Abstract
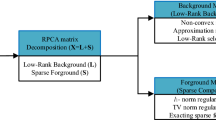
Moving object detection is a fundamental and necessary step in many computer vision algorithms. These algorithms are built in many intelligent devices such as in the smartphones, the tachographs and the personal video recorders. Recently, the methods for performing the moving object detection based on the low-rank representation have been proposed. For these methods, it is assumed that the background is represented by a low-rank matrix. On the other hand, the foreground objects cannot be represented by low-rank matrices. They are seen as the outliers. Hence, detecting the contiguous outliers in the low-rank representation (DECELOR) can be formulated as an extension of the robust principal component analysis problem. This method fully utilizes the spatial continuity of the foreground regions. To achieve a more accurate detection, this paper integrates both the concave penalty function and the priori target rank information into a single optimization problem based on the DECELOR formulation. The optimization problem is efficiently solved by an alternating direction scheme. The computer numerical simulation results on the real-world scenes demonstrate the superiority of our method in terms of the effective handling of a wide range of complex scenarios.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mehdi, S., Hoda, R., Alireza, A., Mahoud, R.H., Shervin, S.: A receiver aware H.264/AVC encoder for decoder complexity control in mobile applications. Signal Image Video Process. 11(3), 431–438 (2016)
Soumya, T., Thampi, S.M.: Self-organized night video enhancement for surveillance systems. Signal Image Video Process. 11(1), 57–64 (2017)
Shi, Y., Wang, X.P., Fan, H.F.: Light-weight white-box encryption scheme with random padding for wearable consumer electronic devices. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 63(1), 44–52 (2017)
Raheja, J.L., Chaudhary, A., Nandhini, K., Maiti, S.: Pre-consultation help necessity detection based on gait recognition. SIViP 9(6), 1357–1363 (2015)
Khan, M., Shah, T., Batool, S.I.: A new implementation of chaotic S-boxes in CAPTCHA. SIViP 10(2), 293–300 (2016)
Artur, J., Leonardo, A.B.T., William, R.S.: Novel approaches to human activity recognition based on accelerometer data. SIViP 12(7), 1387–1394 (2018)
Tao, H., Lu, X.: Contour-based smoky vehicle detection from surveillance video for alarm systems. Signal Image Video Process. 13, 217–225 (2019)
Hadiuzzaman, M., Haque, N., Rahman, F., Hossain, S., Siam, M.R.K., Qiu, T.Z.: Pixel-based heterogeneous traffic measurement considering shadow and illumination variation. SIViP 11(7), 1245–1252 (2017)
Shimada, A., Arita, D., Taniguchi, R.I.: Dynamic control of adaptive mixture-of-Gaussians background model. In: IEEE International Conference on Video and Signal Based Surveillance, pp. 5 (2006)
Barnich, O., Droogenbroeck, M.V.: ViBe: a universal background subtraction algorithm for video sequences. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20(6), 1709–1724 (2011)
Hofmann, M., Tiefenbacher, P., Rigoll, G.: Background segmentation with feedback: the Pixel-based adaptive segmenter. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 38–43 (2012)
Candès, E.J., Li, X., Ma, Y., Wright, J.: Robust principal component analysis? J. ACM 58(3), 1–37 (2009)
Wright, J., Ganesh, A., Rao S., Ma, Y.: Robust principal component analysis: exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices, arXiv:0905.0233v2
Wagner, A., Wright, J., Ganesh, A., Zhou, Z.H., Ma, Y.: Towards a practical face recognition system: robust registration and illumination by sparse representation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 597–604 (2009)
Cai, N., Zhou, Y., Ye, Q., Liu, G., Wan, H., Chen, X.D.: A new IC solder joint inspection via robust principal component analysis. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 7(2), 300–309 (2017)
Peng, Y., Ganesh, A., Wright, J., Xu, W., Ma, Y.: RASL: robust alignment by sparse and low-rank decomposition for linearly correlated images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(11), 2233–2246 (2012)
Yao, M.H., Jie, L.I., Wang, X.B.: Solar cells surface defects detection of using RPCA method. Chin. J. Comput. 36(9), 1943–1952 (2013)
Bouwmans, T., Zahzah, E.H.: Robust PCA via principal component pursuit: a review for a comparative evaluation in video surveillance. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 122, 22–34 (2014)
Bouwmans, T., Sobral, A., Javed, S., Jung, S.K., Zahzah, E.H.: Decomposition into low-rank plus additive matrices for background/foreground separation: a review for a comparative evaluation with a large-scale dataset. Comput. Sci. Rev. 23, 1–71 (2016)
Gao, B., Lu, P., Woo, W.L., Tian, G.Y.: Variational Bayes sub-group adaptive sparse component extraction for diagnostic imaging system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(10), 8142–8152 (2018)
Lu, P., Gao, B., Woo, W.L., Li, X., Tian, G.Y.: Automatic relevance determination of adaptive variational Bayes sparse decomposition for micro-cracks detection in thermal sensing. IEEE Sens. J. 17(16), 5220–5230 (2017)
Zhou, Q., Meng, D.Y., Xu, Z., Zuo, W., Zhang, L.: Robust principal component analysis with complex noise. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 55–63 (2014)
Gan, C., Wang, Y., Wang, X.: Multi-feature robust principal component analysis for video moving object segmentation. J. Image Gr. 18(9), 1124–1132 (2013)
Zhou, X.W., Yang, C., Yu, W.C.: Moving object detection by detecting contiguous outliers in the low-rank representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(3), 597–610 (2013)
Li, S.Z.: Markov Random Field Modeling in Image Analysis. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Lu, C.Y., Tang, J.H., Ya, S.C., Lin, Z.C.: Generalized nonconvex nonsmooth low-rank minimization. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4130–4137 (2014)
Oh, T.H., Kim, H., Tai, Y.W., Bazin, J.C., Kweon, I.S.: Partial sum minimization of singular value in RPCA for low-level vision. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 145–152 (2013)
Lin, Z., Chen, M., Wu, L., Ma, Y.: The augmented Lagrange multiplier method for exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices. In: UIUC Technical Report (2009)
Boykov, Y., Veksler, O., Zabih, R.: Fast approximate energy minimization via graph cuts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 23(11), 1222–1239 (2001)
Kolmogorov, V., Zabih, R.: What energy functions can be minimized via graph cuts? IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26(2), 147–159 (2004)
Davis, J., Goadrich, M.: The relationship between precision-recall and ROC curves. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 233–240 (2006)
Acknowledgements
This paper is supported partly by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Nos. U1701266, 61372173, 61471132 and 61671163), the Guangdong Higher Education Engineering Technology Research Center for Big Data on Manufacturing Knowledge Patent (No. 501130144), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province China (No. 2014A030310346) and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province China (No. 2015A030401090).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Ling, B.WK. Detecting moving objects via the low-rank representation. SIViP 13, 1593–1601 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-019-01503-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-019-01503-7