Abstract
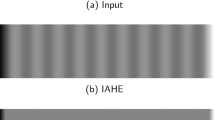
In this paper, we present a new approach to deal with the noise inherent in the microarray image processing procedure. We use the denoising capabilities of decimated and undecimated multiwavelet transforms, DMWT and UMWT respectively, for the removal of noise from microarray data. Multiwavelet transforms, with appropriate initialization, provide sparser representation of signals than wavelet transforms so that their difference from noise can be clearly identified. Also, the redundancy of the UMWT transform is particularly useful in image denoising in order to capture the salient features such as noise or transients. We compare this method with the discrete and stationary wavelet transforms, denoted by DWT and SWT, respectively, and the Wiener filter for denoising microarray images. Results show enhanced image quality using the proposed approach, especially in the undecimated case in which the results are comparable and often outperform that of the stationary wavelet transform. Both multiwavelet transforms outperform the DWT and the Wiener filter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Southern E.M.: Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J. Mol. Biol. 98, 503–517 (1975)
Schena M., Shalon D., Davis R.W., Brown P.O.: Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray. Science 270, 467–470 (1995)
Fodor S.P.A., Read J.L., Pirrung M.C., Stryer L., Lu A.T., Solas D.: Light-directed, spatially addressable parallel chemical synthesis. Science 251, 767–773 (1991)
Perou C.M., Jeffrey S.S., Van de Rijn M., Rees C.A., Eisen M.B., Ross D.T., Ergamenschikov A., Williams C.F., Zhu S.X., Lee J.C.F., Lashkari D., Shalon D., Brown P.O., Botstein D.: Distinctive gene expression patterns in human mammary epithelial cells and breast cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96, 9212–9217 (1999)
Scearce L.M., Brestelli J.E., McWeeney S.K., Lee C.S., Mazzarelli J.P., Deborah F., Pizarro A.S., Stoechert C.J. Jr., Sandra S.P., Permutt M.A., Brown J., Douglas A., Kasestner K.H.: Functional genomics of the endocrine pancreas: the pancreas clone set and Pancchip, new resources for diabetes research. Diabetes 51, 1997–2004 (2002)
Nadler S.T., Stoehr J.P., Schueler K.L., Tanimoto G., Yandel B.S., Attie A.D.: The expression of adipogenic genes is decreased in obesity and diabetes mellitus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 97, 11371–11376 (2000)
Axon Instruments Inc., GenePix Pro User’s Guide. http://www.axon.com/com/, Software and Documentation (2001)
Battiato, S., Di Blasi, G., Farinella, G.M., Gallo, G., Guarnera, G.C.: Ad-hoc segmentation pipeline for microarray image analysis. In: Proceedings of IS&T-SPIE 18th Annual Symposium Electronic Imaging Science and Technology 2006. Image Processing: Algorithms and Systems V, Tracking NO. EI06-EI112-15, San Jose, CA, USA, 15–19 January (2006)
Steinfath M., Wruch W., Seidel H., Lehrach H., Radelof U., O’Brien J.: Automated image analysis for array hybridization experiments. Bioinformatics 17(7), 634–641 (2001)
Bozinov D., Rahnenfuhrer J.: Unsupervised technique for robust target separation and analysis of DNA microarray spots. Bioinformatics 18(5), 747–756 (2002)
Wruch W., Griffiths H., Steinfath M., Lehrach H., Radelof U., O’Brien J.: Xdigitise: visualization of hybridization experiments. Bioinformatics 18(5), 757–760 (2002)
Zapala, M.A., Lockhart, D.J., Pankratz, D.G., Garcia, A.J., Barlow, C., Lockhard, D.J.: Software and methods for oligonucleotide and cDNA array data analysis. Genome Biol. 3(6) (2002)
Jain A.N., Tokuyasu T.A., Snijders A.M., Segraves R., Albertson D.G., Pinkel D.: Fully automatic quantification of microarray image data. Genome Res. 12, 325–332 (2002)
Kerr M.K., Martin M., Churchill G.A.: Analysis of variance gene expression microarray data. J. Comput. Biol. 7, 819 (2001)
Chen, Y., Dougherty, E.R., Bittner, M.L.: Ratio-based decision the quantitative analysis of cDNA microarray images. J. Biomed. Opt. 364–374 (1997)
Ermolaeva M.L., Rastogi M., Pruitt K.D., Schuler G.D., Bittner M.L., Chen Simon R., Meltzer P., Trent J.M., Boguski M.: Data management and analysis for gene expression arrays. Nat. Genet. 20, 19–23 (1998)
Newton M.A., Kendziorski C.M., Richmond C.S., Blattner F.R., Tsui K.W.: On differential variability of expression ratios: improving statistical inference about gene expression changes from microarray data. J. Computat. Biol. 8, 37–52 (2001)
Lonnstedt I., Speed T.: Replicated microarray data. Stat. Sin. 12, 31–46 (2002)
Dror, R., Murnick, J., Rinaldi, N.: A Bayesian approach to transcript estimation from gene array data: the BEAM technique. In: Proceedings of the 6th Anal. Int. Conf. Research in Computational Molecular Biology, Washington, DC, April (2002)
Wang Y., Lu J., Lee R., Gu Z., Clarke R.: Iterative normalization of CDNA microarray data. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 6, 29–37 (2000)
O’Neill P., Magoulas G.D.: Improved processing of microarray data using image reconstruction techniques. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2(4), 176–183 (2003) December
Lukac R., Plataniotis K.N., Smolka B., Venetsanopoulos A.N.: cDNA microarray image processing using fuzzy vector filtering framework. J. Fuzzy Sets Syst. Special Issue on Fuzzy Sets and Systems in Bioinformatics 152(1), 17–35 (2005) May
Mallat S.: A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Machine Intel. 11, 674–693 (1989) July
Chua L.O., Yang L.: Cellular neural networks: theory. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 35, 1257–1272 (1988)
Zhang, X.Y., Chen, F., Zhang, Y.T., Agner, S.G., Akay, M., Lu, Z.H., Waye, M.M.Y., Tsui, S.K.W.: Signal processing techniques in genomic engineering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 90(12), 1822–1833, December (2002)
Arena P., Bucolo M., Fortuna L., Occhipinty L.: Celular neural networks for real-time DNA microarray analysis. IEEE Engl. Med. Biol. 21, 17–25 (2002)
Wang X.H., Istepanian R.S.H., Song Y.H.: Microarray image enhancement by denoising using stationary wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2(4), 184–189 (2003) December
Pesquet J.C., Krim H., Carfantan H.: Time-invariant Orthonormal Wavelet Representations. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 44, 1964–1970 (1996) August
Adjeroh, D.A., Zhang, Y., Parthe, R.: On denoising and compression of DNA microarray images. Pattern Recogn., Special Issue on Bioinformatics, pp. 2478–2493, December (2006)
Goodman T.N.T., Lee S.L.: Wavelets of multiplicity r. Trans. AMS 342, 307–324 (1994)
Strang G., Nguyen T.: Wavelets and Filter Banks. Wellesley-Cambridge Press, Wellesley (1995)
Vetterli M., Strang G.: Time-varying Filter Banks and Multiwavelets. Sixth IEEE DSP workshop, Yosemite (1994)
Nason G.P., Silverman B.W.: The stationary wavelet transform and some statistical applications. In: Antoniadis, A., Oppenheim, G. (eds) Wavelet and Statistics Lecture Notes in Statistics, pp. 281–300. Springer, Heidelberg (1995)
Strela, V., Walden, A.T.: Signal and Image Denoising via Wavelet Thresholding: Orthogonal and Biorthogonal, Scalar and Multiple Wavelet Transforms. Imperial College, Statistics Section, Technical Report TR-98–01 (1998)
Goodman T.N.T., Lee S.L.: Wavelets of multiplicity r. Trans. AMS 342, 307–324 (1994)
Mallat S.: A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Machine Intel. 11, 674–693 (1989) July
Strang G., Nguyen T.: Wavelets and Filter Banks. Wellesley-Cambridge Press, Wellesley (1995)
Vetterli M., Strang G.: Time-varying Filter Banks and Multiwavelets. Sixth IEEE DSP workshop, Yosemite (1994)
Strela V., Heller P., Strang G., Topiwala P., Heil C.: The application of multiwavelet filter banks to signal and image processing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 8, 548–563 (1999) April
Donoho D.L., Johnstone I.M.: Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage. Biometrika 81, 425–455 (1994)
Coifman, R.R., Wickerhauser, M.V.: Entropy based algorithms for the best basis selection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory (38), 713–718 (1992)
Daubechies: Ten Lectures on Wavelets. SIAM, Philadephia (1992)
Geronimo J., Hardin D., Massopust P.R.: Fractal Functions and Wavelet Expansions Based on Several Functions. J. Approx. Theory 78, 373–401 (1994)
Delfino, G., Martinez, F.: Watermarking Insertion in Digital Images (spanish). Available at: http://www.internet.com.uy/fabianm/watermarking.pdf, March (2000)
Jain A.K.: Fundamentals of Digital Image Processing. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey (1989)
Wang Z., Bovik A.: A Universal Image Quality Index. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. Lett. 9, 81–84 March (2002)
Wang, Z., Sheikh, H.R., Bovik, A.C.: No-reference Perceptual Quality Assessment of JPEG Compressed Images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, vol. 1, pp. 477–480 (2002)
Rouchka, E.C.: Lecture 12: Microarray Image Analysis. Available at: http://kbrin.a-bldg.louisville.edu/CECS694/Lecture12.ppt, April (2004)
Chen G.Y., Bui T.D.: Multiwavelets denoising using neighboring coefficients. IEEE Signal process. lett. 10(7), 211–214 (2003)
Hsung, T.C., Lun, D.P.K.: Optimal thresholds for multiwavelet shrinkage. Elect. Lett. 39(5), 6, 473–474 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zifan, A., Moradi, M.H. & Gharibzadeh, S. Microarray image enhancement by denoising using decimated and undecimated multiwavelet transforms. SIViP 4, 177–185 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-009-0109-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-009-0109-4