Abstract
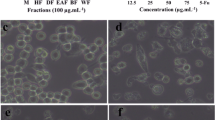
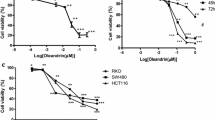
Verbesina encelioides is known to possess antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, and antiviral activities. However, anticancer activity of V. encelioides plant on human colon cancer has not been explored so far. Herein, anticancer potential of ethanolic extract (VE) and aqueous extract (VA) of V. encelioides against human colon cancer cell line (HCT-116) was evaluated. Cell viability assays, morphological analysis, oxidative stress markers (lipid peroxidation (LPO) and glutathione (GSH)), reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), and apoptotic marker genes were studied. VE exhibited a higher cytotoxic effect related to VA at tested concentrations as observed by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2-5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) (MTT), neutral red uptake (NRU) assays, and morphological analysis. The obtained results showed that VE induced LPO level, GSH depletion, ROS production, and depletion of the mitochondrial membrane potential. A mechanistic study has confirmed that VE induces apoptosis in HCT-116 cells by upregulating pro-apoptotic genes (p53, caspase-3 and − 9, and Bax) expression and downregulating Bcl-2 (antiapoptotic gene). Overall, these results clearly exhibited that VE has anticancer potential against HCT-116 cells through oxidative stress, ROS generation, and mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis. The findings of this study suggest that V. encelioides could be a source for the development of new anticancer agents.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCT-116:
-
Human colon cancer cell line
- LPO:
-
lipid peroxidation
- GSH:
-
glutathione
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- MMP:
-
mitochondrial membrane potential
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2-5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide)
- NRU:
-
neutral red uptake
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified eagle’s medium
- DMSO:
-
dimethyl sulfoxide
- TBA:
-
thiobarbituric acid
- DTNB:
-
5,5’-dithio-bis(2-nitrobenzoic acid)
- DCF-DA:
-
2’,7’-dichrolofluorescin diacetate
- Rh-123:
-
Rhodamine-123
- ATCC:
-
American Type Culture Collection
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- SDS:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate
- RT-qPCR:
-
reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction
References
Aamazadeh F, Ostadrahimi A, Saadat YR, Barar J (2020) Bitter apricot ethanolic extract induces apoptosis through increasing expression of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 in PANC-1 pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep 47(3):1895–1904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05286-w
Ahamed A, Panneerselvam A, Alaklabi A, Arif IA, Ambikapathy V, Thajuddin N (2020) Molecular perspective and anticancer activity of medicinal plants. Saudi J Biol Sci 27(2):666–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.11.043
Akhir NA, Chua LS, Majid FA, Sarmidi MR (2011) Cytotoxicity of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Ficus deltoidea on human ovarian carcinoma cell line. Br J Med Med Res 1(4):397–409. https://doi.org/10.9734/BJMMR/2011/507
Albalawi MA, Bashir NA, Tawfik A (2015) Anticancer and antifolate activities of extracts of six Saudi Arabian wild plants used in folk medicine. J Life Sci 9:334–340. https://doi.org/10.17265/1934-7391/2015.07.006
Ali AN, Saeed NA, Omear HA (2021) The anticancer properties of Artemisia aucheri boiss extract on HT29 colon cancer cells. J Gastrointest Cancer 52:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-019-00354-2
Al-Oqail MM, Siddiqui MA, Al-Sheddi ES, Saquib Q, Musarrat J, Al-Khedhairy AA, Farshori NN (2016) Verbesina encelioides: cytotoxicity, cell cycle arrest, and oxidative DNA damage in human liver cancer (HepG2) cell line. BMC Complement Altern Med 16:126. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-016-1106-0
Al-Oqail MM, Al-Sheddi ES, Al-Massarani SM, Siddiqui MA, Ahmad J, Musarrat J, Al-Khedhairy AA, Farshori NN (2017) Nigella sativa seed oil suppresses cell proliferation and induces ROS dependent mitochondrial apoptosis through p53 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. South Afr J Bot 112:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2017.05.019
Alshatwi A (2011) Anti-proliferative effects of organic extracts from root bark of Juglans Regia L.(RBJR) on MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells: role of Bcl-2/Bax, caspases and Tp53. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 12(2):525-530
American Cancer Society (2020) Colorectal cancer facts & figs. 2020–2022. American Cancer Society, Atlanta. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
Ammar RB, Neffati A, Skandrani I, Sghaier MB, Bhouri W, Ghedira K, Chekir-Ghedira L (2011) Anti-lipid peroxidation and induction of apoptosis in the erythroleukaemic cell line K562 by extracts from (Tunisian) Rhamnus alaternus L. (Rhamnaceae). Nat Prod Res 25(11):1047–1058. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2010.490783
Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2017) Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut 66(4):683–691. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310912
Aydoğmuş-Öztürk F, Jahan H, Beyazit N, Günaydın K, Choudhary MI (2019) The anticancer activity of visnagin, isolated from Ammi visnaga L., against the human malignant melanoma cell lines, HT 144. Mol Biol Rep 46(2):1709–1714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04620-1
Bacanli M, Anlar HG, Basaran AA, Basaran N (2017) Assessment of cytotoxicity profiles of different phytochemicals: comparison of neutral red and MTT assays in different cells in different time periods. Turk J Pharm Sci 14(2):95–107. https://doi.org/10.4274/tjps.07078
Benarba B, Meddah B, Hamdani H (2014) Cancer incidence in North West Algeria (Mascara) 2000–2010: results from a population-based cancer registry. EXCLI J 13:709–723. https://doi.org/10.17877/DE290R-6861
Borenfreund E, Puerner JA (1985) A simple quantitative procedure using monolayer cultures for cytotoxicity assays (HTD/NR-90). J Tissue Cult Methods 9(1):7–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01666038
Chandra D, Ramana KV, Wang L, Christensen BN, Bhatnagar A, Srivastava SK (2002) Inhibition of fiber cell globulization and hyperglycemia-induced lens opacification by aminopeptidase inhibitor bestatin. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43(7):2285–2292
Feenstra KR, Clements DR (2008) Biology and Impacts of Pacific Island Invasive Species. 4. Verbesina encelioides, Golden Crownbeard (Magnoliopsida: Asteraceae). Pac Sci 62(2):161–176. http://hdl.handle.net/10125/22690
Gao J, Morgan WA, Sanchez-Medina A, Corcoran O (2011) The ethanol extract of Scutellaria baicalensis and the active compounds induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis including upregulation of p53 and Bax in human lung cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 254(3):221–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2011.03.016
Gautam N, Mantha AK, Mittal S (2014) Essential oils and their constituents as anticancer agents: a mechanistic view. Biomed Res Int 2014:154106. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/154106
Glennie CW, Jain SC (1980) Flavonol 3, 7-diglycosides of Verbesina encelioides. Phytochemistry 19(1):157–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(80)85040-0
Hilton JW (1989) Antioxidants: function, types and necessity of inclusion in pet foods. Can Vet J 30(8):682–684
Jain SC, Purohit M, Sharma R (1988) Pharmacological evaluation of Verbesina encelioides. Phyto Res 2(3):146–148. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.2650020309
Jain SC, Singh R, Jain R (2008) Antimicrobial and antioxidant potentials of Verbesina encelioides (Cav.) Benth. and Hook. Fil ex Gray. Res J Med Plant 2(2):61–65. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjmp.2008.61.65
Joshi KC, Singh P, Singhi CL (1983) Chemical constituents of Verbesina encelioides and Holmskioldia sanguinea. J Indian Chem Soc 60(9):905–906
Kapinová A, Kubatka P, Kružliak P, Mokáň M, Péč M, Kassayová M, Bojková B, Dobrota D (2015) Chlorella pyrenoidosa, young barley and fruit peel polyphenols in rat breast cancer model-the effects on plasma lipid metabolism. Biologia 70(2):268–272. https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2015-0025
Khan T, Ali M, Khan A, Nisar P, Jan SA, Afridi S, Shinwari ZK (2020) Anticancer plants: a review of the active phytochemicals, applications in animal models, and regulatory aspects. Biomolecules 10(1):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010047
Kitagishi Y, Kobayashi M, Matsuda S (2012) Protection against cancer with medicinal herbs via activation of tumor suppressor. J Oncol 2012:236530. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/236530
Mahklouf MH, Abuhadra MN (2020) Infraspecies Identity of Verbesina encelioides (Cav.) Benth. and Hook.(Asteraceae) from Libya. J Plant Sci 15(1):28–32. https://doi.org/10.3923/jps.2020.28.32
Matés JM, Segura JA, Alonso FJ, Márquez J (2012) Oxidative stress in apoptosis and cancer: an update. Arch Toxicol 86(11):1649–1665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0906-3
Millimouno FM, Dong J, Yang L, Li J, Li X (2014) Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer and perspectives with natural compounds from mother nature. Cancer Prev Res 7(11):1081–1107. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-14-0136
Moon SC, Choi HJ, Chung TW, Lee JH, Lee SO, Jung MH, Kim BJ, Choi JY, Ha KT (2018) Sorbus commixta water extract induces apoptotic cell death via a ROSdependent pathway. Oncol Lett 16(4):4193–4200. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.9217
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65(1–2):55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4
Nguyen NH, Ta QT, Pham QT, Luong TN, Phung VT, Duong TH, Vo VG (2020) Anticancer activity of novel plant extracts and compounds from adenosma bracteosum (bonati) in human lung and liver cancer cells. Molecules 25(12):2912. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122912
Njamen D, Bakam BY, Rutz J, Maxeiner S, Awounfack CF, Ndinteh DT, Jüngel E, Zingue S, Blaheta RA (2020) Irvingia excelsa Mildbr. ethanolic extract displays in vitro cytotoxic effects on prostate cancer cells and prevents benign prostatic hyperplasia in Wistar rats. Biologia 75:2053–2062. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00511-0
Nunes SC, Serpa J (2018) Glutathione in ovarian cancer: A double-edged sword. Int J Mol Sci 19(7):1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071882
Oelrichs PB, Vallely PJ, MacLeod JK, Lewis IA (1981) Isolation of galegine from Verbesina enceloiodes. J Nat Prod 44(6):754–755. https://doi.org/10.1021/np50018a029
Ou-Yang F, Tsai I, Tang JY, Yen CY, Cheng YB, Farooqi AA, Chen SR, Yu SY, Kao JK, Chang HW (2019) Antiproliferation for Breast Cancer Cells by Ethyl Acetate Extract of Nepenthes thorellii x (ventricosa x maxima). Int J Mol Sci 20(13):3238. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133238
Prakash O, Kumar A, Kumar P, Ajeet (2013) Anticancer potential of plants and natural products: a review. Am J Pharmacol Sci 1:104–115. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajps-1-6-1
Ramakrishnan CD, Doss D, Vijayabharathi A (2017) Biochemical and antimicrobial characterization of an underexploited medicinal plant-Verbesina encelioides. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 6(12):3407–3416. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.612.396
Ricci JE, Gottlieb RA, Green DR (2003) Caspase-mediated loss of mitochondrial function and generation of reactive oxygen species during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 160(1):65–75. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200208089
Safarzadeh E, Shotorbani SS, Baradaran B (2014) Herbal medicine as inducers of apoptosis in cancer treatment. Adv Pharm Bull 4(Suppl 1):421–427. https://doi.org/10.5681/apb.2014.062
Sayari N, Mekki M, Taleb A (2016) Golden crownbeard (Verbesina encelioides, Asteraceae), first record for the Tunisian flora. Fl Medit 26(1):19–24. https://doi.org/10.7320/FlMedit26.019
Shukla S, Mehta A (2015) Anticancer potential of medicinal plants and their phytochemicals: a review. Braz J Bot 38(2):199–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-015-0135-0
Siddiqui MA, Singh G, Kashyap MP, Khanna VK, Yadav S, Chandra D, Pant AB (2008) Influence of cytotoxic doses of 4-hydroxynonenal on selected neurotransmitter receptors in PC-12 cells. Toxicol In Vitro 22:1681–1688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2008.07.001
Sindhu RK, Kumar P, Singh I, Arora S (2010a) Hypoglycemic potential of Verbesina encelioides Benth. Root. Res J Pharmacogn Phytochem 2(1):41–45e
Sindhu RK, Vasudeva N, Sharma SK (2010b) Pharmacognostical and preliminary phytochemical investigations on Verbesina encelioides benth roots. J Herbal Med Toxicol 4(2):113–118
Tang J, Zhao JJ, Li ZH (2015) Ethanol extract of Artemisia sieversiana exhibits anticancer effects and induces apoptosis through a mitochondrial pathway involving DNA damage in COLO-205 colon carcinoma cells. Bangladesh J Pharmacol 10(3):518–523. https://doi.org/10.3329/bjp.v10i3.23196
Tiwari H, Rao P, Sambasiva V (1978) Constituents of Verbesina encelioides: isolation of triterpenoids from a Verbesina species. Indian J Chem 16:1133
Van Giau V, An SS, Hulme JP (2018) Mitochondrial therapeutic interventions in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 395:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2018.09.033
Zhang YS, Shen Q, Li J (2016) Traditional Chinese medicine targeting apoptotic mechanisms for esophageal cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin 37(3):295–302. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.116
Acknowledgements
This research project was supported by a grant from the “Research Centre of the Female Scientific and Medical Colleges”, Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This paper does not contain any studies with human or animals.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farshori, N.N. Verbesina encelioides-induced cytotoxicity and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human colon cancer cells through ROS generation. Biologia 76, 2711–2720 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00781-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00781-2