Abstract
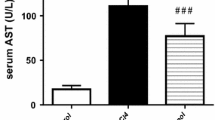
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the therapeutic and prophylactic effects of thiamine in mice with thioacetamide (TAA)-induced liver damage. In this study, 50 male CD-1 mice were used, and the study lasted 2 months. Group 1 was designated as the control group and given drinking water for 2 months. In addition, group 2 received 50 mg/100 mL of thiamine in water daily for 2 months. Group 3 received the same dosage of thiamine in water for 1 month and then 200 mg/kg of TAA intraperitoneally twice a week for 1 month. Group 4 received TAA for 1 month followed by thiamine in water ad libitum, and Group 5 was administered TAA for 1 month. At the end of the study, the mice were anesthetized and decapitated. Liver samples were collected for histopathological examination and blood samples for the evaluation of biochemical parameters. During necropsy, the liver samples from Group 5 were pale and swollen. Furthermore, histopathological changes were evaluated, and caspase-3 expression was examined immunohistochemically in the liver samples. It was found that all the parameters examined in the liver function test using serum samples increased significantly in Group 5. Therefore, TAA caused severe liver degeneration and necrosis. When thiamine was given after TAA, it improved the biochemical, pathological, and immunohistochemical findings. The improvement was more prominent in Group 4 than in Group 3. According to the results of this study, thiamine has a protective effect against cell damage on many cells, as well as a minor but significant therapeutic effect on liver cells against TAA toxicity.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NAFLD:
-
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- NASH:
-
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- NEFA:
-
Non-esterified fatty acids
- TAA:
-
Thioacetamide
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- IP:
-
Intraperitoneal
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- DAB:
-
Diaminobenzidine
- HE:
-
Hematoxylin–eosin
- TAG:
-
Triacylglycerol
- ALF:
-
Acute liver failure
References
Akhtar T, Sheikh N (2013) An overview of thioacetamide-induced hepatotoxicity. Toxin Rev 32:43–46. https://doi.org/10.3109/15569543.2013.805144
Algandaby MM (2018) Antifibrotic effects of crocin on thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Saudi J Biol Sci 25:747–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.10.007
Algandaby MM, Breikaa RM, Eid BG, Neamatallah TA, Abdel-Naim AB, Ashour OM (2017) Icariin protects against thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats: Implication of anti-angiogenic and anti-autophagic properties. Pharmacol Rep 69(4):616–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.02.016
Ashkani-Esfahania S, Bagheria F, Azarpirab N, Esmaeilzadeha E, Emamia Y, Hassanabadia N, Keshtkarc M (2017) Protective effects of quercetin on thioacetamide-induced acute liver damage and its related biochemical and pathological alterations. Egypt J Intern Med 28:123–127. https://doi.org/10.4103/1110-7782.200965
Baraka SM, Saleh DO, Ghaly NS, Melek FR (2020) Gamal El Din AA, Khalil WKB, Said MM, Medhat AM (2020) Flavonoids from Barnebydendron riedelii leaf extract mitigate thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy in rats: The interplay of NF-κB/IL-6 and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Bioorg Chem 105:104444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bio.2020.104444
Bobe G, Young JW, Beitz DC (2004) Pathology, etiology, prevention, and treatment of fatty liver in dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 87:3105–3024. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(04)73446-3
Bozic M, Guzmán C, Benet M, Sánchez-Campos S, García-Monzón C, Gari E, Gatius S, Valdivielso JM, Jover R (2016) Hepatocyte vitamin D receptor regulates lipid metabolism and mediates experimental diet-induced steatosis. Hepatology 65:748–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.05.031
Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, Nuremberg P, Horton JD, Cohen JC, Grundy SM, Hobbs HH (2004) Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology 40:1387e95. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.20466
Bruck R, Aeed H, Shirin H, Matas Z, Zaidel L, Avni Y, Halpern Z (1999) The hydroxyl radical scavengers dimethylsulfoxide and dimethylthiourea protect rats against thioacetamide-induced fulminant hepatic failure. J Hepatol 31:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-8278(99)80160-3
Bruck R, Aeed H, Schey R, Matas Z, Reifen R, Zaiger G, Avni Y (2002) Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate protects against thioacetamide-induced fulminant hepatic failure in rats. J Hepatol 36:370–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-8278(01)00290-2
Bruck R, Aeed H, Avni Y, Shirin H, Matas Z, Shahmurov M, Avinoach I, Zozulya G, Weizman N, Hochman A (2004) Melatonin inhibits nuclear factor kappa B activation and oxidative stress and protects against thioacetamide induced liver damage in rats. J Hepatol 40:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-8278(03)00504-x
Bruck R, Ashkenazi M, Weiss S, Goldiner I, Shapiro H, Aeed H, Genina O, Helpern Z, Pines M (2007) Prevention of liver cirrhosis in rats by curcumin. Liver Int 27(3):373–383. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1478-3231.2007.01453.x
Center AS (2005) Feline Hepatic Lipidosis. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim 35:225–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvsm.2004.10.002
Dai K, Qi JY, Tian DY (2005) Leptin administration exacerbates thioacetamide induced liver fibrosis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 11:4822–4826. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i31.4822
Dallak M, Al-Hashem F, Haidara MA, Ellatif MA, Kamar SS, Shamseldeen AM, Dawood AF, Ebrahim HA, Al-Ani B (2020) Suppression of thioacetamide-induced hepatic injury in rats by resveratrol: role of mammalian target of rapamycin (mtor) cell signaling. Int J Morphol 38:558–564
Demetriou AA, Brown RS Jr, Busuttil RW, Fair J, McGuire BM, Rosenthal P, Am Esch JS 2nd, Lerut J, Nyberg SL, Salizzoni M, Fagan EA, de Hemptinne B, Broelsch CE, Muraca M, Salmeron JM, Rabkin JM, Metselaar HJ, Pratt D, De La Mata M, McChesney LP, Everson GT, Lavin PT, Stevens AC, Pitkin Z, Solomon BA (2004) Prospective, randomized, multicenter, controlled trial of a bioartificial liver in treating acute liver failure. Ann Surg 239:660–670. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sla.0000124298.74199.e5
Dietrich P, Hellerbrand C (2014) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 28:637e653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpg.2014.07.008
Drackley JK (1999) Biology of dairy cows during the transition period: The final frontier? J Dairy Sci 82:2259–2273. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(99)75474-3
El Sebaey AM, Abramov PN (2019) Clinical, laboratory, ultrasonographic and histopathological findings in dogs affected by subclinical chronic hepatitis. Beтepинapия, 5:11–20. https://doi.org/10.26155/vet.zoo.bio.201905002.
Ghosh S, Sarkar A, Bhattacharyya S, Sil PC (2016) Silymarin protects mouse liver and kidney from thioacetamide induced toxicity by scavenging reactive oxygen species and activating PI3K-Akt pathway. Front Pharmacol 7:481. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2016.00481
Goff JP, Horst RL (1997) Physiological changes at parturition and their relationship to metabolic disorders. J Dairy Sci 80:1260–1268. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(97)76055-7
Gruffat D, Durand D, Graulet B, Bauchart D (1996) Regulation of VLDL synthesis and secretion of the liver. Reprod Nutr Dev 36:375–389. https://doi.org/10.1051/rnd:19960404
Grummer RR (1993) Etiology of lipid-related metabolic disorders in periparturient dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 76:3882–3896. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(93)77729-2
Hada N, Kuramochi M, Izawa T, Kuwamura M (2020) Yamate J (2020) Effects of dexamethasone on hepatic macrophages in normal livers and thioacetamide-induced acute liver lesions in rats. J Toxicol Pathol 33:237–246. https://doi.org/10.1293/tox.2020-0016
Hajovsky H, Hu G, Koen Y, Sarma D, Cui W, Moore DS, Staudinger JL, Hanzliket RP (2012) Metabolism and toxicity of thioacetamide and thioacetamide S-oxide in rat hepatocytes. Chem Res Toxicol 25:1955–1963. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx3002719
Hassan SA, Hammam O, Hussein SAM, Aziz WM (2021) Thioacetamide-induced acute liver failure and prospect of nano antioxidant based therapy [herbal approach]. Egypt J Chem 64:6835–6856
Herdt TH (2000) Ruminant adaptation to negative energy balance. Influences on the etiology of ketosis and fatty liver. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim 16:215–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0749-0720(15)30102-x
Huang W, Huang H, Hsu Y, Su W, Shen S, Lee M, Lin C, Huang C (2018) The effects of thiamine tetrahydrofurfuryl disulfide on physiological adaption and exercise performance improvement. Nutrients 10:851. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070851
Jain A, Mehta R, Al-Ani M, Hill JA, Winchester DE (2015) Determining the role of thiamine deficiency in systolic heart failure: A meta-analysis and systematic review. J Card Fail 21:1000–1007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardfail.2015.10.005
Jiao F-Z, Wang Y, Zhang W-B, Zhang H-Y, Chen Q, Shi C-X, Wang L-W, Gong Z-J (2019) Protective role of AGK2 on thioacetamide-induced acute liver failure in mice. Life Sci 230:68–75. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920012803762710
Jorritsma R, Jorritsma H, Schukken YH, Wentink GH (2000) Relationships between fatty liver and fertility and some periparturient diseases in commercial Dutch dairy herds. Theriogenology 54:1065–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0093-691x(00)00415-5
Jorritsma R, Jorritsma H, Schukken YH, Bartlett PC, Wensing T, Wentink GH (2001) Prevalence and indicators of post-partum fatty infiltration of the liver in nine commercial dairy herds in the Netherlands. Livest Prod Sci 68:53–60
Kleszczewska E (2001) Biological role of reactions of l-ascorbic acid with metals. Postepy Higieny i Medycyna Doswiadczalnej 55:81–94
Lee JW, Shin KD, Lee M, Kim EJ, Han SS, Han MY, Ha H, Jeong TC, Koh WS (2003) Role of metabolism by flavin-containing monooxygenase in thioacetamide-induced immunosuppression. Toxicol Lett 136:163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4274(02)00333-8
Li X (2002) Reproducible production of thioacetamide-induced macronodular cirrhosis in the rat with no mortality. J Hepatol 36:488–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-8278(02)00011-9
Li S, Hong M, Tan HY, Wang N, Feng YB (2016) Insights into the role and interdependence of oxidative stress and inflammation in liver diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:4234061. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4234061
Lu SC, Huang ZZ, Yang H, Tsukamoto H (1999) Effect of thioacetamide on the hepatic expression of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase subunits in the Rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 159:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1006/taap.1999.8729
Marciniak S, Wnorowski A, Smolińska K, Walczyna B, Turski W, Kocki T, Paluszkiewicz P, Parada-Turska J (2018) Kynurenic acid protects against thioacetamide-induced liver injury in rats. Anal Cell Pathol Article ID 1270483. 11 pages. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1270483.
McIlwain DR, Berger T, Mak TW (2013) Caspase functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5:a008656. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a008656
McNamara JP (2000) Integrating genotype and nutrition on utilization of body reserves during lactation of dairy cattle. Pages 353– 370 in Symposium on Ruminant Physiology. P. B. Cronje, ed. CAB Int., London, UK
Mishra GD, McNaughton SA, O’Connell MA, Prynne CJ, Kuh D (2009) Intake of B vitamins in childhood and adult life in relation to psychological distress among women in a British birth cohort. Public Health Nutr 12:166–174. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980008002413
Moya M, Gómez-Lechón MJ, Castell JV, Jover R (2010) Enhanced steatosis by nuclear receptor ligands: a study in cultured human hepatocytes and hepatoma cells with a characterized nuclear receptor expression profile. Chem Biol Interact 184:376–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2010.01.008
Ortega-Cuellar D, Velazquez-Arellano A (2016) Thiamine deprivation produces a liver atp deficit and metabolic and genomic effects in mice: Findings are parallel to those of biotin deficiency and have implications for energy disorders. J Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics 9:287–299. https://doi.org/10.1159/000456663
Quintanilha LF, Takami T, Hirose Y, Fujisawa K, Murata Y, Yamamoto N, Goldenberg RC, Terai S, Sakaida I (2014) Canine mesenchymal stem cells show antioxidant properties against thioacetamide-induced liver injury in vitro and in vivo. Hepatology Res 44:E206-217. https://doi.org/10.1111/hepr.12204
Riedl SJ, Shi Y (2004) Molecular mechanisms of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:897–907. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1496
Roberts CJ, Reid IM, Rowlands GJ, Patterson A (1981) A fat mobilization syndrome in dairy cows in early lactation. Vet Rec 108:7–9. https://doi.org/10.1136/vr.108.1.7
Sambon M, Napp A, Demelenne A, Vignisse J, Wins P, Fillet M, Bettendorffa L (2019) Thiamine and benfotiamine protect neuroblastoma cells against paraquat and β-amyloid toxicity by a coenzyme-independent mechanism. Heliyon 5:e01710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01710
Shin M-R, Lee JA, Kim M, Lee S, Oh M, Moon J, Nam J-W, Choi H, Mun Y-J, Roh S-S (2021) Gardeniae fructus attenuates thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in mice via both AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB pathway and Nrf2 signaling. Antioxidants 10:1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111837
Shirai M, Arakawa S, Miida H, Matsuyama T, Kinoshita J, Makino T, Kai K, Teranishi M (2013) Thioacetamide-induced hepatocellular necrosis is attenuated in diet-induced obese mice. J Toxicol Pathol 26:175–186. https://doi.org/10.1293/tox.26.175
Spicker JS, Brunak S, Frederiksen KS, Toft H (2008) Integration of clinical chemistry, expression, and metabolite data leads to better toxicological class separation. Toxicol Sci 102:444–454. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfn001
Upasani CD, Khera A, Balaraman R (2001) Effect of lead with Vitamins E, C, or Spirulina on malondialdehyde: conjugated dienes and hydroperoxides in rats. Indian J Exp Biol 39:70–74
Vernon G, Baranova A, Younossi ZM (2011) Systematic review: the epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Alimentary Pharmacol Ther 34:274e85. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04724.x
Veteläinen RL, Bennink RJ, de Bruin K, van Vliet A, van Gulik TM (2006) Hepatobiliary function assessed by 99mTc-mebrofenin cholescintigraphy in the evaluation of severity of steatosis in a rat model. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 33:1107–1114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-006-0125-3
Vluggens A, Reddy JK (2012) Nuclear receptors and transcription factors in the development of fatty liver disease. Curr Drug Metab 13:1422–1435. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920012803762710
Wang C, Fei G, Pan X, Sang S, Wang L, Zhong C, Jin L (2018) High thiamine diphosphate level as a protective factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Res 2:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2018.1460704
Weiskirchen R (2016) Hepatoprotective and anti-fibrotic agents: It’s time to take the next step. Front Pharmacol 6:303. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2015.00303
Williams CD, Stengel J, Asike MI, Torres DM, Shaw J, Contreras M, Landt CL, Harrison SA (2011) Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis among a largely middle-aged population utilizing ultrasound and liver biopsy: a prospective study. Gastroenterology 140:124e31. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2010.09.038
Wree A, Broderick L, Canbay A, Hoffman HM, Feldstein AE (2013) From NAFLD to NASH to cirrhosis-new insights into disease mechanisms. Nature Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 10:627–636. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2013.149
Zhang X, Barile G, Chang S, Hays A, Pachydaki A, Schiff W, Sparrow J (2005) Apoptosis and cell proliferation in proliferative retinal disorders: PCNA, Ki-67, caspase-3, and PARP expression. Curr Eye Res 30:395–403. https://doi.org/10.1080/02713680590956306
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Scientific Projects Commission of University of Burdur Mehmet Akif Ersoy (Project number: 0606-YL-19).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agirca Tasan, S., Ozmen, O. Investigation of the protective and therapeutic effects of thiamine in thioacetamide-induced liver injury. Biologia 77, 1953–1964 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01062-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01062-2



