Abstract
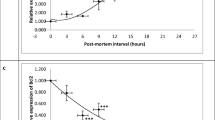
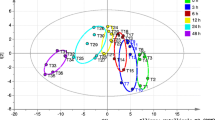
Postmortem changes (PMCs) not only affect the results of experimental studies, but also determine postmortem intervals in forensic sciences. The present study aimed to assess the effects of two methods of laboratory animals’ euthanasia on PMCs in rats. In this experimental study, 10 female rats were randomly assigned to two equal groups and were euthanized using the inhalation of CO2 (gas-treated group) or over-dose intramuscular injection of ketamine/xylazine (drug-treated group). Kidney and liver tissue samples were collected at baseline and 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 24, and 48 h after euthanasia and were subjected to histopathological examinations. The expression of liver-specific microRNA-122 (miR-122) was also assessed in each time point via a SYBR green real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay. Finally, miR-122 target genes and related functional pathways were identified through bioinformatics analysis. The progression of PMCs in the drug-treated group was faster than the gas-treated group. The expression of miR-122 was significantly (P < 0.0001) upregulated in the drug-treated group at 4, 10, and 24 h in comparison to the gas-treated group; however, it was downregulated at 6, 8, and 48 h after euthanasia. The biosynthesis of amino acids, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, and carbon metabolism as well as the glucagon, Hedgehog, cGMP-PKG, and neurotrophin signaling pathways were identified as the significant pathways related to miR-122 target genes. The findings indicated that methods of euthanasia for laboratory animals could cause changes at microscopic and molecular levels. Therefore, researchers should consider this issue in the design phase of their studies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Amara M, Yang SY, Seifalian A, Davidson B, Fuller B (2012) The nitric oxide pathway–evidence and mechanisms for protection against liver ischaemia reperfusion injury. Liver Int 32(4):531–543
Al-Mousawi AM, Kulp GA, Branski LK, Kraft R, Mecott GA, Williams FN, Herndon DN, Jeschke MG (2010) Impact of anesthesia, analgesia and euthanasia technique on the inflammatory cytokine profile in a rodent model of severe burn injury. Shock 34(3):261–268
Allen-Worthington KH, Brice AK, Marx JO, Hankenson FC (2015) Intraperitoneal injection of ethanol for the euthanasia of laboratory mice (Mus musculus) and rats (Rattus norvegicus). J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 54(6):769–778
Bandiera S, Pfeffer S, Baumert TF, Zeisel MB (2015) miR-122–a key factor and therapeutic target in liver disease. J Hepatol 62(2):448–457
Brockbals L, Wartmann Y, Mantinieks D, Glowacki LL, Gerostamoulos D, Kraemer T, Steuer AE (2021) Postmortem metabolomics: strategies to assess time-dependent postmortem changes of diazepam, nordiazepam, morphine, codeine, mirtazapine and citalopram. Metabolites 11(9):643–659
Brooks J (2016) Postmortem changes in animal carcasses and estimation of the postmortem interval. Vet Pathol 53(5):929–940
Bucław M, Lepczyński A, Herosimczyk A, Ożgo M, Szczerbińska D, Majewska D, Liput K, Pierzchała M (2021) Post mortem changes in M. iliotibialis lateralis muscle protein profile of emu (Dromaius novaehollandiae). Meat Sci 180:108562
Charron MJ, Vuguin PM (2015) Lack of glucagon receptor signaling and its implications beyond glucose homeostasis. J Endocrinol 224(3):123–130
Clarke JI, Forootan SS, Lea JD, Howell LS, Rodriguez JM, Kipar A, Goldring CE, Park BK, Copple IM, Antoine DJ (2017) Circulating levels of miR-122 increase post-mortem, particularly following lethal dosing with pentobarbital sodium: implications for pre-clinical liver injury studies. Toxicol Res 6(4):406–411
Dejong CH, van de Poll MC, Soeters PB, Jalan R, Olde Damink SW (2007) Aromatic amino acid metabolism during liver failure. J Nutr 137(6):1579–1585
Derakhshanfar A, Moayedi J, Vahedi M, Valizadeh A (2020) Arum conophalloides aqueous extract induced hepatotoxicity in rat; histopathological, biochemical, and mir-122 assessments. MicroRNA 9(3):224–231
Ding Z, Wei Q, Liu C, Zhang H, Huang F (2022) The quality changes and proteomic analysis of cattle muscle postmortem during rigor mortis. Foods 11(2):217–233
Donaldson AE, Lamont IL (2013) Biochemistry changes that occur after death: potential markers for determining post-mortem interval. PLoS ONE 8(11):e82011
Ducker GS, Rabinowitz JD (2017) One-carbon metabolism in health and disease. Cell Metab 25(1):27–42
Dwivedi Y, Rizavi HS, Zhang H, Mondal AC, Roberts RC, Conley RR, Pandey GN (2009) Neurotrophin receptor activation and expression in human postmortem brain: effect of suicide. Biol Psychiatry 65(4):319–328
Ebuehi O, Amode M, Balogun A, Fowora A (2015) Postmortem time affects brain, liver, kidney and heart DNA in male rat. Am J Biochem 5(1):1–5
Fordyce SL, Kampmann M-L, Van Doorn NL, Gilbert MTP (2013) Long-term RNA persistence in postmortem contexts. Investig Genet 4(1):1–7
Francis SH, Busch JL, Corbin JD (2010) cGMP-dependent protein kinases and cGMP phosphodiesterases in nitric oxide and cGMP action. Pharmacol Rev 62(3):525–563
Gomaa MS, Abd El-Khalek AM, Sameer MM (2013) The relationship between the postmortem interval and the DNA degradation in brain and liver of adult albino rats. J Am Sci 9(5):535–540
Grieves J, Dick E Jr, Schlabritz-Loutsevich N, Butler S, Leland M, Price S, Schmidt C, Nathanielsz P, Hubbard G (2008) Barbiturate euthanasia solution-induced tissue artifact in nonhuman primates. J Med Primatol 37(3):154–161
Han H-S, Kang G, Kim JS, Choi BH, Koo S-H (2016) Regulation of glucose metabolism from a liver-centric perspective. Exp Mol Med 48(3):218–218
Ibrahim SF, Ali MM, Basyouni H, Rashed LA, Amer EA, Abd El-Kareem D (2019) Histological and miRNAs postmortem changes in incisional wound. Egypt J Forensic Sci 9(1):1–6
Jung Y, Brown KD, Witek RP, Omenetti A, Yang L, Vandongen M, Milton RJ, Hines IN, Rippe RA, Spahr L (2008) Accumulation of hedgehog-responsive progenitors parallels alcoholic liver disease severity in mice and humans. Gastroenterology 134(5):1532–1543
Kakimoto Y, Kamiguchi H, Ochiai E, Satoh F, Osawa M (2015) MicroRNA stability in postmortem FFPE tissues: quantitative analysis using autoptic samples from acute myocardial infarction patients. PLoS ONE 10(6):e0129338
Karadzic R, Ilic G, Antovic A, Kostic Banovic L (2010) Autolytic ultrastructural changes in rat and human hepatocytes. Rom J Legal Med 18(4):247–252
Ko MJ, Mulia GE, Van Rijn RM (2019) Commonly used anesthesia/euthanasia methods for brain collection differentially impact MAPK activity in male and female C57BL/6 mice. Front Cell Neurosci 13(96):1–10
Lardizábal MN, Nocito AL, Daniele SM, Ornella LA, Palatnik JF, Veggi LM (2012) Reference genes for real-time PCR quantification of microRNAs and messenger RNAs in rat models of hepatotoxicity. PLoS ONE 7(5):e36323
Lei H, Grinberg O, Nwaigwe C, Hou H, Williams H, Swartz H, Dunn J (2001) The effects of ketamine–xylazine anesthesia on cerebral blood flow and oxygenation observed using nuclear magnetic resonance perfusion imaging and electron paramagnetic resonance oximetry. Brain Res 913(2):174–179
Li X, Elwell M, Ryan A, Ochoa R (2003) Morphogenesis of postmortem hepatocyte vacuolation and liver weight increases in Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol Pathol 31(6):682–688
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Lukey MJ, Katt WP, Cerione RA (2017) Targeting amino acid metabolism for cancer therapy. Drug Discov Today 22(5):796–804
Lv Y-H, Ma J-L, Pan H, Zeng Y, Tao L, Zhang H, Li W-C, Ma K-J, Chen L (2017) Estimation of the human postmortem interval using an established rat mathematical model and multi-RNA markers. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 13(1):20–27
Lv Y-H, Ma K-J, Zhang H, He M, Zhang P, Shen Y-W, Jiang N, Ma D, Chen L (2014) A time course study demonstrating mRNA, microRNA, 18S rRNA, and U6 snRNA changes to estimate PMI in deceased rat’s spleen. J Forensic Sci 59(5):1286–1294
Machado MV, Diehl AM (2018) Hedgehog signalling in liver pathophysiology. J Hepatol 68(3):550–562
Mahdipour M, van Tol HT, Stout TA, Roelen BA (2015) Validating reference microRNAs for normalizing qRT-PCR data in bovine oocytes and preimplantation embryos. BMC Dev Biol 15(1):1–10
Mansur RB, Fries GR, Subramaniapillai M, Frangou S, De Felice FG, Rasgon N, McEwen B, Brietzke E, McIntyre RS (2018) Expression of dopamine signaling genes in the post-mortem brain of individuals with mental illnesses is moderated by body mass index and mediated by insulin signaling genes. J Psychiatr Res 107:128–135
Melotti A, Mas C, Kuciak M, Lorente-Trigos A, Borges I, Ruiz i Altaba A (2014) The river blindness drug I vermectin and related macrocyclic lactones inhibit WNT-TCF pathway responses in human cancer. EMBO Mol Med 6(10):1263–1278
Moayedi J, Hashempour T, Musavi Z, Arefian E, Naderi M, Heidari MR, Dehghani B, Hasanshahi Z, Merat S (2020) Evaluation of miR-122 serum level and IFN-λ3 genotypes in patients with chronic HCV and HCV-infected liver transplant candidate. MicroRNA 10(4):1–6
Mohamed AS, Hosney M, Bassiony H, Hassanein SS, Soliman AM, Fahmy SR, Gaafar K (2020) Sodium pentobarbital dosages for exsanguination affect biochemical, molecular and histological measurements in rats. Sci Rep 10(1):1–13
Mole CG, Heyns M (2019) Animal models in forensic science research: justified use or ethical exploitation? Sci Eng Ethics 25(4):1095–1110
Omenetti A, Yang L, Li Y-X, McCall SJ, Jung Y, Sicklick JK, Huang J, Choi S, Suzuki A, Diehl AM (2007) Hedgehog-mediated mesenchymal–epithelial interactions modulate hepatic response to bile duct ligation. Lab Invest 87(5):499–514
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L (2002) Relative expression software tool (REST©) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 30(9):36–46
Pham DD, Do HT, Bruelle C, Kukkonen JP, Eriksson O, Mogollón I, Korhonen LT, Arumäe U, Lindholm D (2016) p75 neurotrophin receptor signaling activates sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 in hepatocyte cells via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and caspase-3. J Biol Chem 291(20):10747–10758
Prabhakar S (2012) Translational research challenges: finding the right animal models. J Investig Med 60(8):1141–1146
Roderburg C, Benz F, Vargas Cardenas D, Koch A, Janssen J, Vucur M, Gautheron J, Schneider AT, Koppe C, Kreggenwinkel K (2015) Elevated miR-122 serum levels are an independent marker of liver injury in inflammatory diseases. Liver Int 35(4):1172–1184
Sampaio-Silva F, Magalhães T, Carvalho F, Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Silvestre R (2013) Profiling of RNA degradation for estimation of post morterm interval. PLoS ONE 8(2):e56507
Schlosser K, McIntyre LA, White RJ, Stewart DJ (2015) Customized internal reference controls for improved assessment of circulating MicroRNAs in disease. PLoS ONE 10(5):e0127443
Sharapova T, Devanarayan V, LeRoy B, Liguori M, Blomme E, Buck W, Maher J (2016) Evaluation of miR-122 as a serum biomarker for hepatotoxicity in investigative rat toxicology studies. Vet Pathol 53(1):211–221
Shomer NH, Allen-Worthington KH, Hickman DL, Jonnalagadda M, Newsome JT, Slate AR, Valentine H, Williams AM, Wilkinson M (2020) Review of rodent euthanasia methods. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 59(3):242–253
Sinclair EM, Yusta B, Streutker C, Baggio LL, Koehler J, Charron MJ, Drucker DJ (2008) Glucagon receptor signaling is essential for control of murine hepatocyte survival. Gastroenterology 135(6):2096–2106
Staib-Lasarzik I, Kriege O, Timaru-Kast R, Pieter D, Werner C, Engelhard K, Thal SC (2014) Anesthesia for euthanasia influences mRNA expression in healthy mice and after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 31(19):1664–1671
Tsun Z-Y, Possemato R (2015) Amino acid management in cancer. Elsevier, Semin Cell Dev Biol
Tu C, Du T, Ye X, Shao C, Xie J, Shen Y (2019) Using miRNAs and circRNAs to estimate PMI in advanced stage. Legal Med 38:51–57
Welson NN, Gaber SS, Batiha GE-S, Ahmed SM (2021) Evaluation of time passed since death by examination of oxidative stress markers, histopathological, and molecular changes of major organs in male albino rats. Int J Legal Med 135(1):269–280
Zhang H, Zhang P, Ma K-J, Lv Y-H, Li W-C, Luo C-L, Li L-L, Shen Y-W, He M, Jiang J-Q (2013) The selection of endogenous genes in human postmortem tissues. Sci Justice 53(2):115–120
Acknowledgements
Hereby, the authors would like to thank Ms. A. Keivanshekouh at the Research Consultation Center (RCC) of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences for improving the use of English in the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by grant no. 95–01-45–13692 from the Vice-chancellor for Research Affairs of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All animal experiments were approved by the local Ethics Committee of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran (Approval ID: IR.SUMS.REC.1395.S1241). All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Derakhshanfar, A., Kian, M., Dehghan, Z. et al. Comparison of the effects of two methods of euthanasia on post mortem changes in rats: histopathological and molecular findings. Comp Clin Pathol 31, 815–826 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-022-03385-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-022-03385-7