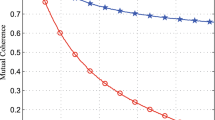
Abstract
Compressive sensing (CS) provides a set of powerful techniques for the reconstruction of signals with a sparse representation in some particular domain, based on a reduced number of available samples (measurements). The CS application on real-life signals is directly affected by the existence of a basis or a dictionary in which the signal is sparse or highly concentrated (approximately sparse). Motivated by the fact that the time-axis scaling (dilation) factor of Hermite functions (HF) considerably affects the signal sparsity and concentration, in this paper, we propose a CS framework for the signal reconstruction based on a matching pursuit approach using an optimal dilation factor.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sandryhaila, A., Saba, S., Puschel, M., Kovacevic, J.: Efficient compression of QRS complexes using Hermite expansion. IEEE Trans. Signal Proccess. 60(2), 947–955 (2012)
Sandryhaila, A., Kovacevic, J., Püschel, M.: Compression of QRS complexes using Hermite expansion. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 581–584. (2011)
Márquez, D.G., Otero, A., García, C.A., Presedo, J.: A study on the representation of QRS complexes with the optimum number of Hermite functions. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 22, 11–18 (2015)
Mahadevan, A., Acharya, S., Sheffer, D.B., Mugler, D.H.: Ballistocardiogram artifact removal in EEG-fMRI signals using discrete Hermite transforms. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2(6), 839–853 (2008)
Brajović, M., Orović, I., Daković, M., Stanković, S.: Gradient-based signal reconstruction algorithm in the Hermite transform domain. Electron. Lett. 52(1), 41–43 (2016)
Brajović, M., Orović, I., Daković, M., Stanković, S.: On the parameterization of Hermite transform with application to the compression of QRS complexes. Signal Process 131, 113–119 (2017)
Conte, L.R.L., Merletti, R., Sandri, G.V.: Hermite expansion of compact support waveforms: applications to myoelectric signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 41(12), 1147–1159 (1994)
Laguna, P., Jané, R., Olmos, S., Thakor, N.V., Rix, H., Caminal, P.: Adaptive estimation of QRS complex wave features of ECG signal by the Hermite model. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 34(1), 58–68 (1996)
Brajović, M., Orović, I., Beko, M., Stanković, S.: Parameter optimization of orthogonal discrete Hermite transform formed using eigenvectors of a symmetric tridiagonal matrix. Digital Signal Process. 117, 103140 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2021.103140
Ghavami, M., Michael, L.B., Kohno, R.: Ultra Wideband Signals and Systems in Communication Engineering, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (2007)
Brajović, M., Orović, I., Daković, M., Stanković, S.: Compressive sensing of sparse signals in the Hermite transform basis. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 54(2), 950–967 (2018)
Clary, S., Mugler, D.H.: Shifted Fourier matrices and their tridiagonal commutors. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 24(3), 809–821 (2003)
de Oliveira Neto, J.R., Lima, J.B.: Discrete fractional Fourier transforms based on closed-form Hermite–Gaussian-like DFT eigenvectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65(23), 6171–6184 (2017)
Pei, S.C., Lai, Y.C.: Signal scaling by centered discrete dilated Hermite functions. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(1), 498–503 (2012)
Kuznetsov, A., Kwaśnicki, M.: Minimal Hermite-type eigenbasis of the discrete Fourier transform. J Fourier Anal Appl 25, 1053–1079 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00041-018-9600-z
Lagerholm, M., Peterson, C., Braccini, G., Edenbranhdt, L., Sörnmo, L.: Clustering ECG complexes using Hermite functions and self-organizing maps. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 47(7), 838–848 (2000)
Lazaridis, P., Debarge, G., Gallion, P.: Discrete orthogonal Gauss–Hermite transform for optical pulse propagation analysis. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 20, 1508–1513 (2003)
Park, W., Leibon, G., Rockmore, D.N., Chirikjian, G.S.: Accurate image rotation using Hermite expansions. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 18(9), 1988–2003 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2009.2024582
Leibon, G., Rockmore, D.N., Park, W., Taintor, R., Chirikjian, G.S.: A fast Hermite transform. Theor. Comput. Sci. 409(2), 211–228 (2008)
Kortchagine, D., Krylov, A.: Image Database Retrieval by Fast Hermite Projection Method. International Conference Graphicon, pp. 308–311, Russia (2005)
Sejdić, E., Can, A., Chaparro, L.F., Steele, C.M., Chau, T.: Compressive sampling of swallowing accelerometry signals using time-frequency dictionaries based on modulated discrete prolate spheroidal sequences. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2012, 101 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-6180-2012-101
Stanković, L.J., Mandic, D., Daković, M., Kisil, I.: Demystifying the coherence index in compressive sensing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 37(1), 152–162 (2020)
Stanković, L.J., Stanković, S., Amin, M.: Missing samples analysis in signals for applications to L-estimation and compressive sensing. Signal Process. 94, 401–408 (2014)
Needell, D., Tropp, J.A.: CoSaMP: iterative signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples. App. Comput. Harmonic Anal. 20(3), 301–321 (2009)
Stanković, L.J., Brajović, M., Stanković, I., Lerga, J., Daković, M.: RANSAC-Based Signal Denoising Using Compressive Sensing. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 40, 3907–3928 (2021)
Candès, E.J.: The restricted isometry property and its implications for compressed sensing. Comptes Rendus Mathematique 346(9), 589–592 (2008)
PhysioNet: MIT-BIH ECG Compression Test Database, http://www.physionet.org/physiobank/database/cdb, last access – May (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Brajović, M., Orović, I., Beko, M. et al. Reconstruction of signals with sparse representation in optimally dilated Hermite basis. SIViP 17, 2789–2797 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02496-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02496-0