Abstract
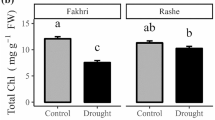
Nanoparticles (NPs) of CaO (Ca2+) are significant components that act as signal transductors in plants' adaptive and developmental processes. The responses of two different landrace varieties (Uzuntekne and Barış) of Onobrychis viciifolia to the mannitol stress of CaO NPs were investigated in this study. Their response to various morphological and physiological processes under in vitro conditions was analyzed in this study. Two Onobrychis viciifolia cultivars were used in the presence of 50 and 150 mM of mannitol, including 0.5 ppm and 1.5 ppm Ca2+ nanoparticles. The effects of CaO NPs were induced by mannitol which, root, stem, leaf development, MDA, H2O2, chlorophyll content, gene expression, and SEM images were determined for the in vitro seedlings. CaO remarkably increased the activation of growth parameters in two tested cultivars. Synergistic treatments of NPs affected the seedlings more than the sole treatments. In terms of MDA, H2O2, and chlorophyll content, it was found that the Ca2+ NPs treatment was significant, and it exhibited a high level related to the resistance degrees of cultivars. The chlorophyll content demonstrated a reducing trend in response to increasing concentrations of mannitol. However, there were significant differences between the control group samples and the CaO mannitol treatment samples in response to H2O2 and MDA. The gene expression analysis revealed that MtdDehyd and MtRD2 genes were expressed at various degrees in the seedlings of two Onobyrchis cultivars subjected to drought treatments. Improving resistance to drought stress in tested cultivars can be regulated by expressing MtdDehyd and MtRD2 genes in vitro conditions. SEM images in stomatal structures of cells were easily changed in the mannitol treatment samples in the presence of CaO, and a different stress severity level was detected in their control treatments.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NPs:
-
Nanoparticles
- Ca2+ :
-
CaO
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- SEM:
-
Scanning Electron Microscopy
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
References
Arnon D (1949) Copper enzymes isolated chloroplasts, polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.24.1.1
Bernstein N, Meiri A, Zilberstaine M (2004) Root growth of avocado is more sensitive to salinity than shoot growth. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 129(2):188–192. https://doi.org/10.21273/JASHS.129.2.0188
Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL (2003) Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4(7):517–529. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1155
Erdal S (2012) Androsterone-induced molecular and physiological changes in maize seedlings in response to chilling stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 57:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.04.016
Geyik-Şimşek M, Yazıcılar B, Bezirganoglu İ (2022) Microscopic and physiological analysis of somatic embryos under in vitro culture in triticale. Icontech Int J 6(1):73–80. https://doi.org/10.46291/ICONTECHvol6iss1
Ghassemi-Golezani K, Farhadi N, Nikpour-Rashidabad N (2018) Responses of in vitro-cultured Allium hirtifolium to exogenous sodium nitroprusside under PEG-imposed drought stress. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult (PCTOC) 133(2):237–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1377-2
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125(1):189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
Hu L, Xie Y, Fan S, Wang Z et al (2018) Comparative analysis of root transcriptome profiles between drought-tolerant and susceptible wheat genotypes in response to water stress. Plant Sci 272:276–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci
Irani S, Majidi MM, Mirlohi A, Zargar M, Karami M (2015) Assessment of drought tolerance in sainfoin: physiological and drought tolerance indices. Agron J 107(5):1771–1781. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj15.0131
Jaleel CA, Gopi R, Sankar B, Manivannan P, Kishorekumar A, Sridharan R, Panneerselvam R (2007) Studies on germination, seedling vigour, lipid peroxidation and proline metabolism in Catharanthus roseus seedlings under salt stress. S Afr J Bot 73(2):190–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2006.11.001
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lone A, Majeed W, Yaqoob NU, John R (2021) Exogenous brassinosteroid and jasmonic acid improve drought tolerance in Brassica rapa L. genotypes by modulating osmolytes, antioxidants and photosynthetic system. Plant Cell Rep 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-021-02763-9
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nazir MM, Li Q, Noman M, Ulhassan Z et al (2022) Calcium Oxide Nanoparticles Have the Role of Alleviating Arsenic Toxicity of Barley. In Plant Science 13:843795. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.843795
Pornsiriwong W, Estavillo GM, Chan KX, Tee EE et al (2017) A chloroplast retrograde signal, 3’-phosphoadenosine 5’-phosphate, acts as a secondary messenger in abscisic acid signalling in stomatal closure and germination. Elife 6:23361. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.23361.001
Rao S, Patil P (2012) In vitro selection of salt tolerant calli lines and regeneration of salt tolerant Plantlets in Mung Bean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek). Biotechnol-Mol Stud Novel Appl Improved Qual Hum Life 198–206
Sergiev I, Alexieva V, Karanov E (1997) Effect of spermine, atrazine and combination between them on some endogenous protective systems and stress markers in plants. Compt Rend Acad Bulg Sci 51(3):121–124. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.2001.00778.x
Spadafora ND, Doonan JH, Herbert RJ, Bitonti MB et al (2011) Arabidopsis T-DNA insertional lines for CDC25 are hypersensitive to hydroxyurea but not to zeocin or salt stress. Ann Bot 107(7):1183–1192. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcq142
Sun XL, Yu QY, Tang LL et al (2013) GsSRK, a G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine protein kinase, is a positive regulator of plant tolerance to salt stress. J Plant Physiol 170(5):505–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2012.11.017
Taran N, Storozhenko V, Svietlova N, Batsmanova L, Shvartau V, Kovalenko M (2017) Effect of zinc and copper nanoparticles on drought resistance of wheat seedlings. Nanoscale Res Lett 12(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-017-1839-9
Thor K (2019) Calcium—nutrient and messenger. Front Plant Sci 10:440. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00440
Thorpe TA (2007) History of plant tissue culture. Mol Biotechnol 37(2):169–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-007-0031-3
Todaka D, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2015) Recent advances in the dissection of drought-stress regulatory networks and strategies for development of drought-tolerant transgenic rice plants. Front Plant Sci 6:84. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00084
Van Nguyen D, Nguyen HM, Le NT et al (2021) Copper nanoparticle application enhances plant growth and grain yield in maize under drought stress conditions. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10301-w
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants: protective role of exogenous polyamines. Plant Sci 151(1):59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(99)00197-1
Yavaş İ (2021) The Effect of Nanoparticle Applications on Plants under Some Stress Conditions. Turk J Range Forage Sci 2(2):52–62. https://doi.org/10.51801/turkjrfs.954843
Yazıcılar B, Böke F, Alaylı A, Nadaroglu H, Gedikli S, Bezirganoğlu İ (2021) In vitro effects of CaO nanoparticles on triticale callus exposed to short and long-term salt stress. Plant Cell Rep 40(1):29–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-020-02613-0
Yıldız Ş (2018) Investigation of the Effects of SiO2 Nanoparticle Application on Leaves of Barley Plants Under Drought Stress. Mersin University. Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences. Department of Biotechnology. Master Thesis. Mersin, pp 52
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank İsmail BEZİRGANOĞLU (Assoc. Prof. Dr., Erzurum Technical University) for providing the laboratory facilities and Hayrunisa NADAROĞLU (Prof. Dr., Ataturk University) for providing CaO NPs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MME and BY contributed to the project idea. BY designed and applied the study and conducting laboratory analyses. MME supervised the experiment and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The publication of the manuscript has been approved by all co-authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key messages
Ca2+ NPs for stimulation of plant growth and development and drought stress reduction by enhancing their physiological activity and MtdDehyd and MtRD2 gene expression, SEM analysis confirming drought resistance on stoma cells.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ertuş, M.M., Yazıcılar, B. CaO nanoparticle enhances the seedling growth of Onobrycis viciifolia under drought stress via mannitol use. Biologia 78, 1119–1127 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01313-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01313-w