Abstract
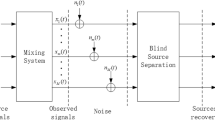
It is essential to accurately estimate the mixing matrix and determine the number of source signals in the problem of underdetermined blind source separation. The problem is solved in this paper via sparse subspace clustering, which can be used to found low-dimensional data structures in observed data. To enhance the linear clustering characteristics of time-frequency points, the high energy points are reserved first, and the angle difference of real and imaginary portions is employed to screen single source points. After that, the time-frequency points are clustered using sparse subspace clustering, and the number of source signals is identified. Finally, the local density of eigenvectors is used to determine the mixing matrix. The proposed algorithm is capable of accurately estimating the mixing matrix. It has strong robustness and adaptable to a wide range of mixing circumstances. The proposed method’s effectiveness is demonstrated by theoretical analysis and experimental data.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sadhu, A., Narasimhan, S.: A review of output-only structural mode identification literature employing blind source separation methods. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 94, 415–431 (2017)
Miyabe, S., Ono, N., Makino, S.: Blind compensation of interchannel sampling frequency mismatch for ad hoc microphone array based on maximum likelihood estimation. Signal Process. 107, 185–196 (2015)
Yang, Y., Nagarajaiah, S.: Output-only modal identification by compressed sensing: Non-uniform low-rate random sampling. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 56–57, 15–34 (2015)
Xiong, K.-L., Yang, A.: Blind array signal separation and DOA estimation method based on eigenvalue decomposition. Signal Image Video Process. 15, 1107–1113 (2021)
Mucarquer, J.A., Prado, P., Escobar, M.-J., et al.: Improving EEG muscle artifact removal with an EMG array. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 69(3), 815–824 (2020)
Li, Y., Nie, W., Ye, F., et al.: A complex mixing matrix estimation algorithm in under-determined blind source separation problems. Signal Image Video Process. 11, 301–308 (2017)
Yu, K., Yang, K., Bai, Y.: Estimation of modal parameters using the sparse component analysis based underdetermined blind source separation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 45(2), 302–316 (2014)
Li, Y., Wang, Y., Dong, Q.: A novel mixing matrix estimation algorithm in instantaneous underdetermined blind source separation. Signal Image Video Process. 14, 1001–1008 (2020)
Zou, L., Chen, X., Wang, Z.J.: Underdetermined joint blind source separation for two datasets based on tensor decomposition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(5), 673–677 (2016)
Bofill, P., Zibulevsky, M.: Underdetermined blind source separation using sparse representations. Signal Process. 81(11), 2353–2362 (2001)
Rongjie, W., Yiju, Z., Haifeng, Z.: Retracted: a method of underdetermined blind source separation with an unknown number of sources. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. (2011)
Amini, F., Hedayati, Y.: Underdetermined blind modal identification of structures by earthquake and ambient vibration measurements via sparse component analysis. J. Sound Vib. 366, 117–132 (2016)
Yang, J.-J., Liu, H.-L.: Blind identification of the underdetermined mixing matrix based on k-weighted hyperline clustering. Neurocomputing 149, 483–489 (2015)
Sun, J., Li, Y., Wen, J., et al.: Novel mixing matrix estimation approach in underdetermined blind source separation. Neurocomputing 173, 623–632 (2016)
Lu, J., Cheng, W., He, D., et al.: A novel underdetermined blind source separation method with noise and unknown source number. J. Sound Vib. 457, 67–91 (2019)
Li, C.-G., You, C., Vidal, R.: Structured sparse subspace clustering: A joint affinity learning and subspace clustering framework. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(6), 2988–3001 (2017)
Elhamifar, E., Vidal, R.: Clustering disjoint subspaces via sparse representation, pp. 1926–1929 (2010)
Boyd, S., Parikh, N., Chu, E., et al.: Distributed Optimization and Statistical Learning via the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 2011)
Luxburg, U.: A tutorial on spectral clustering. Stat. Comput. 17, 395–416 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y. et al. A novel mixing matrix estimation method for underdetermined blind source separation based on sparse subspace clustering. SIViP 17, 91–98 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-022-02207-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-022-02207-1