, opportunities, and a research agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 53, 102104 (2020)
Borghesi, M., Ahmed, H., Nam, R., Schaeffer, E., Schiavina, R., Taneja, S., Weidner, W., Loeb, S.: Complications after systematic, random, and image-guided prostate biopsy. Eur. Urol. 71(3), 353–365 (2017)
Mottet, N., Bellmunt, J., Bolla, M., Briers, E., Cumberbatch, M.G., De Santis, M., Fossati, N., Gross, T., Henry, A.M., Joniau, S., et al.: Eau-estro-siog guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur. Urol. 71(4), 618–629 (2017)
Walz, J., Graefen, M., Chun, F.K.-H., Erbersdobler, A., Haese, A., Steuber, T., Schlomm, T., Huland, H., Karakiewicz, P.I.: High incidence of prostate cancer detected by saturation biopsy after previous negative biopsy series. Eur. Urol. 50(3), 498–505 (2006)
Robertson, N.L., Emberton, M., Moore, C.M.: Mri-targeted prostate biopsy: a review of technique and results. Nat. Rev. Urol. 10(10), 589–597 (2013)
Cai, K., Zhang, W., Foda, M.F., Li, X., Zhang, J., Zhong, Y., Liang, H., Li, H., Han, H., Zhai, T.: Miniature hollow gold nanorods with enhanced effect for in vivo photoacoustic imaging in the nir-ii window. Small 16(37), 2002748 (2020)
Wang, X., Tong, J., He, Z., Yang, X., Meng, F., Liang, H., Zhang, X., Luo, L.: Paclitaxel-potentiated photodynamic theranostics for synergistic tumor ablation and precise anticancer efficacy monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(5), 5476–5487 (2020)
Chen, J., Shuai, Z., Zhang, H., Zhao, W.: Path following control of autonomous four-wheel-independent-drive electric vehicles via second-order sliding mode and nonlinear disturbance observer techniques. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 68(3), 2460–2469 (2020)
Howe, R.D., Matsuoka, Y.: Robotics for surgery. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1(1), 211–240 (1999)
Satava, R.M.: Surgical robotics: the early chronicles: a personal historical perspective. Surg. Laparoscopy Endoscopy Percutaneous Tech. 12(1), 6–16 (2002)
Simaan, N., Yasin, R.M., Wang, L.: Medical technologies and challenges of robot-assisted minimally invasive intervention and diagnostics. Annu. Rev. Control Robot. Autonom. Syst. 1, 465–490 (2018)
Yulin, X., Ling, C., Xin, L., Aolei, Y., Yanran, L., Chunli, Z., Yanbo, L., Zhang, J.: Remote patrol service robot system design. J. Syst. Simul. 30(9), 3238 (2018)
Hagn, U., Nickl, M., Jörg, S., Passig, G., Bahls, T., Nothhelfer, A., Hacker, F., Le-Tien, L., Albu-Schäffer, A., Konietschke, R., et al.: The dlr miro: a versatile lightweight robot for surgical applications. Indust. Robot: Int. J. 35(4), 324–336 (2008)
Abolhassani, N., Patel, R., Moallem, M.: Needle insertion into soft tissue: a survey. Med. Eng. Phys. 29(4), 413–431 (2007)
Erp, J.B.V., Veen, H.A.V., Jansen, C., Dobbins, T.: Waypoint navigation with a vibrotactile waist belt. ACM Trans. Appl. Percept. (TAP) 2(2), 106–117 (2005)
Kuchenbecker, K.J., Gewirtz, J., McMahan, W., Standish, D., Martin, P., Bohren, J., Mendoza, P.J., Lee, D.I.: Verrotouch: High-frequency acceleration feedback for telerobotic surgery. In: Haptics: Generating and Perceiving Tangible Sensations: International Conference, EuroHaptics 2010, Amsterdam, July 8-10, 2010. Proceedings, Part I, pp. 189–196. Springer (2010)
Taylor, R.H., Mittelstadt, B.D., Paul, H.A., Hanson, W., Kazanzides, P., Zuhars, J.F., Williamson, B., Musits, B.L., Glassman, E., Bargar, W.L.: An image-directed robotic system for precise orthopaedic surgery. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 10(3), 261–275 (1994)
Searle, A., Kirkup, L.: A direct comparison of wet, dry and insulating bioelectric recording electrodes. Physiol. Meas. 21(2), 271 (2000)
Abolhassani, N., Patel, R.: Deflection of a flexible needle during insertion into soft tissue. In: 2006 International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 3858–3861. IEEE (2006)
Okamura, A.M., Simone, C., O’leary, M.D.: Force modeling for needle insertion into soft tissue. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51(10), 1707–1716 (2004)
Abolhassani, N., Patel, R.: Minimization of needle deflection in robot-assisted prostate brachytherapy. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 1, 269–271 (2006)
Albu-Schäffer, A., Ott, C., Hirzinger, G.: A unified passivity-based control framework for position, torque and impedance control of flexible joint robots. Int. J. Robot. Res. 26(1), 23–39 (2007)
Le Tien, L., Schaffer, A.A., Hirzinger, G.: Mimo state feedback controller for a flexible joint robot with strong joint coupling. In: Proceedings 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 3824–3830. IEEE (2007)
Zhu, B., Zhou, L., Pu, S., Fan, J., Ye, Y.: Advances and challenges in multimodal remote sensing image registration. IEEE J. Miniaturiz. Air Space Syst. (2023)
Zhu, F., Zhu, X., Huang, Z., Ding, M., Li, Q., Zhang, X.: Deep learning based data-adaptive descriptor for non-rigid multi-modal medical image registration. Signal Process. 183, 108023 (2021)
Zhou, Q., Guo, J., Ding, M., Zhang, X.: Guided filtering-based nonlocal means despeckling of optical coherence tomography images. Opt. Lett. 45(19), 5600–5603 (2020)
Cheng, J., Li, H., Xiao, F., Fenster, A., Zhang, X., He, X., Li, L., Ding, M.: Fully automatic plaque segmentation in 3-d carotid ultrasound images. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 39(12), 2431–2446 (2013)
Ghaffari, M., Samarasinghe, G., Jameson, M., Aly, F., Holloway, L., Chlap, P., Koh, E.-S., Sowmya, A., Oliver, R.: Automated post-operative brain tumour segmentation: a deep learning model based on transfer learning from pre-operative images. Magn. Reson. Imaging 86, 28–36 (2022)
Dong, X., Yan, S., Duan, C.: A lightweight vehicles detection network model based on yolov5. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 113, 104914 (2022)
Di Ieva, A., Russo, C., Liu, S., Jian, A., Bai, M.Y., Qian, Y., Magnussen, J.S.: Application of deep learning for automatic segmentation of brain tumors on magnetic resonance imaging: a heuristic approach in the clinical scenario. Neuroradiology 63, 1253–1262 (2021)
Salcudean, S.E., Sahebjavaher, R.S., Goksel, O., Baghani, A., Mahdavi, S.S., Nir, G., Sinkus, R., Moradi, M.: Biomechanical modeling of the prostate for procedure guidance and simulation. Soft tissue biomechanical modeling for computer assisted surgery, 169–198 (2012)
He, Y., Anderson, B.M., Cazoulat, G., Rigaud, B., Almodovar-Abreu, L., Pollard-Larkin, J., Balter, P., Liao, Z., Mohan, R., Odisio, B., et al.: Optimization of mesh generation for geometric accuracy, robustness, and efficiency of biomechanical-model-based deformable image registration. Med. Phys. 50(1), 323–329 (2023)
Shao, H.-C., Wang, J., Bai, T., Chun, J., Park, J.C., Jiang, S., Zhang, Y.: Real-time liver tumor localization via a single x-ray projection using deep graph neural network-assisted biomechanical modeling. Phys. Med. Biol. 67(11), 115009 (2022)
Ji, S., Ghajari, M., Mao, H., Kraft, R.H., Hajiaghamemar, M., Panzer, M.B., Willinger, R., Gilchrist, M.D., Kleiven, S., Stitzel, J.D.: Use of brain biomechanical models for monitoring impact exposure in contact sports. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 50(11), 1389–1408 (2022)
Hu, Y., Carter, T.J., Ahmed, H.U., Emberton, M., Allen, C., Hawkes, D.J., Barratt, D.C.: Modelling prostate motion for data fusion during image-guided interventions. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 30(11), 1887–1900 (2011)
Hu, Y., Ahmed, H.U., Taylor, Z., Allen, C., Emberton, M., Hawkes, D., Barratt, D.: Mr to ultrasound registration for image-guided prostate interventions. Med. Image Anal. 16(3), 687–703 (2012)
Hu, Y., Gibson, E., Ahmed, H.U., Moore, C.M., Emberton, M., Barratt, D.C.: Population-based prediction of subject-specific prostate deformation for mr-to-ultrasound image registration. Med. Image Anal. 26(1), 332–344 (2015)
Wang, Y., Cheng, J.-Z., Ni, D., Lin, M., Qin, J., Luo, X., Xu, M., Xie, X., Heng, P.A.: Towards personalized statistical deformable model and hybrid point matching for robust mr-trus registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(2), 589–604 (2015)
Wang, Y., Ni, D., Qin, J., Xu, M., Xie, X., Heng, P.-A.: Patient-specific deformation modelling via elastography: Application to image-guided prostate interventions. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 27386 (2016)
Lin, Y.-M., Paolucci, I., O’Connor, C.S., Anderson, B.M., Rigaud, B., Fellman, B.M., Jones, K.A., Brock, K.K., Odisio, B.C.: Ablative margins of colorectal liver metastases using deformable ct image registration and autosegmentation. Radiology 307(2), 221373 (2023)
Ramsey, C., Peterson, B., Hebert-Losier, K.: Measurement and reporting of footwear characteristics in running biomechanics: a systematic search and narrative synthesis of contemporary research methods. Sports Biomech. 22(3), 351–387 (2023)
Velec, M., Moseley, J., Svensson, S., Craig, T., Menard, C., Hårdemark, B., Brock, K., Jaffray, D.: Evaluation of biomechanical deformable image registration (dir) in a commercial radiation therapy planning system. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 93(3), 215–216 (2015)
Pan, Y., Wang, D., Chaudhary, M.F., Shao, W., Gerard, S.E., Durumeric, O.C., Bhatt, S.P., Barr, R.G., Hoffman, E.A., Reinhardt, J.M., et al.: Robust measures of image-registration-derived lung biomechanics in spiromics. J. Imaging 8(11), 309 (2022)
Xu, M., Wang, L.: Left ventricular myocardial motion tracking in cardiac cine magnetic resonance images based on a biomechanical model. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. (Preprint), 1–19 (2023)
Ben-Zikri, Y.K., Helguera, M., Fetzer, D., Shrier, D.A., Aylward, S.R., Chittajallu, D., Niethammer, M., Cahill, N.D., Linte, C.A.: A feature-based affine registration method for capturing background lung tissue deformation for ground glass nodule tracking. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng.: Imaging Visual. 10(5), 521–539 (2022)
Chen, J., Tian, J.: Real-time multi-modal rigid registration based on a novel symmetric-sift descriptor. Prog. Nat. Sci. 19(5), 643–651 (2009)
Theljani, A., Chen, K.: An augmented lagrangian method for solving a new variational model based on gradients similarity measures and high order regularization for multimodality registration. Inverse Problems and Imaging (2019)
Zhu, F., Ding, M., Zhang, X.: Self-similarity inspired local descriptor for non-rigid multi-modal image registration. Inf. Sci. 372, 16–31 (2016)
Li, Z., Huang, F., Zhang, J., Dashtbozorg, B., Abbasi-Sureshjani, S., Sun, Y., Long, X., Yu, Q., Haar Romeny, B., Tan, T.: Multi-modal and multi-vendor retina image registration. Biomed. Opt. Express 9(2), 410–422 (2018)
Heinrich, M.P., Jenkinson, M., Bhushan, M., Matin, T., Gleeson, F.V., Brady, M., Schnabel, J.A.: Mind: Modality independent neighbourhood descriptor for multi-modal deformable registration. Med. Image Anal. 16(7), 1423–1435 (2012)
Heinrich, M.P., Jenkinson, M., Papież, B.W., Brady, S.M., Schnabel, J.A.: Towards realtime multimodal fusion for image-guided interventions using self-similarities. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2013: 16th International Conference, Nagoya, Japan, September 22-26, 2013, Proceedings, Part I 16, pp. 187–194. Springer (2013)
Heinrich, M.P., Jenkinson, M., Papież, B.W., Glesson, F.V., Brady, S.M., Schnabel, J.A.: Edge-and detail-preserving sparse image representations for deformable registration of chest mri and ct volumes. In: Information Processing in Medical Imaging: 23rd International Conference, IPMI 2013, Asilomar, CA, USA, June 28–July 3, 2013. Proceedings 23, pp. 463–474. Springer (2013)
Kasiri, K., Fieguth, P., Clausi, D.A.: Self-similarity measure for multi-modal image registration. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 4498–4502. IEEE (2016)
Yang, F., Ding, M., Zhang, X., Hou, W., Zhong, C.: Non-rigid multi-modal medical image registration by combining l-bfgs-b with cat swarm optimization. Inf. Sci. 316, 440–456 (2015)
Abdel-Basset, M., Fakhry, A.E., El-Henawy, I., Qiu, T., Sangaiah, A.K.: Feature and intensity based medical image registration using particle swarm optimization. J. Med. Syst. 41, 1–15 (2017)
Shen, L., Huang, X., Fan, C., Li, Y.: Enhanced mutual information-based medical image registration using a hybrid optimisation technique. Electron. Lett. 54(15), 926–928 (2018)
Powell, M.J.: An efficient method for finding the minimum of a function of several variables without calculating derivatives. Comput. J. 7(2), 155–162 (1964)
Thevenaz, P., Unser, M.A.: Spline pyramids for intermodal image registration using mutual information. Wavelet Appl. Signal Image Process. V 3169, 236–247 (1997). (SPIE)
Thévenaz, P., Unser, M.: Optimization of mutual information for multiresolution image registration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 9(12), 2083–2099 (2000)
Woo, J., Stone, M., Prince, J.L.: Multimodal registration via mutual information incorporating geometric and spatial context. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(2), 757–769 (2014)
Rivaz, H., Karimaghaloo, Z., Collins, D.L.: Self-similarity weighted mutual information: a new nonrigid image registration metric. Med. Image Anal. 18(2), 343–358 (2014)
Razlighi, Q.R., Kehtarnavaz, N.: Spatial mutual information as similarity measure for 3-d brain image registration. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2, 27–34 (2014)
Lou, Y., Irimia, A., Vela, P.A., Chambers, M.C., Van Horn, J.D., Vespa, P.M., Tannenbaum, A.R.: Multimodal deformable registration of traumatic brain injury mr volumes via the Bhattacharyya distance. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60(9), 2511–2520 (2013)
Loeckx, D., Slagmolen, P., Maes, F., Vandermeulen, D., Suetens, P.: Nonrigid image registration using conditional mutual information. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 29(1), 19–29 (2009)
Wang, F., Vemuri, B.C., Rao, M., Chen, Y.: A new & robust information theoretic measure and its application to image alignment. In: Biennial International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging, pp. 388–400. Springer (2003)
Chen, H.-M., Varshney, P.K.: Mutual information-based ct-mr brain image registration using generalized partial volume joint histogram estimation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 22(9), 1111–1119 (2003)
Chen, H.-M., Varshney, P.K., Arora, M.K.: Performance of mutual information similarity measure for registration of multitemporal remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 41(11), 2445–2454 (2003)
Studholme, C., Hill, D.L., Hawkes, D.J.: An overlap invariant entropy measure of 3d medical image alignment. Pattern Recogn. 32(1), 71–86 (1999)
Viola, P., Wells, W.M., III.: Alignment by maximization of mutual information. Int. J. Comput. Vision 24(2), 137–154 (1997)
Rueckert, D., Sonoda, L.I., Hayes, C., Hill, D.L., Leach, M.O., Hawkes, D.J.: Nonrigid registration using free-form deformations: application to breast mr images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 18(8), 712–721 (1999)
Shamonin, D.P., Bron, E.E., Lelieveldt, B.P., Smits, M., Klein, S., Staring, M., Initiative, A.D.N.: Fast parallel image registration on cpu and gpu for diagnostic classification of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neuroinform. 7, 50 (2014)
Lin, Y., Medioni, G.: Mutual information computation and maximization using gpu. In: 2008 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 1–6. IEEE (2008)
Hu, Y., Modat, M., Gibson, E., Ghavami, N., Bonmati, E., Moore, C.M., Emberton, M., Noble, J.A., Barratt, D.C., Vercauteren, T.: Label-driven weakly-supervised learning for multimodal deformable image registration. In: 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), pp. 1070–1074. IEEE (2018)
Yang, X., Kwitt, R., Styner, M., Niethammer, M.: Quicksilver: Fast predictive image registration-a deep learning approach. Neuroimage 158, 378–396 (2017)
Zhao, S., Lau, T., Luo, J., Eric, I., Chang, C., Xu, Y.: Unsupervised 3d end-to-end medical image registration with volume tweening network. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 24(5), 1394–1404 (2019)
Balakrishnan, G., Zhao, A., Sabuncu, M.R., Guttag, J., Dalca, A.V.: An unsupervised learning model for deformable medical image registration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9252–9260 (2018)
Kim, B., Kim, D.H., Park, S.H., Kim, J., Lee, J.-G., Ye, J.C.: Cyclemorph: cycle consistent unsupervised deformable image registration. Med. Image Anal. 71, 102036 (2021)
Fan, J., Cao, X., Xue, Z., Yap, P.-T., Shen, D.: Adversarial similarity network for evaluating image alignment in deep learning based registration. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2018: 21st International Conference, Granada, Spain, September 16-20, 2018, Proceedings, Part I, pp. 739–746. Springer (2018)
Duan, L., Yuan, G., Gong, L., Fu, T., Yang, X., Chen, X., Zheng, J.: Adversarial learning for deformable registration of brain mr image using a multi-scale fully convolutional network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 53, 101562 (2019)
Cai, C., Sun, C., Han, Y., Zhang, Q.: Clinical flexible needle puncture path planning based on particle swarm optimization. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 193, 105511 (2020)
Zhang, L., Li, C., Fan, Y., Zhang, X., Zhao, J.: Physician-friendly tool center point calibration method for robot-assisted puncture surgery. Sensors 21(2), 366 (2021)
Zhang, W., Ma, Z., Wang, H., Deng, J., Li, P., Jia, Y., Dong, Y., Sha, H., Yan, F., Tu, W.: Study on automatic ultrasound scanning of lumbar spine and visualization system for path planning in lumbar puncture surgery. Math. Biosci. Eng. 20(1), 613–623 (2023)
Duindam, V., Xu, J., Alterovitz, R., Sastry, S., Goldberg, K.: Three-dimensional motion planning algorithms for steerable needles using inverse kinematics. Int. J. Robot. Res. 29(7), 789–800 (2010)
Alterovitz, R., Lim, A., Goldberg, K., Chirikjian, G.S., Okamura, A.M.: Steering flexible needles under markov motion uncertainty. In: 2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 1570–1575. IEEE (2005)
Ratschan, S., She, Z.: Safety verification of hybrid systems by constraint propagation-based abstraction refinement. ACM Trans. Embedded Comput. Syst. (TECS) 6(1), 8 (2007)
Zan, J.: Research on robot path perception and optimization technology based on whale optimization algorithm. J. Comput. Cogn. Eng. 1(4), 201–208 (2022)
Alterovitz, R., Siméon, T., Goldberg, K.: The stochastic motion roadmap: A sampling framework for planning with markov motion uncertainty. In: Robotics: Science and Systems (2007)
Duindam, V., Xu, J., Alterovitz, R., Sastry, S., Goldberg, K.: 3d motion planning algorithms for steerable needles using inverse kinematics. In: Algorithmic Foundation of Robotics VIII: Selected Contributions of the Eight International Workshop on the Algorithmic Foundations of Robotics, pp. 535–549. Springer (2010)
Wu, T., Liu, J., Liu, J., Huang, Z., Wu, H., Zhang, C., Bai, B., Zhang, G.: A novel ai-based framework for aoi-optimal trajectory planning in uav-assisted wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 21(4), 2462–2475 (2021)
Madridano, A., Al-Kaff, A., Martín, D., De La Escalera, A.: Trajectory planning for multi-robot systems: Methods and applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 173, 114660 (2021)
Baaj, M.H., Mahmassani, H.S.: An ai-based approach for transit route system planning and design. J. Adv. Transp. 25(2), 187–209 (1991)
Patil, S., Alterovitz, R.: Interactive motion planning for steerable needles in 3d environments with obstacles. In: 2010 3rd IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, pp. 893–899. IEEE (2010)
Moreira, P., Patil, S., Alterovitz, R., Misra, S.: Needle steering in biological tissue using ultrasound-based online curvature estimation. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 4368–4373. IEEE (2014)
Sun, W., Patil, S., Alterovitz, R.: High-frequency replanning under uncertainty using parallel sampling-based motion planning. IEEE Trans. Rob. 31(1), 104–116 (2015)
Xiong, J., Li, X., Gan, Y., Xia, Z.: Path planning for flexible needle insertion system based on improved rapidly-exploring random tree algorithm. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, pp. 1545–1550. IEEE (2015)
Tsumura, R., Kim, J.S., Iwata, H., Iordachita, I.: Preoperative needle insertion path planning for minimizing deflection in multilayered tissues. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 3(3), 2129–2136 (2018)
Silva, M., Ambrósio, J.: Kinematic data consistency in the inverse dynamic analysis of biomechanical systems. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 8, 219–239 (2002)
Li, G., Fang, Q., Xu, T., Zhao, J., Cai, H., Zhu, Y.: Inverse kinematic analysis and trajectory planning of a modular upper limb rehabilitation exoskeleton. Technol. Health Care 27(S1), 123–132 (2019)
Liu, T., Jackson, R., Franson, D., Poirot, N.L., Criss, R.K., Seiberlich, N., Griswold, M.A., Çavuşoğlu, M.C.: Iterative Jacobian-based inverse kinematics and open-loop control of an mri-guided magnetically actuated steerable catheter system. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 22(4), 1765–1776 (2017)
Huda, M.A.N., Susilo, S.H., Adhi, P.M.: Implementation of inverse kinematic and trajectory planning on 6-dof robotic arm for straight-flat welding movement. Logic: Jurnal Rancang Bangun dan Teknologi 22(1), 51–61 (2022)
Silva, D., Garrido, J., Riveiro, E.: Stewart platform motion control automation with industrial resources to perform cycloidal and oceanic wave trajectories. Machines 10(8), 711 (2022)
Xu, J., Duindam, V., Alterovitz, R., Goldberg, K.: Motion planning for steerable needles in 3d environments with obstacles using rapidly-exploring random trees and backchaining. In: 2008 IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering, pp. 41–46. IEEE (2008)
Lu, J., She, Z., Liu, B., Ge, S.S.: Analysis and verification of input-to-state stability for nonautonomous discrete-time switched systems via semidefinite programming. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 66(9), 4452–4459 (2020)
She, Z., Li, M.: Over-and under-approximations of reachable sets with series representations of evolution functions. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 66(3), 1414–1421 (2020)
Zhang, X., Zhan, Y., Ding, M., Hou, W., Yin, Z.: Decision-based non-local means filter for removing impulse noise from digital images. Signal Process. 93(2), 517–524 (2013)
Wu, K., Li, B., Zhang, Y., Dai, X.: Review of research on path planning and control methods of flexible steerable needle puncture robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 27(1), 91–112 (2022)
Kallem, V., Cowan, N.J.: Image guidance of flexible tip-steerable needles. IEEE Trans. Rob. 25(1), 191–196 (2009)
Khadem, M., Rossa, C., Usmani, N., Sloboda, R.S., Tavakoli, M.: Feedback-linearization-based 3d needle steering in a Frenet-Serret frame using a reduced order bicycle model. In: 2017 American Control Conference (ACC), pp. 1438–1443. IEEE (2017)
Lapouge, G., Troccaz, J., Poignet, P.: Multi-rate unscented Kalman filtering for pose and curvature estimation in 3d ultrasound-guided needle steering. Control. Eng. Pract. 80, 116–124 (2018)
Rucker, D.C., Das, J., Gilbert, H.B., Swaney, P.J., Miga, M.I., Sarkar, N., Webster, R.J.: Sliding mode control of steerable needles. IEEE Trans. Rob. 29(5), 1289–1299 (2013)
Motaharifar, M., Talebi, H.A., Abdollahi, F., Afshar, A.: Nonlinear adaptive output-feedback controller design for guidance of flexible needles. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 20(4), 1912–1919 (2014)
Fallahi, B., Rossa, C., Sloboda, R.S., Usmani, N., Tavakoli, M.: Sliding-based image-guided 3d needle steering in soft tissue. Control. Eng. Pract. 63, 34–43 (2017)
Fallahi, B., Waine, M., Rossa, C., Sloboda, R., Usmani, N., Tavakoli, M.: An integrator-backstepping control approach for three-dimensional needle steering. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 24(5), 2204–2214 (2019)
Khadem, M., Rossa, C., Usmani, N., Sloboda, R.S., Tavakoli, M.: Geometric control of 3d needle steering in soft-tissue. Automatica 101, 36–43 (2019)
Lu, M., Zhang, Y., Lim, C.M., Ren, H.: Flexible needle steering with tethered and untethered actuation: Current states, targeting errors, challenges and opportunities. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 51(5), 905–924 (2023)
Karimi, S., Konh, B.: Kinematics modelling and dynamics analysis of an sma-actuated active flexible needle for feedback-controlled manipulation in phantom. Med. Eng. Phys. 107, 103846 (2022)
Chen, X., Yan, Y., Li, A., Wang, T., Wang, Y.: Robot-assisted needle insertion for ct-guided puncture: Experimental study with a phantom and animals. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 46(1), 128–135 (2023)
Sugiyama, K., Matsuno, T., Kamegawa, T., Hiraki, T., Nakaya, H., Yanou, A., Minami, M.: Reaction force analysis of puncture robot for ct-guided interventional radiology in animal experiment. In: 2015 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), pp. 7–12. IEEE (2015)
Martinez, R.M., Ptacek, W., Schweitzer, W., Kronreif, G., Fürst, M., Thali, M.J., Ebert, L.C.: Ct-guided, minimally invasive, postmortem needle biopsy using the b-r ob ii needle-positioning robot. J. Forensic Sci. 59(2), 517–521 (2014)
Maurin, B., Doignon, C., Gangloff, J., Bayle, B., Mathelin, M., Piccin, O., Gangi, A.: Ctbot: A stereotactic-guided robotic assistant for percutaneous procedures of the abdomen. In: Medical Imaging 2005: Visualization, Image-Guided Procedures, and Display, vol. 5744, pp. 241–250. SPIE (2005)
Fischer, G.S., Iordachita, I., Csoma, C., Tokuda, J., DiMaio, S.P., Tempany, C.M., Hata, N., Fichtinger, G.: Mri-compatible pneumatic robot for transperineal prostate needle placement. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 13(3), 295–305 (2008)
Bricault, I., Zemiti, N., Jouniaux, E., Fouard, C., Taillant, E., Dorandeu, F., Cinquin, P.: Light puncture robot for ct and mri interventions. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 27(3), 42–50 (2008)
Song, S.-E., Cho, N.B., Fischer, G., Hata, N., Tempany, C., Fichtinger, G., Iordachita, I.: Development of a pneumatic robot for mri-guided transperineal prostate biopsy and brachytherapy: New approaches. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 2580–2585. IEEE (2010)
Seitel, A., Walsh, C.J., Hanumara, N.C., Shepard, J.-A., Slocum, A.H., Meinzer, H.-P., Gupta, R., Maier-Hein, L.: Development and evaluation of a new image-based user interface for robot-assisted needle placements with the robopsy system. In: Medical Imaging 2009: Visualization, Image-Guided Procedures, and Modeling, vol. 7261, pp. 305–313. SPIE (2009)
Liu, H.-H., Li, L.-J., Shi, B., Xu, C.-W., Luo, E.: Robotic surgical systems in maxillofacial surgery: a review. Int. J. Oral Sci. 9(2), 63–73 (2017)
Tianmiao, W., Jun, W., Da, L., Lei, H., Wenyong, L.: An internet robot assistant tele-neurosurgery system case. In: 2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 2845–2849. IEEE (2006)
Duan, X.-G., Bian, G.-B., Zhao, H.-H., Wang, X.-T., Huang, Q.: A medical robot for needle placement therapy in liver cancer. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 11, 263–269 (2010)
Jiang, S., Feng, W., Lou, J., Yang, Z., Liu, J., Yang, J.: Modelling and control of a five-degrees-of-freedom pneumatically actuated magnetic resonance-compatible robot. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 10(2), 170–179 (2014)
Jiang, S., Yuan, W., Yang, Y., Zhang, D., Liu, N., Wang, W.: Modelling and analysis of a novel ct-guided puncture robot for lung brachytherapy. Adv. Robot. 31(11), 557–569 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFE0206900).
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No.2018YFE0206900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SL.Z. JC.C. and HK.S. wrote the main manuscript text, SL.Z. and JC.C. prepared Figures 1–3, SL.Z. and HK.S. prepared figures 4–8, SL.Z. Z.Q and H.Z. prepared figures 9. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
I declare that the authors have no conflict of interest as defined by Springer, or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion reported in this paper.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
I have read and understood the publishing policy, and submit this manuscript in accordance with this policy.
Consent for publication
I have read and understood the publishing policy and submit this manuscript in accordance with this policy.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Chen, J., Sun, H. et al. A scientometric review of medical flexible needle systems in surgery: signal processing, navigation and control. SIViP (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03179-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03179-0