Abstract
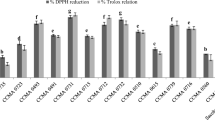
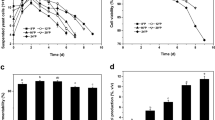
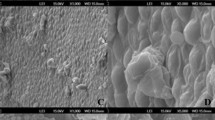
Food preservatives especially used to prevent microbiological spoilage in nutritional products are among the most indispensable additives. Here, the biochemical effects of three commonly used preservatives, sodium benzoate (SB), potassium sorbate (PS) and sodium nitrite (SN), on Saccharomyces cerevisiae were investigated. 5–100 mM SB, 300 ppm PS and 25–100 mM SN significantly inhibited early exponential yeast cell proliferation compared to the control after 12 h exposure. Cell metabolic activity percentages were also significantly inhibited at the studied highest three concentrations. While glutathione S-transferase activity generally increased after SB and PS treatments, superoxide dismutase activity increased only after 50 mM SB treatment. Although the lipid peroxidation marker malondialdehyde levels generally increased as a result of treatments with food additives, significant increases were determined in 300 ppm PS, and 50 and 100 mM SN groups. According to the principal component and hierarchical cluster analysis, food additive treated groups clearly discriminated from control. Finally, the principal component analysis (PCA) loading plots showed that higher doses of food additives altered lipid concentration, disrupted proteins and increased the concentrations of mannans and β-glucans. These findings are significant in terms of better understanding the underlying mechanism of food additive induced toxicity for the control of yeast cell proliferation.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- ATR:
-
Attenuated total reflectance
- CCK:
-
Cell counting kit
- CDNB:
-
1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene
- EFSA:
-
European Food Safety Authority
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration of the United States
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GRAS:
-
Generally recognized as safe
- GST:
-
Gluthathione S-transferase
- HCA:
-
Hierarchical cluster analysis
- IR:
-
Infrared
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MIC:
-
Minimum growth inhibitory concentration
- OD:
-
Optical density
- PC:
-
Principal component
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- PS:
-
Potassium sorbate
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SB:
-
Sodium benzoate
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- SN:
-
Sodium nitrite
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TBA:
-
Thiobarburitic acid
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
- UATR:
-
Universal attenuated total reflectance
- WST:
-
Water soluble tetrazolium
- XO:
-
Xanthine oxidase
- YPD:
-
Yeast extract peptone dextrose
- YPDA:
-
Yeast extract peptone dextrose agar
References
Abdulmumeen HA, Risikat AN, Sururah AR (2012) Food: its preservatives, additives and applications. Int J Chem Biochem Sci 1:36–47. https://doi.org/10.13140/2.1.1623.5208
Al-Ashmawy MA, Ibrahim JI (2009) Influence of potassium sorbate on the growth of yeasts and moulds in yogurt. Int J Dairy Technol 62(2):224–227. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0307.2009.00463.x
Alzate P, Gerschenson L, Flores S (2020) Ultrasound application for production of nano-structured particles from esterified starches to retain potassium sorbate. Carbohydr Polym 247:116759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116759
Asefa DT, Møretrø T, Gjerde RO et al (2009) Yeast diversity and dynamics in the production processes of Norwegian dry-cured meat products. Int J Food Microbiol 133(1–2):135–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2009.05.011
Bearth A, Cousin M-E, Siegrist M The consumer’s perception of artificial food additives: influences on acceptance, risk and benefit perceptions. Food Qual Prefer 2014, 38:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2014.05.008
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Branen AL, Haggerty R (2001) Introduction to food additive. In: Branen AL, Davidson PM, Salminen S, Thorngate JH III (eds) Food additives, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780824741709.CH1
Burattini E, Cavagna M, Dell’ Anna R et al (2008) A FTIR microspectroscopy study of autolysis in cells of the wine yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Vib Spectrosc 47(2):139–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2008.04.007
Cabiscol Català E, Piulats Combalia E, Echave Lozano P, Herrero Perpiñán E, Ros Salvador J (2000) Oxidative stress promotes specific protein damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 275(35):27393–27398. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M003140200
Caetano Júnior PC, Strixino JF, Raniero L (2015) Analysis of saliva by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for diagnosis of physiological stress in athletes. Res Biomed Eng 31(2):116–124. https://doi.org/10.1590/2446-4740.0664
Carocho M, Morales P, Ferreira IC (2015) Natural food additives: Quo vadis? Trends Food Sci Technol 45(2):284–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2015.06.007
Cavagna M, Dell’ Anna R, Monti F, Rossi F, Torriani S (2010) Use of ATR-FTIR microspectroscopy to monitor autolysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells in a base wine. J Agric Food Chem 58(1):39–45. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf902369s
Codex Alimentarius In: Codex Alimentarius (n.d.). http://www.codexalimentarius.org/standards/gsfa/
Dai Y, LA ML, Weiss J, Peleg M (2010a) Concentration and application order effects of sodium benzoate and eugenol mixtures on the growth inhibition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Zygosaccharomyces bailii. J Food Sci 75(7):M482–M488. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2010.01772.x
Dai Y, Normand MD, Weiss J, Peleg M (2010b) Modeling the efficacy of triplet antimicrobial combinations: yeast suppression by lauric arginate, cinnamic acid, and sodium benzoate or potassium sorbate as a case study. J Food Prot 73(3):515–523. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028x-73.3.515
Dehghan P, Mohammadi A, Mohammadzadeh-Aghdash H, Dolatabadi JEN (2018) Pharmacokinetic and toxicological aspects of potassium sorbate food additive and its constituents. Trends Food Sci Technol 80:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.07.012
Dwivedi S, Prajapati P, Vyas N, Malviya S, Kharia A (2017) A review on food preservation: methods, harmful effects and better alternatives. Asian J Pharma Pharmacol 3(6):193–199
EFSA REfSA (n.d.), Regulation No. 1333/2008 (2008) In. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:32008R1333&from=EN
FDA FaDAotUSoA (2015) In. http://www.fda.gov/Food/IngredientsPackagingLabeling/FoodAdditivesIngredients/ucm094211.htm#foodadd
Fernandez-Pacheco P, Arévalo-Villena M, Bevilacqua A, Corbo MR, Pérez AB (2018) Probiotic characteristics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains: properties for application in food industries. Lwt 97:332–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.07.007
Flores Llovera M, Toldrá Vilardell F (2021) Chemistry, safety, and regulatory considerations in the use of nitrite and nitrate from natural origin in meat products. Meat Sci 171:108272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2020.108272
Frank CJ, Redd DC, Gansler TS, RL MC (1994) Characterization of human breast biopsy specimens with near-IR Raman spectroscopy. Anal Chem 66(3):319–326. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00075a002
Galichet A, Sockalingum G, Belarbi A, Manfait M (2001) FTIR spectroscopic analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell walls: study of an anomalous strain exhibiting a pink-colored cell phenotype. FEMS Microbiol Lett 197(2):179–186. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10601.x
Hazan R, Levine A, Abeliovich H (2004) Benzoic acid, a weak organic acid food preservative, exerts specific effects on intracellular membrane trafficking pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(8):4449–4457. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.8.4449-4457.2004
Hinze H, Holzer H (1985) Accumulation of nitrite and sulfite in yeast cells and synergistic depletion of the intracellular ATP content. Z Lebensm-Unters-Forsch 180(2):117–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01042634
Kansiz M, Heraud P, Wood B, Burden F, Beardall J, McNaughton D (1999) Fourier transform infrared microspectroscopy and chemometrics as a tool for the discrimination of cyanobacterial strains. Phytochemistry 52(3):407–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00212-5
Khoshnoud MJ, Siavashpour A, Bakhshizadeh M, Rashedinia M (2018) Effects of sodium benzoate, a commonly used food preservative, on learning, memory, and oxidative stress in brain of mice. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 32(2):e22022. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22022
Kolakowska, A. (2003) Lipid oxidation in food systems, chemical and functional properties of food lipids. In: Sikorski, Z.E., Kolakowska, A. (Ed.), CRC Press LLC. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420031997
Laganà P, Avventuroso E, Romano G, et al. (2017) Classification and technological purposes of food additives: the European point of view. Chemistry and hygiene of food additives. Springer, p 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-57042-6_1
Li X, Lin J, Ding J, Wang S, Liu Q, Qing S (2004) Raman spectroscopy and fluorescence for the detection of liver cancer and abnormal liver tissue. In: The 26th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, vol 1. IEEE, p 212–215. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2004.1403129
López-Malo A, Guerrero S, Alzamora S (2000) Probabilistic modeling of Saccharomyces cerevisiae inhibition under the effects of water activity, pH, and potassium sorbate concentration. J Food Prot 63(1):91–95. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028x-63.1.91
Marnett LJ (1999) Lipid peroxidation-DNA damage by malondialdehyde. Mutat Res 424(1–2):83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0027-5107(99)00010-x
Mihoubi W, Sahli E, Gargouri A, Amiel C (2017) FTIR spectroscopy of whole cells for the monitoring of yeast apoptosis mediated by p53 over-expression and its suppression by Nigella sativa extracts. PLoS One 12(7):e0180680. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0180680
Motarjemi Y, Moy G, Todd E (2013) Encyclopedia of food safety. Academic Press
Öksüztepe G, Ilhak OI, Dikici A, Çalıcıoğlu M, Patır B (2010) Effect of potassium sorbate on some microbiological properties of cokelek stored at different temperatures. Kafkas Univ Vet Fak Derg 16:S99–S105. https://doi.org/10.9775/kvfd.2010.1840
Ozdemir C, Demirci M (2006) Selected microbiological properties of Kashar cheese samples preserved with potassium sorbate. Int J Food Prop 9(3):515–521. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942910600596191
Pebotuwa S, Kochan K, Peleg A, Wood BR, Heraud P (2020) Influence of the sample preparation method in discriminating Candida spp. using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Molecules 25(7):1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071551
Piper PW (1999) Yeast superoxide dismutase mutants reveal a pro-oxidant action of weak organic acid food preservatives. Free Radic Biol Med 27(11–12):1219–1227. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0891-5849(99)00147-1
Piper JD, Piper PW (2017) Benzoate and sorbate salts: a systematic review of the potential hazards of these invaluable preservatives and the expanding spectrum of clinical uses for sodium benzoate. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 16(5):868–880. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12284
Pueyo E, Martínez-Rodríguez A, Polo MC, Santa-María G, Bartolomé B (2000) Release of lipids during yeast autolysis in a model wine system. J Agric Food Chem 48(1):116–122. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf990036e
Saltmarsh M, Saltmarsh M (2013) Essential guide to food additives. R Soc Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/9781849734981
Schmedes A, Hølmer G (1989) A new thiobarbituric acid (TBA) method for determining free malondialdehyde (MDA) and hydroperoxides selectively as a measure of lipid peroxidation. J Am Oil Chem Soc 66(6):813–817. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02653674
Shahmohammadi M, Javadi M, Nassiri-Asl M (2016) An overview on the effects of sodium benzoate as a preservative in food products. Biotech Health Sci 3(3):7–11. https://doi.org/10.17795/bhs-35084
Shimazaki A, Sakamoto JJ, Furuta M, Tsuchido T (2016) Antifugal activity of diglycerin ester of fatty acids against yeasts and its comparison with those of sucrose monopalmitate and sodium benzoate. Biocontrol Sci 21(2):123–130. https://doi.org/10.4265/bio.21.123
Sprague GF, Winans SC (2006) Eukaryotes learn how to count: quorum sensing by yeast. Genes Dev 20(9):1045–1049. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1432906
Stanojevic D, Comic L, Stefanovic O, Solujic-Sukdolak S (2009) Antimicrobial effects of sodium benzoate, sodium nitrite and potassium sorbate and their synergistic action in vitro. Bulg J Agric Sci 15(4):307–311
Wang L, Mizaikoff B (2008) Application of multivariate data-analysis techniques to biomedical diagnostics based on mid-infrared spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem 391(5):1641–1654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-1989-9
Yigit A, Korukluoglu M (2007) The effect of potassium sorbate, NaCl and pH on the growth of food spoilage fungi. Ann Microbiol 57(2):209–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03175209
Younus H (2018) Therapeutic potentials of superoxide dismutase. Int J Health Sci 12(3):88
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Berna Kavakcıoğlu Yardımcı designed, and supervised the project, performed the experiments, computations, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript, provided financial support and final approval of the manuscript. Sevilay Cengiz Şahin and Nurettin İlter Sever contributed to the study conception and design, performed the experiments and reviewed the manuscript. Nihal Simsek Özek performed the chemometric computations, analyzed the data and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
Competing interests
Berna Kavakcıoğlu Yardımcı, Sevilay Cengiz Şahin, Nurettin İlter Sever and Nihal Simsek Özek declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary material
ESM 1
Docx
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yardimci, B.K., Sahin, S.C., Sever, N.I. et al. Biochemical effects of sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate and sodium nitrite on food spoilage yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biologia 77, 547–557 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00964-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00964-x