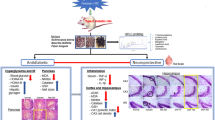
Abstract
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder caused due to the destruction of insulin-producing β-cells. Most diabetic patients consume aspartame as an artificial sweetener to feel the sugar taste. The present study explores the effect of aspartame consumption on cognitive behavior, biochemical changes, and histopathological alterations in selected brain regions of streptozotocin-induced diabetic Wistar rats. The animals were divided into four groups based on the treatment they received, and each group consisted of six rats. The groups include control (C), diabetes (D), aspartame (ASP), and diabetes in combination with aspartame (D + ASP). The morphometric studies, including the general appearance of animals, and food & water intake, were observed daily; additionally, body weight and blood sugar levels were also noted weekly. Besides, behavioral studies were performed at the end day of the experiment. After completing a thirty-days experimental period, the rats were sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and different parts of the brain regions were isolated for biochemical and histopathological studies. Our results demonstrated that aspartame administered to diabetic rats had significantly elevated blood glucose levels, food and water intake, and neurodegenerative changes in different brain regions compared to control. At the same time, the bodyweights, cognitive and gross behavioral activities, and the levels of acetylcholine, acetylcholinesterase, and total ATPases in various brain regions were significantly reduced. Our results conclude that aspartame administration to diabetic rats has shown adverse effects linked to cognitive dysfunction.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- ASP:
-
Aspartame
- IDF:
-
International Diabetes Federation
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- US-FDA:
-
United States Food and Drug Administration
- STZ:
-
Streptozotocin
- NAAT:
-
Neutral amino acid transporter
- BBB:
-
Blood-brain barrier
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- ACh:
-
Acetylcholine
- AChE:
-
Acetylcholinesterase
- GL:
-
Granular Layer
- MDC:
-
Mild Degenerative Changes
- PC:
-
Purkinje Cells
- WM:
-
White Matter
- ML:
-
Molecular Layer
- GC:
-
Glial Cells
References
Abhilash M, Alex M, Mathews VV, Nair RH (2014) Chronic effect of aspartame on ionic homeostasis and monoamine neurotransmitters in the rat brain. Int J Toxicol 33:332–341. https://doi.org/10.1177/1091581814537087
Alsuhaibani AMA, Al-Kuraieef AN (2018) Effect of low-calorie pumpkin jams fortified with soybean on diabetic rats: Study of chemical and sensory properties. J Food Qual 2018:9408715 https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9408715
Ashok I, Sheeladevi R, Wankhar D (2013) Long term effect of aspartame (artificial sweetener) on membrane homeostatic imbalance and histopathology in the rat brain. Free Radicals Antioxidants 3:S42–S49
Ashok I, Wankhar D, Wankhar W, Sheeladevi R (2015) Neurobehavioral changes and activation of neurodegenerative apoptosis on long-term consumption of aspartame in the rat brain. J Nutr Intermed Metab 2:76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnim.2015.09.001
Association AD (2009) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 32:S62–S67. https://doi.org/10.2337/DC09-S062
Augustinsson KB (1957) Assay methods for cholinesterases. Meth Biochem Anal 5:1–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470110218.ch1
Babu PVA, Sabitha KE, Shyamaladevi CS (2006) Green tea impedes dyslipidemia, lipid peroxidation, protein glycation and ameliorates Ca2+-ATPase and Na+/K+-ATPase activity in the heart of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Chem Biol Interact 162:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CBI.2006.05.020
Bhosale UA, Yegnanarayan R, Pophale PD et al (2011) Study of central nervous system depressant and behavioral activity of an ethanol extract of Achyranthes aspera (Agadha) in different animal models. Int J Appl Basic Med Res 1:104. https://doi.org/10.4103/2229-516X.91154
Biessels GJ, Kerssen A, de Haan EHF, Kappelle LJ (2007) Cognitive dysfunction and diabetes: implications for primary care. Prim Care Diabetes 1:187–193
Brown RJ, De Banate MA, Rother KI (2010) Artificial sweeteners: a systematic review of metabolic effects in youth. Int J Pediatr Obes 5:305–312
Buccellato FR, D’Anca M, Galimberti D et al (2021) Role of oxidative damage in Alzheimer’s disease and neurodegeneration: from pathogenic mechanisms to biomarker discovery. Antioxidants 10:1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ANTIOX10091353
Carageorgiou H, Pantos C, Zarros A et al (2005) Changes in antioxidant status, protein concentration, acetylcholinesterase, (Na+,K+)-, and Mg2+-ATPase activities in the brain of hyper- and hypothyroid adult rats. Metab Brain Dis 20:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11011-005-4150-X
Castelli V, Benedetti E, Antonosante A et al (2019) Neuronal cells rearrangement during aging and neurodegenerative disease: metabolism, oxidative stress and organelles dynamic. Front Mol Neurosci 12:132. https://doi.org/10.3389/FNMOL.2019.00132/XML/NLM
Chen ZR, Huang JB, Yang SL, Hong FF (2022) Role of cholinergic signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Molecules 27:1816. https://doi.org/10.3390/MOLECULES27061816
Desaiah D, Ho IK (1979) Effects of acute and continuous morphine administration on catecholamine-sensitive adenosine triphosphatase in mouse brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 208(1):80–85
Dews PB (1953) The measurement of the influence of drugs on voluntary activity in mice. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 8:46–48. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1476-5381.1953.TB00749.X
Eleazu CO, Eleazu KC, Chukwuma S, Essien UN (2013) Review of the mechanism of cell death resulting from streptozotocin challenge in experimental animals, its practical use and potential risk to humans. J Diabetes Metab Disord 12:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/2251-6581-12-60
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Elsworth JD, Roth RH (1997) Dopamine synthesis, uptake, metabolism, and receptors: relevance to gene therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 144:4–9. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.1996.6379
Fernstrom JD, Fernstrom MH, Gillis MA (1983) Acute effects of aspartame on large neutral amino acids and monoamines in rat brain. Life Sci 32:1651–1658. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-3205(83)90873-1
Filla LA, Edwards JL (2016) Metabolomics in diabetic complications. Mol Biosyst 12:1090–1105. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6mb00014b
Finamor I, Pérez S, Bressan CA et al (2017) Chronic aspartame intake causes changes in the trans-sulphuration pathway, glutathione depletion and liver damage in mice. Redox Biol 11:701–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.019
Fiske CH, Subbarow Y (1925) The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J Biol Chem 66:375–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)84756-1
Fowler SP, Williams K, Resendez RG et al (2008) Fueling the obesity epidemic? Artificially sweetened beverage use and long-term weight gain. Obesity 16:1894–1900. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2008.284
Fritz PJ, Hamrick ME (1966) Enzymatic analysis of adenosinetriphosphatase. Enzymologia 30:57–64
Glowinski J, Iversen LL (1966) Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. J Neurochem 13:655–669. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09873.x
Grieb P (2016) Intracerebroventricular streptozotocin injections as a model of Alzheimer’s disease: in search of a relevant mechanism. Mol Neurobiol 53:1741–1752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9132-3
Humphries P, Pretorius E, Naudé H (2008) Direct and indirect cellular effects of aspartame on the brain. Eur J Clin Nutr 62:451–462
IG B (1998) Nutritional effects of dietary protein restriction in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Nutr 128(2):337S–339. https://doi.org/10.1093/JN/128.2.337S. S
Kavalali G, Tuncel H, Göksel S, Hatemi HH (2003) Hypoglycemic activity of Urtica pilulifera in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol 84:241–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-8741(02)00315-X
Khan MB, Ahmad M, Ahmad S et al (2014) Bacopa monniera ameliorates cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration induced by intracerebroventricular-streptozotocin in rat: behavioral, biochemical, immunohistochemical and histopathological evidences. Metab Brain Dis 30:115–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9593-5
Kulkarni AS, Burns MR, Brundin P, Wesson DW (2022) Linking α-synuclein-induced synaptopathy and neural network dysfunction in early Parkinson’s disease. Brain Commun 4(4):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1093/BRAINCOMMS/FCAC165
Kumar Poshala K (2020) Artificial Sweeteners: a review. IJESC 10:27416–27421
Lange FT, Scheurer M, Brauch HJ (2012) Artificial sweeteners - a recently recognized class of emerging environmental contaminants: a review. Anal Bioanal Chem 403:2503–2518. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00216-012-5892-Z
Lenzen S (2008) The mechanisms of alloxan- and streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia 51:216–226
Lobo V, Patil A, Phatak A, Chandra N (2010) Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: impact on human health. Pharmacogn Rev 4:118. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.70902
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)52451-6
Magnuson BA, Burdock GA, Doull J et al (2007) Aspartame: a safety evaluation based on current use levels, regulations, and toxicological and epidemiological studies. Crit Rev Toxicol 37:629–727. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408440701516184
Mathur, Agrawal RK, Nagpure S, Deshpande D (2021) Effect of artificial sweeteners on insulin resistance among type-2 diabetes mellitus patients. J Fam Med Prim Care 9:69. https://doi.org/10.4103/JFMPC.JFMPC_329_19
Mishra OP, Delivoria-Papadopoulos M, Cahillane G, Craig Wagerle L (1989) Lipid peroxidation as the mechanism of modification of the affinity of the Na+, K+-ATPase active sites for ATP, K+, Na+, and strophanthidin in vitro. Neurochem Res 14:845–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964813
Moneim AEA (2015) Oxidant/antioxidant imbalance and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 12:335. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567205012666150325182702
Montano ME, Molpeceres V, Mauriz JL et al (2010) Effect of melatonin supplementation on food and water intake in streptozotocin-diabetic and non-diabetic male Wistar rats. Nutr Hosp 25:931–938. https://doi.org/10.3305/nh.2010.25.6.4803
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(84)90007-4
Moylan JS, Reid MB (2007) Oxidative stress, chronic disease, and muscle wasting. Muscle & Nerve 35(4):411–429. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.20743
Muriach M, Flores-Bellver M, Romero FJ, Barcia JM (2014) Diabetes and the brain: oxidative stress, inflammation, and autophagy. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014:102158. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/102158
Palsamy P, Subramanian S (2008) Resveratrol, a natural phytoalexin, normalizes hyperglycemia in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced experimental diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 62:598–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2008.06.037
Pekiner B, Ulusu NN, Das-Evcimen N et al (2002) In vivo treatment with stobadine prevents lipid peroxidation, protein glycation and calcium overload but does not ameliorate Ca2+-ATPase activity in heart and liver of streptozotocin-diabetic rats: comparison with vitamin E. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1588:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4439(02)00141-2
Pennanen L, Wolfer DP, Nitsch RM, Götz J (2006) Impaired spatial reference memory and increased exploratory behavior in P301L tau transgenic mice. Genes Brain Behav 5:369–379. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1601-183X.2005.00165.X
Prabhakar S, Saraf MK, Banik A, Anand A (2011) Bacopa monniera selectively attenuates suppressed superoxide dismutase activity in diazepam induced amnesic mice. Ann Neurosci 18:8–13. https://doi.org/10.5214/ans.0972.7531.1118104
Pragasam V, Kalaiselvi P, Sumitra K et al (2005) Counteraction of oxalate induced nitrosative stress by supplementation of l-arginine, a potent antilithic agent. Clin Chim Acta 354:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CCCN.2004.11.029
Prokić MD, Paunović MG, Matić MM et al (2014) Prooxidative effects of aspartame on antioxidant defense status in erythrocytes of rats. J Biosci 39:859–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-014-9487-z
Puchtler H, Sweat F, Levine M (1962) On the binding of congo red by amyloid. J Histochem Cytochem 10:355–364. https://doi.org/10.1177/10.3.355
Rajamani R, Muthuvel A, Senthilvelan M, Sheeladevi R (2009) Oxidative stress induced by methotrexate alone and in the presence of methanol in discrete regions of the rodent brain, retina and optic nerve. Toxicol Lett 165:265–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TOXLET.2006.05.005
Ranney RE, Oppermann JA, Muldoon E, McMahon FG (1976) Comparative metabolism of aspartame in experimental animals and humans. J Toxicol Environ Health 2:441–451. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287397609529445
Reddy DS, Kulkarni SK (1998) Possible role of nitric oxide in the nootropic and antiamnesic effects of neurosteroids on aging- and dizocilpine-induced learning impairment. Brain Res 799:215–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(98)00419-3
Rencüzoǧullari E, Tüylü BA, Topaktaş M et al (2004) Genotoxicity of aspartame. Drug Chem Toxicol 27:257–268. https://doi.org/10.1081/DCT-120037506
Rico EP, Rosemberg DB, Senger MR et al (2006) Methanol alters ecto-nucleotidases and acetylcholinesterase in zebrafish brain. Neurotoxicol Teratol 28:489–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NTT.2006.05.001
Sanberg PR, Newman MB, Manresa JJ et al (2001) Mecamylamine effects on haloperidol-induced catalepsy and defecation. Int J Neurosci 109:81–90. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207450108986527
Shanmugam KR, Mallikarjuna K, Kesireddy N, Sathyavelu Reddy K (2011) Neuroprotective effect of ginger on anti-oxidant enzymes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Chem Toxicol 49:893–897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.12.013
Sharma G, Parihar A, Talaiya T et al (2020) Cognitive impairments in type 2 diabetes, risk factors and preventive strategies. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 31:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1515/JBCPP-2019-0105/PDF
Shearer J, Swithers SE (2016) Artificial sweeteners and metabolic dysregulation: Lessons learned from agriculture and the laboratory. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 17:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11154-016-9372-1
Simintzi I, Schulpis KH, Angelogianni P et al (2007) The effect of aspartame on acetylcholinesterase activity in hippocampal homogenates of suckling rats. Pharmacol Res 56:155–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2007.05.003
Singh A, Kukreti R, Saso L, Kukreti S (2019) Oxidative stress: a key modulator in neurodegenerative diseases. Molecules 24:1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/MOLECULES24081583
Sureda FX, Camins A, Trullas R et al (1996) A flow cytometric study of N-methyl-D-aspartate effects on dissociated cerebellar cells. Brain Res 723:110–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(96)00230-2
Tirri R, Lagerspetz KYH, Kohonen J (1973) Temperature dependence of the ATP-ase activities in brain homogenates during the postnatal development of the rat. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B Comp Biochem 44:473–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0491(73)90021-7
Tuzcu M, Baydas G (2006) Effect of melatonin and vitamin E on diabetes-induced learning and memory impairment in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 537:106–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EJPHAR.2006.03.024
Usuda K, Kawase T, Shigeno Y et al (2018) Hippocampal metabolism of amino acids by L-amino acid oxidase is involved in fear learning and memory. Sci Rep 8:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28885-x
Wall PM, Messier C (2000) Ethological confirmatory factor analysis of anxiety-like behaviour in the murine elevated plus-maze. Behav Brain Res 114:199–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4328(00)00229-1
Wang K, Li J, Zhang Y et al (2021) Central nervous system diseases related to pathological microglial phagocytosis. CNS Neurosci Ther 27:528–539. https://doi.org/10.1111/CNS.13619
Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C, Shaw J (2011) IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 94:311–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2011.10.029
Wild S, Bchir MB, Roglic G et al (2004) Global prevalence of diabetes estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 27(5):1045–1053. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.27.5.1047
Yang Q (2010) Gain weight by “going diet?” Artificial sweeteners and the neurobiology of sugar cravings Neuroscience. Yale J Biol Med 83(2):101–108
Zhang J, Yakovlieva L, de Haan BJ et al (2020) Selective modification of streptozotocin at the C3 position to improve its bioactivity as antibiotic and reduce its cytotoxicity towards insulin-producing β cells. Antibiotics 9:182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ANTIBIOTICS9040182
Zhang X-F, Tan BK-H (2000) Antihyperglycaemic and anti-oxidant properties of Andrographis paniculata in normal and diabetic rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 27:358–363. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1681.2000.03253.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ediga, M., Annapureddy, S., Salikineedy, K. et al. Aspartame consumption causes cognitive impairment in streptozotocin-induced diabetic Wistar rats. Biologia 78, 2393–2407 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01363-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01363-0