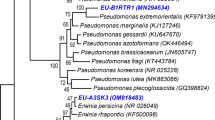
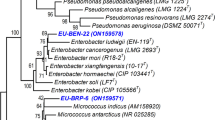
Abstract
Agrochemicals provide vital nutrients for plant growth to enhance crops yield, but they can pose major agro-environmental issues. Bioinoculants have attracted more and more attention due to their cost effective-eco-friendly and pollution-free characteristics. The aim of this study was to determine whether using a variety of bioinoculants that include both individual and group members could reduce the need for chemical fertilizer. In the modern era, individual and multiple strain formulation as bioinoculants and bacterial consortium is need of agricultural sustainability. A total 132 bacteria were sorted out from soil and internal tissues of the plant and screened for PGP characteristics including nitrogen fixer, phosphorus, and potassium solubilization. Among 132 bacteria, 13 were found to fix nitrogen, 17 and 14 bacteria were able to solubilize phosphorus, and potassium respectively. Efficient bacterial isolates were identified using 16S rRNA gene sequencing as Bacillus thuringiensis EU-CRP-15 (P-solubilizer), Bacillus horikoshii EU-CRK-18 (K-solubilizer), and Pseudomonas trivialis EU-CEN-2 (N-fixer). Inoculation of individual and consortium bioinoculants had a favorable effect on seed sprouting with the increase concentrations of inoculum. These three compatible and individual bacterial strains inoculated on sweet pepper enriched the growth and physiological characteristic of plant (plant length, root length, fresh weight, and biomass of the plant), and (chlorophyll, carotenoids, flavonoids, phenolics, and total soluble sugar content) over chemical fertilizers and untreated control plant. The plant growth promoting bacteria viz; N2-fixer as well as P and K solubilizers can be utilized as bioinoculants for the growth promotion of plants and increasing soil fertility.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PGP microbes:
-
Plant growth promoting microbes
- PGPR:
-
Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria
- CFU:
-
Colony Forming Unit
References
Abaid-Ullah M, Nadeem M, Hassan M, Ganter J, Muhammad B, Nawaz K, Shah AS, Hafeez FY (2015) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: an alternate way to improve yield and quality of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Int J Agric Biol 17:51–60
Armada E, Probanza A, Roldán A, Azcón R (2016) Native plant growth promoting bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis and mixed or individual mycorrhizal species improved drought tolerance and oxidative metabolism in Lavandula dentata plants. J Plant Physiol 192:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2015.11.007
Bakker AW, Schippers B (1987) Microbial cyanide production in the rhizosphere in relation to potato yield reduction and Pseudomonas spp-mediated plant growth-stimulation. Soil Biol Biochem 19:451–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(87)90037-X
Barea J (2015) Future challenges and perspectives for applying microbial biotechnology in sustainable agriculture based on a better understanding of plant-microbiome interactions. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 15:261–282. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162015005000021
Behrendt U, Ulrich A, Schumann P (2003) Fluorescent pseudomonads associated with the phyllosphere of grasses; Pseudomonas trivialis sp. nov., Pseudomonas poae sp. nov. and Pseudomonas congelans sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1461–1469. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02567-0
Blanco-Vargas A, Rodríguez-Gacha LM, Sánchez-Castro N, Garzón-Jaramillo R, Pedroza-Camacho LD, Poutou-Piñales RA (2020) Phosphate-solubilizing Pseudomonas sp., and Serratia sp., co-culture for Allium cepa L. growth promotion. Heliyon 6:e05218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05218
Cappucino J, Sherman N (1992) Nitrogen cycle. Icrobiology: a laboratory manual, 4th edn. Benjamin/Cumming Publishing Co, New York
Castillo C, Sotomayor L, Ortiz C, Leonelli G, Borie F, Rubio R (2009) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on an ecological crop of chili peppers (Capsicum annuum L.). Chilean J Agric Res 69:79–87
Cavalcante VA, Dobereiner J (1988) A new acid-tolerant nitrogen-fixing bacterium associated with sugarcane. Plant Soil 108:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370096
Cherif-Silini H, Silini A, Yahiaoui B, Ouzari I, Boudabous A (2016) Phylogenetic and plant-growth-promoting characteristics of Bacillus isolated from the wheat rhizosphere. Ann Microbiol 66:1087–1097. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-016-1194-6
Clewer AG, Scarisbrick DH (2013) Practical statistics and experimental design for plant and crop science. John Wiley & Sons
Conn VM, Franco CM (2004) Effect of microbial inoculants on the indigenous actinobacterial endophyte population in the roots of wheat as determined by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6407–6413. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.11.6407-6413.2004
Data F (2011) Greening agriculture in India: an overview of opportunities and constraints. http://www.fao.org/docrep/article/agrippa/658_en00.htm%23TopOfPage
De Almeida JR, Bonatelli ML, Batista BD, Teixeira-Silva NS, Mondin M, Dos Santos RC (2021) Bacillus thuringiensis RZ2MS9, a tropical plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium, colonizes maize endophytically and alters the plant's production of volatile organic compounds during co-inoculation with Azospirillum brasilense ab-V5. Environ Microbiol Rep 13:812–882. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.13004
Delfim J, Schoebitz M, Paulino L, Hirzel J, Zagal E (2018) Phosphorus availability in wheat, in volcanic soils inoculated with phosphate-solubilizing Bacillus thuringiensis. Sustainability 10:144. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010144
Dutta SC, Neog B (2016) Accumulation of secondary metabolites in response to antioxidant activity of turmeric rhizomes co-inoculated with native arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Sci Hortic 204:179–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2016.03.028
Fahid M, Ali S, Shabir G, Rashid Ahmad S, Yasmeen T, Afzal M et al (2020) Cyperus laevigatus L. enhances diesel oil remediation in synergism with bacterial inoculation in floating treatment wetlands. Sustainability 12:2353. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062353
Fao F (2011) Available online at: http://faostat.fao.org/site/291/default.aspx. Food and Agriculture Organization
Fasim F, Ahmed N, Parsons R, Gadd GM (2002) Solubilization of zinc salts by a bacterium isolated from the air environment of a tannery. FEMS Microbiol Lett 213:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2002.tb11277.x
García-Fraile P, Menéndez E, Rivas R (2015) Role of bacterial biofertilizers in agriculture and forestry. AIMS Bioeng 2:183–205. https://doi.org/10.3934/bioeng.2015.3.183
Godfray H, Beddington J, Crute I, Haddad L, Lawrence D, Muir J (2010) Food security: the challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science: Amm Assoc Adv Sci 327:812–818. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1185383
Gulati A, Swarnkar MK, Vyas P, Rahi P, Thakur R, Thakur N (2015) Complete genome sequence of the rhizobacterium Pseudomonas trivialis strain IHBB745 with multiple plant growth-promoting activities and tolerance to desiccation and alkalinity. Genome Announc 3:e00943–e00915. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00943-15
Han SO, New PB (1998) Variation in nitrogen fixing ability among natural isolates of Azospirillum. Microb Ecol 36:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002489900106
Hu X, Chen J, Guo J (2006) Two phosphate-and potassium-solubilizing bacteria isolated from Tianmu Mountain, Zhejiang, China. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:983–990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9144-2
Irigoyen JJ, Einerich DW, Sánchez-Díaz M (1992) Water stress induced changes in concentrations of proline and total soluble sugars in nodulated alfalfa (Medicago sativd) plants. Physiol Plant 84:55–60. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1992.tb08764.x
Jain A, Singh A, Singh S, Singh HB (2015) Phenols enhancement effect of microbial consortium in pea plants restrains Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Biol Control 89:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2015.04.013
Khan N, Bano A, Babar MA (2019) Metabolic and physiological changes induced by plant growth regulators and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and their impact on drought tolerance in Cicer arietinum L. PLoS One 14:e0213040. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213040
Kim KY, Jordan D, Krishnan HB (1997) Rahnella aquatilis, a bacterium isolated from soybean rhizosphere, can solubilize hydroxyapatite. FEMS Microbiol Lett 153:273–277. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1997.tb12585.x3
Kim D-O, Jeong SW, Lee CY (2003) Antioxidant capacity of phenolic phytochemicals from various cultivars of plums. Food Chem 81:321–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(02)00423-5
Kloepper JW, Ryu C-M, Zhang S (2004) Induced systemic resistance and promotion of plant growth by Bacillus spp. Phytopathology 94:1259–1266. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO.2004.94.11.1259
Kumar A, Maurya BR, Raghuwanshi R (2021) The microbial consortium of indigenous rhizobacteria improving plant health, yield and nutrient content in wheat (Triticum aestivum). J Plant Nutr 44:1942–1956. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2021.1884706
Li HB, Singh RK, Singh P, Song QQ, Xing YX, Yang LT (2017) Genetic diversity of nitrogen-fixing and plant growth promoting Pseudomonas species isolated from sugarcane rhizosphere. Front Microbiol 8:1268. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01268
Liu X, Chen C, Wang J, Zou S, Long X (2021) Phosphorus solubilizing bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis and Pantoea ananatis simultaneously promote soil inorganic phosphate dissolution and soil Pb immobilization. Rhizosphere 20:100448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2021.100448
Madaan R, Bansal G, Kumar S, Sharma A (2011) Estimation of total phenols and flavonoids in extracts of Actaea spicata roots and antioxidant activity studies. Indian J Pharm Sci 73:666. https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474X.100242
Mirza MS, Mehnaz S, Normand P, Prigent-Combaret C, Moënne-Loccoz Y, Bally R (2006) Molecular characterization and PCR detection of a nitrogen-fixing Pseudomonas strain promoting rice growth. Biol Fertil Soil 43:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-006-0074-9
Mishra PK, Mishra S, Selvakumar G, Kundu S, Shankar Gupta H (2009) Enhanced soybean (Glycine max L.) plant growth and nodulation by Bradyrhizobium japonicum-SB1 in presence of Bacillus thuringiensis-KR1. Acta Agric Scand Sect B Soil Plant Sci 59:189–196. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064710802040558
Molina-Romero D, Juárez-Sánchez S, Venegas B, Ortíz-González CS, Baez A, Morales-García YE, Muñoz-Rojas J (2021) A bacterial consortium interacts with different varieties of maize, promotes the plant growth, and reduces the application of chemical fertilizer under field conditions. Front Sustain Food Syst 293. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2020.616757
Moretti LG, Crusciol CAC, Bossolani JW, Momesso L, Garcia A, Kuramae EE, Hungria M (2020) Bacterial consortium and microbial metabolites increase grain quality and soybean yield. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:1923–1934. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00263-5
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88444-5
Pérez JMS, Antiguedad I, Arrate I, Garcıa-Linares C, Morell I (2003) The influence of nitrate leaching through unsaturated soil on groundwater pollution in an agricultural area of the Basque country: a case study. Sci Total Environ 317:173–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00262-6
Pikovskaya R (1948) Mobilization of phosphorus in soil in connection with vital activity of some microbial species. Mikrobiologiya 17:362–370
Rajawat MVS, Singh S, Saxena AK (2014) A new spectrophotometric method for quantification of potassium solubilized by bacterial cultures. Indian J Exp Biol 51:167–171
Rojas-Solís D, Hernández-Pacheco CE, Santoyo G (2016) Evaluation of Bacillus and Pseudomonas to colonize the rhizosphere and their effect on growth promotion in tomato (Physalis ixocarpa Brot. Ex Horm.). Rev Chapingo Ser Hortic 22:45–58. https://doi.org/10.5154/r.rchsh.2015.06.009
Ruanchaiman S, Kumsopa A, Boontanon N, Prapagdee B (2009) Dispersion of cadmium-resistant bacteria in cadmium-contaminated soils at Mae Sot district, Tak province. Appl Environ Res 31:35–48
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Schwyn B, Neilands J (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9
Singh S, Kumar V, Sidhu GK, Datta S, Dhanjal DS, Koul B, Janeja HS, Singh J (2019) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria from heavy metal contaminated soil promote growth attributes of Pisum sativum L. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 17:665–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.01.035
Sreedhara D, Kerutagi M, Basavaraja H, Kunnal L, Dodamani M (2014) Economics of capsicum production under protected conditions in northern Karnataka. arnataka J Agric Sci 26:217–219
Sudheer S, Bai RG, Usmani Z, Sharma M (2020) Insights on engineered microbes in sustainable agriculture: biotechnological developments and future prospects. Curr Genomics 21:321–333
Syed S, Tollamadugu NP, Lian B (2020) Aspergillus and fusarium control in the early stages of Arachis hypogaea (groundnut crop) by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) consortium. Microbiol Res 240:126562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2020.126562
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msm092
Verma P, Yadav A, Kazy S, Saxena A, Suman A (2013) Elucidating the diversity and plant growth promoting attributes of wheat (Triticum aestivum) associated acidotolerant bacteria from southern hills zone of India. http://krishi.icar.gov.in/jspui/handle/123456789/65733
Verma P, Yadav AN, Khannam KS, Panjiar N, Kumar S, Saxena AK, Suman A (2015) Assessment of genetic diversity and plant growth promoting attributes of psychrotolerant bacteria allied with wheat (Triticum aestivum) from the northern hills zone of India. Ann Microbiol 65:1885–1899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-1027-4
Verma P, Yadav AN, Khannam KS, Kumar S, Saxena AK, Suman A (2016) Molecular diversity and multifarious plant growth promoting attributes of Bacilli associated with wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) rhizosphere from six diverse agro-ecological zones of India. J Basic Microbiol 56:44–58. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201500459
Verma P, Yadav A N, Khannam K S, Saxena A K, Suman A (2017) Microorganisms for Green Revolution: Volume 1: Microbes for Sustainable Crop Production. Panpatte DG, Jhala YK, Vyas RV and Shelat HN (eds). Singapore: Springer Singapore, 125–149
Wang T, Liu M-Q, Li H-X (2014) Inoculation of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis B1 increases available phosphorus and growth of peanut in acidic soil. Acta Agric Scand Sect B Soil Plant Sci 64:252–259. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064710.2014.905624
Wang S, Ji B, Su X, Li H, Dong C, Chen S, Zhu Y, Feng W (2020) Isolation of endophytic bacteria from Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch and their potential to promote plant growth. J General Appl Microbiol 66:279–288. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.2019.12.001
Xia M, Chakraborty R, Terry N, Singh RP, Fu D (2020) Promotion of saltgrass growth in a saline petroleum hydrocarbons contaminated soil using a plant growth promoting bacterial consortium. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 146:104808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2019.104808
Yadav SK, Singh S, Singh HB, Sarma BK (2017) Compatible rhizosphere-competent microbial consortium adds value to the nutritional quality in edible parts of chickpea. J Agric Food Chem 65:6122–6130. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b01326
Zarza E, Alcaraz LD, Aguilar-Salinas B, Islas A, Olmedo-Álvarez G (2017) Complete genome sequence of Bacillus horikoshii strain 20a from Cuatro Cienegas, Coahuila, Mexico. Genome Announc 5:e00592–e00517. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00592-17
Zhang L-N, Wang D-C, Hu Q, Dai X-Q, Xie Y-S, Li Q et al (2019) Consortium of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria strains suppresses sweet pepper disease by altering the rhizosphere microbiota. Front Microbiol 10:1668. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01668
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Department of Biotechnology, Akal College of Agriculture, Eternal University, Baru Sahib and Department of Environment, Science & Technology (DEST), Shimla, HP funded project “Development of microbial consortium as bio-inoculants for drought and low temperature growing crops for organic farming in Himachal Pradesh” for providing the facilities support, to undertake the investigations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RD complied the manuscript; TK design the experiments; DK and KKC made the figures and tables; ANY give the hypothesis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Author declares that there is no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 21 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Devi, R., Kaur, T., Negi, R. et al. Indigenous plant growth-promoting rhizospheric and endophytic bacteria as liquid bioinoculants for growth of sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Biologia 78, 2623–2633 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01410-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01410-w