Abstract
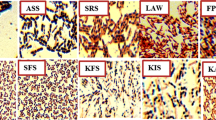
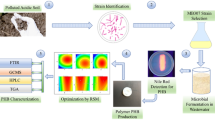
Extensive usage of synthetic plastics poses a negative impact on environment and concomitantly increasing fossil fuel demand. Hence, bioplastic like polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) has gained attention due to their analogous properties with synthetic plastics. However, its cost competitiveness is a big confront. In this context design of a substrate facilitator, mixed bacterial culture (MBC) can address this burning issue and augment avenue to industrial PHAs production. Herein, PHAs production by MBC comprised of Bacillus species was investigated. Eight preserved PHAs producing Bacillus species were selected of which 04 strains showed accumulation of PHAs granule. Among them, Bacillus sp. C1 and Bacillus sp. O6 were compatible to each other as revealed from antagonistic activity. Independently, Bacillus sp. C1 (2013) and Bacillus sp. O6 produced 0.90 ± 0.01 g/L & 1.30 ± 0.02 g/L PHAs. However, 2.70 ± 0.01 g/L of PHAs was recovered from MBC through submerged fermentation. Infra-red spectra illustrated sharp peak at 1719.86 cm−1 denoting carbonyl-ester (C = O) functional group of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB). It was degraded within 21 days as confirmed from open windrow composting. This research represents a new approach for PHAs production however before pilot scale operation, evaluation of inexpensive carbon sources as substrate is highly indispensable.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PHAs:
-
Polyhydroxyalkanoates
- MBC:
-
Mixed bacterial culture
- (C = O):
-
Carbonyl-ester
- PHB:
-
Polyhydroxybutyrate
- Mt:
-
Metric tons
- NA:
-
Nutrient agar
- GM:
-
Growth media
- MSM:
-
Mineral salt medium
- OFAT:
-
One factor at a time
- DCW:
-
Dry cell weight
- ATR:
-
Attenuated total reflectance
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- IR:
-
Infra-red
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
References
Anburajan P, Kumar N, Sabapathy A et al (2019) Polyhydroxy butyrate production by Acinetobacter junii bp25, Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966, and their co-culture using a feast and famine strategy. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122062
Bhatia SK, Yoon JJ, Kim HJ et al (2018) Engineering of artificial microbial consortia of Ralstonia eutropha and Bacillus subtilis for Poly (3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-3-Hydroxyvalerate) copolymer production from sugarcane sugar without precursor feeding. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.02.056
Boyandin AN, Prudnikova SV, Filipenko ML et al (2012) Biodegradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates by soil microbial communities of different structures and detection of PHAs degrading microorganisms. Appl Biochem Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683812010024
Carpa R, Barbu-Tudoran L (2011) Investigation of the poly-β-hyroxybutyrate (PHB) producing in mountain bacterial strains by transmission electron microscopy. Rom Biotechnol Lett 16:5989–5995
Cavaille L, Albuquerque M, Grousseau E et al (2016) Understanding of polyhydroxybutyrate production under carbon and phosphorus-limited growth conditions in non-axenic continuous culture. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.11.003
Chen Z, Guo Z, Wen Q et al (2015) A new method for polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) accumulating bacteria selection under physical selective pressure. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.10.027
Coats ER, Watson BS, Brinkman CK (2016) Polyhydroxyalkanoates synthesis by mixed microbial consortia cultured on fermented dairy manure: effect of aeration on process rates/yields and the associated microbial ecology. Water Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.09.039
Colombo B, Sciarria TP, Reis M, Scaglia B, Adani F (2016) Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) production from fermented cheese whey by using a mixed microbial culture. Bioresour Technol 218:692–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.024
Dagher F, Nickzad A, Zheng J, Hoffmann M, Déziel E (2021) Characterization of the biocontrol activity of three bacterial isolates against the phytopathogen Erwinia amylovora. Microbiologyopen 10(3):e1202. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.1202
Dash A, Mohanty S, Samantaray DP (2020) Effect of carbon/nitrogen ratio on polyhydroxyalkanoates production by Bacillus species under submerged fermentation. J Environ Biol 41(1):118–124. https://doi.org/10.22438/jeb/41/1/MRN-1138
Geyer R, Jambeck JR, Law KL (2017) Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci Adv. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1700782
Javaid H, Nawaz A, Riaz N, Mukhtar H, Ul-Haq I, Shah KA, Khan H, Naqvi SM, Shakoor S, Rasool A, Ullah K, Manzoor R, Kaleem I, Murtaza G (2020) Biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) by the valorization of biomass and synthetic waste. Molecules 25(23):5539. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235539
Khokhar I, Haider MS, Mukhtar I et al (2012) Biological control of Aspergillus niger, the cause of black-rot disease of Allium cepa L. (onion) by Penicillium species. J Agrobiol. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10146-012-0003-5
Koller M, Niebelschutz H, Braunegg G (2013) Strategies for recovery and purification of PHAs biopolyesters from surrounding biomass. Eng Life Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201300021
Liu Y, Yang S, Jia X (2020) Construction of a “nutrition supply-detoxification” coculture consortium for medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate production with a glucose-xylose mixture. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-020-02267-7
Lowe H, Hobmeier K, Moos M et al (2017) Photoautotrophic production of polyhydroxyalkanoates in a synthetic mixed culture of Synechococcus elongatus cscb and Pseudomonas putida cscab. Biotechnol Biofuels. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0875-0
Maity S, Das S, Mohapatra S et al (2020) Growth associated polyhydroxybutyrate production by the novel Zobellellae tiwanensis strain DD5 from banana peels under submerged fermentation. Int J Bio. Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac
Maity S, Das S, Samantaray DP (2017) Polyhydroxyalkanoates production by Zobellella species isolated from fish industrial effluents and its primary characterization. J Environ Biol. https://doi.org/10.22438/jeb/38/6/MRN-533
Mohapatra S, Mohanta PR, Sarkar B et al (2015). Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) by Bacillus strain isolated from waste water and its biochemical characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0626-6
Mohapatra S, Pattnaik S, Maity S et al (2020) Comparative analysis of PHAs production by Bacillus megaterium OUAT 016 under submerged and solid-state fermentation. Saudi J Biol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.02.001
Mohapatra S, Rath SN, Pradhan SK et al (2016a) Secondary structural models (16S rRNA) of polyhydroxyalkanoates producing Bacillus species isolated from different rhizospheric soil, phylogenetics and chemical analysis. Int J Bioautomation 20:329–338
Mohapatra S, Samantaray DP, Samantaray SM (2014) Phylogenetic heterogeneity of the rhizospheric soil bacterial isolates producing PHAs revealed by comparative analysis of 16s-rRNA. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 3:680–690
Mohapatra S, Samantaray DP, Samantaray SM et al. (2016b) Structural and thermal characterization of PHAs produced by Lysinibacillus sp. through submerged fermentation process. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.09.077
Mohapatra S, Sarkar B, Samantaray DP et al (2017) Bioconversion of fish solid waste into PHB using Bacillus subtilis based submerged fermentation process. Environ Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1291759
Montiel-Jarillo G, Carrera J, Suarez-Ojeda ME (2017) Enrichment of a mixed microbial culture for polyhydroxyalkanoates production: effect of pH and N and P concentrations. Sci Total Environ 583:300–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.06017.01.069
Muneer F, Rasul I, Azeem F et al (2020) Microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs): efficient replacement of synthetic polymers. J Polym Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01772-1
Pati S, Maity S, Dash A et al (2020) Biocompatible PHB production from Bacillus species under submerged and solid-state fermentation and extraction through different downstream processing. Curr Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-01922-7
Rebocho AT, Pereira JR, Neves LA et al (2020) Preparation and characterization of films based on a natural P(3HB)/mcl-PHA blend obtained through the co-culture of Cupriavidus necator and Pseudomonas citronellolis in apple pulp waste. Bioengineering. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7020034
Rodrigues PR, Assis DJ, Druzian JI (2019) Simultaneous production of polyhydroxyalkanoate and xanthan gum: from axenic to mixed cultivation. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.095
Sawant SS, Salunke BK, Kim BS (2017) Enhanced agarose and xylan degradation for production of polyhydroxyalkanoates by co-culture of marine bacterium, Saccharophagus degradans and its contaminant, Bacillus cereus. Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7030225
Uma V, Gandhimati R (2020) Effectiveness of ozone pre-treatment on bioconversion of oily bilge water into biopolymer. J Water Process Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101275
Varsha YM, Savitha R (2011) Overview on polyhydroxyalkanoates: a promising biopol. J Microb Biochem Technol. https://doi.org/10.4172/1948-5948.1000059
Volova TG, Prudnikova SV, Vinogradova ON, Syrvacheva DA, Shishatskaya EI (2016) Microbial degradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates with different chemical compositions and their biodegradability. Microb Ecol 73(2):353–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-016-0852-3
Zhang Y, Wusiman A, Liu X, Wan C, Lee DJ, Tay JH (2018) Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) production from phenol in an acclimated consortium: batch study and impacts of operational conditions. J Biotechnol 267:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2018.01.001
Zhu Y, Ai M, Jia X (2022) Optimization of a two-species microbial consortium for improved mcl-PHA production from glucose–xylose mixtures. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.794331
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Devadarshini, D., Mohapatra, S., Pati, S. et al. Evaluation of PHAs production by mixed bacterial culture under submerged fermentation. Biologia 78, 895–902 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01302-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01302-5