Abstract
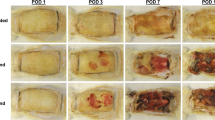
Bacterial virulence factors play a key role in the outcome of burn wound infections. We aimed to assess the differences in virulence properties of multidrug-resistant (MDR) isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) between in vitro and in vivo environments. Scald burns were induced in 50 adult male rats and the animals were randomly infected with one of the MDR isolates of P. aeruginosa. Isolate-1 expressed the virulence-related genes (exoU, exoS, pilB, nan1, ampC, and rpoD) in vitro, while Isolate-2 only expressed ampC and rpoD genes in vitro. The infected burn wounds in both groups were excised at different time points (2, 4, 6, 8, and 14 days post-burn) for histopathological examinations. The expressions of virulence-related genes within the infected skin tissues were also evaluated using SYBR green real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays. At the first time point, both MDR isolates caused the same depth of tissue damage. However, during follow-ups, Isolate-2 exhibited a lower degree of inflammation and fibrinous exudate, but faster re-epithelialization, scab formation, and granulation tissue compared to Isolate-1. The results also revealed significant differences between the in vitro and in vivo environments in terms of the expression of virulence-related genes. All virulence-related genes, except pilB, were expressed in burned skin infected by Isolate-2, while they were not detectably expressed in vitro. Based on the findings, the MDR isolates of P. aeruginosa demonstrated distinct virulence properties within in vitro and in vivo environments. This highlights the risks of relying solely on laboratory findings in clinical decision-making for burn wound infections.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current research are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CFU/mL:
-
Colony-forming units per milliliter
- CO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- exoA:
-
Exotoxin A
- exoU:
-
Exoenzyme U
- exoS:
-
Exoenzyme S
- MDR:
-
Multidrug-resistant
- nan:
-
Neuraminidase
- NTC:
-
No-template control
- OD:
-
Optical density
- P. aeruginosa :
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PCR:
-
Polymerase Chain Reaction
- RNA:
-
Ribonucleic acid
- TSB:
-
Tryptic soy broth
References
Abazari M, Ghaffari A, Rashidzadeh H, Badeleh SM, Maleki Y (2020) A systematic review on classification, identification, and healing process of burn wound healing. Int J Low Extrem Wounds 21:18–30. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534734620924857
Abdeldjelil M, Messai A, Boudebza A, Beghoul S (2017) Practical aspects to generate cutaneous experimental burns in a rat model. Pharm Lett 9:70–84
Abdullahi A, Amini-Nik S, Jeschke M (2014) Animal models in burn research. Cell Mol Life Sci 71:3241–3255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1612-5
Asada M, Nakagami G, Minematsu T, Nagase T, Akase T, Huang L, Yoshimura K, Sanada H (2012) Novel models for bacterial colonization and infection of full-thickness wounds in rats. Wound Repair Regen 20:601–610. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-475X.2012.00800.x
AttaranRezaie F, NaserpourFarivar T, Aslanimehr M, Shapouri R, Azimi A, Johari P (2014) Evaluation of AmpC gene expression in carbapenem resistant pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from severely burned patients with secondary infection in hospitals. Biotech Health Sci 1:e24879. https://doi.org/10.17795/bhs-24879
Balabanova L, Shkryl Y, Slepchenko L, Cheraneva D, Podvolotskaya A, Bakunina I, Nedashkovskaya O, Son O, Tekutyeva L (2020) Genomic features of a food-derived Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAEM and biofilm-associated gene expression under a marine bacterial α-galactosidase. Int J Mol Sci 21:7666–7691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207666
Balasubramanian D, Schneper L, Kumari H, Mathee K (2012) A dynamic and intricate regulatory network determines Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Nucleic Acids Res 41:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1039
Baquero F, Coque TM, Galán JC, Martinez JL (2021) The origin of niches and species in the bacterial world. Front Microbiol 12:657986. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.657986
Béatrice J, Maud P, Stéphane A, François C, Frédéric G, Benoit G, Marie-Odile H (2005) Relative expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes analyzed by a real time RT-PCR method during lung infection in rats. FEMS Microbiol Lett 243:271–278
Blaauboer BJ (2002) The necessity of biokinetic information in the interpretation of in vitro toxicity data. Altern Lab Anim 30:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1177/026119290203002S13
Blaauboer BJ (2003) Biokinetic and toxicodynamic modelling and its role in toxicological research and risk assessment. Altern Lab Anim 31:277–281. https://doi.org/10.1177/026119290303100
Blaauboer BJ (2010) Biokinetic modeling and in vitro–in vivo extrapolations. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 13:242–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937404.2010.483940
Boyles T, Wasserman S (2015) Diagnosis of bacterial infection. S Afr Med J 105:1–3. https://doi.org/10.7196/SAMJ.9647
Bracken MB (2009) Why animal studies are often poor predictors of human reactions to exposure. J R Soc Med 102:120–122. https://doi.org/10.1258/jrsm.2008.08k033
Brown ED, Wright GD (2016) Antibacterial drug discovery in the resistance era. Nature 529:336–343. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17042
Buchan BW, Ledeboer NA (2014) Emerging technologies for the clinical microbiology laboratory. Clin Microbiol Rev 27:783–822. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00003-14
Campelo APBS, Campelo MWS, Britto GAdC, Ayala AP, Guimarães SB, Vasconcelos PRLd (2011) An optimized animal model for partial and total skin thickness burns studies. Acta Cir Bras 26:38–42. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0102-86502011000700008
Cheung AL, Bayer AS, Zhang G, Gresham H, Xiong YQ (2004) Regulation of virulence determinants in vitro and in vivo in Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 40:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0928-8244(03)00309-2
Derakhshanfar A, Hashemi S-S, Moayedi J, Vahedi M, Mehrabani D, Valizadeh A (2019a) A study on the effects of Perovskia abrotanoides karel on experimental skin burn in male rat: in-vivo and in-vitro findings. J Adv Med Biomed Res 27:17–22. https://doi.org/10.30699/jambs.27.122.17
Derakhshanfar A, Mehrabani D, Moayedi J, Jamhiri I (2019b) Healing effect of Perovskia abrotanoides karel and expression of VEGF and TGF-Β genes in burn injury of rats. Int J Nutr Sci 4:175–180. https://doi.org/10.30476/IJNS.2019.83490.1035
Derakhshanfar A, Moayedi J, Hashemi S-S, Vahedi M, Valizadeh A (2019c) Comparative study on the effects of heated brass bar and scald methods in experimental skin burn in rat. Comp Clin Path 28:1381–1385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-019-02975-2
Derakhshanfar A, Kian M, Dehghan Z, Valizadeh A, Moayedi J (2022) Comparison of the effects of two methods of euthanasia on post mortem changes in rats: histopathological and molecular findings. Comp Clin Path 31:815–826. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-022-03385-7
Gajic I, Kabic J, Kekic D, Jovicevic M, Milenkovic M, MiticCulafic D, Trudic A, Ranin L, Opavski N (2022) Antimicrobial susceptibility testing: a comprehensive review of currently used methods. Antibiotics 11:427–453. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040427
Grada A, Mervis J, Falanga V (2018) Research techniques made simple: animal models of wound healing. J Invest Dermatol 138:2095–2105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2018.08.005
Guo H-F, Ali RM, Hamid RA, Zaini AA, Khaza’ai H (2017) A new model for studying deep partial-thickness burns in rats. Int J Burns Trauma 7:107–114
Habibi A, Honarmand R (2015) Profile of virulence factors in the multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains of human urinary tract infections (UTI). Iran Red Crescent Med J 17:e26095. https://doi.org/10.5812/ircmj.26095
Irazoqui JE, Troemel ER, Feinbaum RL, Luhachack LG, Cezairliyan BO, Ausubel FM (2010) Distinct pathogenesis and host responses during infection of C. elegans by P. aeruginosa and S. aureus. PLoS Pathog 6:e1000982. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000982
Koohsari H, Ghaemi EA, Mozaffari NA, Moradi A, Sadegh-Sheshpoli M, Javid S-N (2017) The effect of adding blood on the virulence genes expression of Staphylococcus aureus in exponential and stationary growth phase. Jundishapur J Microbiol 10:e14380. https://doi.org/10.5812/jjm.14380
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lorian V (1988) Differences between in vitro and in vivo studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 32:1600. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.32.10.1600
Moxon R, Tang C (2000) Challenge of investigating biologically relevant functions of virulence factors in bacterial pathogens. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 355:643–656. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2000.0605
Nightingale J (1987) Clinical limitations of in vitro testing of microorganism susceptibility. Am J Health Syst Pharm 44:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajhp/44.1.131
Pachori P, Gothalwal R, Gandhi P (2019) Emergence of antibiotic resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa in intensive care unit; a critical review. Genes Dis 6:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2019.04.001
Pang Z, Raudonis R, Glick BR, Lin T-J, Cheng Z (2019) Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Biotechnol Adv 37:177–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.11.013
Porumb V, Trandabăț AF, Terinte C, Căruntu ID, Porumb-Andrese E, Dimofte MG, Pieptu D (2017) Design and testing of an experimental steam-induced burn model in rats. Biomed Res Int 2017:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9878109
Potvin E, Sanschagrin F, Levesque RC (2008) Sigma factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:38–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00092.x
Qu M, Nourbakhsh M (2017) Current experimental models of burns. Discov Med 23:95–103
Roberts AE, Kragh KN, Bjarnsholt T, Diggle SP (2015) The limitations of in vitro experimentation in understanding biofilms and chronic infection. J Mol Biol 427:3646–3661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2015.09.002
Rocha AJ, Barsottini MRdO, Rocha RR, Laurindo MV, Moraes FLLd, Rocha SLd (2019) Pseudomonas aeruginosa: virulence factors and antibiotic resistance genes. Braz Arch Biol Technol 62:e19180503. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4324-2019180503
Ronin I, Katsowich N, Rosenshine I, Balaban NQ (2017) A long-term epigenetic memory switch controls bacterial virulence bimodality. Elife 6:e19599. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.19599
Rowan MP, Cancio LC, Elster EA, Burmeister DM, Rose LF, Natesan S, Chan RK, Christy RJ, Chung KK (2015) Burn wound healing and treatment: review and advancements. Crit Care 19:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-015-0961-2
Rumbaugh KP, Griswold JA, Iglewski BH, Hamood AN (1999) Contribution of quorum sensing to the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in burn wound infections. Infect Immun 67:5854–5862. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.67.11.5854-5862.1999
Saeidnia S, Manayi A, Abdollahi M (2015) From in vitro experiments to in vivo and clinical studies; pros and cons. Curr Drug Discov Technol 12:218–224. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570163813666160114093140
Savli H, Karadenizli A, Kolayli F, Gundes S, Ozbek U, Vahaboglu H (2003) Expression stability of six housekeeping genes: a proposal for resistance gene quantification studies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by real-time quantitative RT-PCR. J Med Microbiol 52:403–408. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.05132-0
Sharifi H, Pouladfar G, Shakibaie MR, Pourabbas B, Mardaneh J, Mansouri S (2019) Prevalence of β-lactamase genes, class 1 integrons, major virulence factors and clonal relationships of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from hospitalized patients in southeast of Iran. Iran J Basic Med Sci 22:806–812. https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2019.35063.8340
Shi H, Cheer K, Simanainen U, Lesmana B, Ma D, Hew JJ, Parungao RJ, Li Z, Cooper MS, Handelsman DJ (2021) The contradictory role of androgens in cutaneous and major burn wound healing. Burns Trauma 9:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1093/burnst/tkaa046
Sonmezer MC, Ertem G, Erdinc FS, Kaya Kilic E, Tulek N, Adiloglu A, Hatipoglu C (2016) Evaluation of risk factors for antibiotic resistance in patients with nosocomial infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol 2016:1321487. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1321487
Tachi M, Hirabayashi S, Yonehara Y, Suzuki Y, Bowler P (2004) Development of an experimental model of infected skin ulcer. Int Wound J 1:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-481x.2004.00006.x
Tavares Pereira DdS, Lima-Ribeiro MHM, de Pontes-Filho NT, Carneiro-Leão AMdA, Correia MTdS (2012) Development of animal model for studying deep second-degree thermal burns. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:460841. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/460841
Tomic-Canic M, Burgess JL, O’Neill KE, Strbo N, Pastar I (2020) Skin microbiota and its interplay with wound healing. Am J Clin Dermatol 21:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-020-00536-w
Tompkins RG (2015) Survival from burns in the new millennium: 70 years experience from a single institution. Ann Surg 261:263–268
Trøstrup H, Laulund ASB, Moser C (2020) Insights into host-pathogen interactions in biofilm-infected wounds reveal possibilities for new treatment strategies. Antibiotics 9:396–410. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070396
Turner KH, Everett J, Trivedi U, Rumbaugh KP, Whiteley M (2014) Requirements for Pseudomonas aeruginosa acute burn and chronic surgical wound infection. PLoS Genet 10:e1004518. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004518
Vincent J-L, Rello J, Marshall J, Silva E, Anzueto A, Martin CD, Moreno R, Lipman J, Gomersall C, Sakr Y (2009) International study of the prevalence and outcomes of infection in intensive care units. J Am Med Assoc 302:2323–2329. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.1754
Wenzler E, Maximos M, Asempa TE, Biehle L, Schuetz AN, Hirsch EB (2023) Antimicrobial susceptibility testing: an updated primer for clinicians in the era of antimicrobial resistance: insights from the society of infectious diseases pharmacists. Pharmacotherapy 43:264–278. https://doi.org/10.1002/phar.2781
Xiong Y-Q, Van Wamel W, Nast CC, Yeaman MR, Cheung AL, Bayer AS (2002) Activation and transcriptional interaction between agr RNAII and RNAIII in Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in an experimental endocarditis model. J Infect Dis 186:668–677. https://doi.org/10.1086/342046
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Ms. A. Keivanshekouh at the Research Consultation Center (RCC) of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences for her invaluable assistance in editing this manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by grant no. 1396–01-45–14310 from the Vice-Chancellor for Research Affairs of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AD: conceptualization, study design, funding acquisition, supervision.
JM: conceptualization, study design, methodology, statistical analysis, writing the original draft.
HS: methodology, interpretation of the data, review and editing the manuscript.
AH: methodology, review and editing the manuscript.
AV: methodology, review and editing the manuscript.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The research protocol received approval from the local Ethics Committee of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran (Approval ID: IR.SUMS.REC.1396.S337; Accepted on July 22, 2017). We followed all applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Derakhshanfar, A., Moayedi, J., Sharifi, H. et al. Different characteristics of multidrug-resistant isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in in vitro and in vivo conditions. Biologia 79, 585–596 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01576-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01576-3